SpringMVC参数绑定(四)
1.默认支持的参数类型
处理器形参中添加如下类型的参数处理适配器会默认识别并进行赋值。
HttpServletRequest
通过request对象获取请求信息
HttpServletResponse
通过response处理响应信息
HttpSession
通过session对象得到session中存放的对象
2.Model/ModelMap
(1) Model
除了ModelAndView以外,还可以使用Model来向页面传递数据,
Model是一个接口,在参数里直接声明model即可。
如果使用Model则可以不使用ModelAndView对象,Model对象可以向页面传递数据,View对象则可以使用String返回值替代。
不管是Model还是ModelAndView,其本质都是使用Request对象向jsp传递数据。
代码实现:
/** * 根据id查询商品,使用Model * * @param request * @param model * @return */ @RequestMapping("/itemEdit") public String queryItemById(HttpServletRequest request, Model model) { // 从request中获取请求参数 String strId = request.getParameter("id"); Integer id = Integer.valueOf(strId); // 根据id查询商品数据 Item item = this.itemService.queryItemById(id); // 把商品数据放在模型中 model.addAttribute("item", item); return "itemEdit"; }
(2)ModelMap
ModelMap是Model接口的实现类,也可以通过ModelMap向页面传递数据
使用Model和ModelMap的效果一样,如果直接使用Model,springmvc会实例化ModelMap。
代码实现:
/** * 根据id查询商品,使用ModelMap * * @param request * @param model * @return */ @RequestMapping("/itemEdit") public String queryItemById(HttpServletRequest request, ModelMap model) { // 从request中获取请求参数 String strId = request.getParameter("id"); Integer id = Integer.valueOf(strId); // 根据id查询商品数据 Item item = this.itemService.queryItemById(id); // 把商品数据放在模型中 model.addAttribute("item", item); return "itemEdit"; }
3.绑定简单类型
(1) 支持的数据类型
参数类型推荐使用包装数据类型,因为基础数据类型不可以为null
整形:Integer、int
字符串:String
单精度:Float、float
双精度:Double、double
布尔型:Boolean、boolean
说明:对于布尔类型的参数,请求的参数值为true或false。或者1或0
请求url:
http://localhost:8080/xxx.action?id=2&status=false
处理器方法:
public String editItem(Model model,Integer id,Boolean status)
当请求的参数名称和处理器形参名称一致时会将请求参数与形参进行绑定。
这样,从Request取参数的方法就可以进一步简化。
@RequestMapping("/itemEdit")
public String queryItemById(int id, ModelMap model) {
// 根据id查询商品数据
Item item = this.itemService.queryItemById(id);
// 把商品数据放在模型中
model.addAttribute("item", item);
return "itemEdit";
}
(2) @RequestParam
使用@RequestParam常用于处理简单类型的绑定。
value:参数名字,即入参的请求参数名字,如value=“itemId”表示请求的参数 区中的名字为itemId的参数的值将传入(也就是我们传入参数的name的值,严格区分大小写)
required:是否必须,默认是true,表示请求中一定要有相应的参数,否则将报错
TTP Status 400 - Required Integer parameter 'XXXX' is not present
defaultValue:默认值,表示如果请求中没有同名参数时的默认值
(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") String upDicId)与下面这句话等价:
if(upDicId==null){
upDicId = "1";
}
定义如下:
@RequestMapping("/itemEdit")
public String queryItemById(@RequestParam(value = "itemId", required = true, defaultValue = "1") Integer id,
ModelMap modelMap) {
// 根据id查询商品数据
Item item = this.itemService.queryItemById(id);
// 把商品数据放在模型中
modelMap.addAttribute("item", item);
return "itemEdit";
}
3.使用pojo接收表单数据(不同于struts的是不用user.name)
如果提交的参数很多,或者提交的表单中的内容很多的时候,可以使用简单类型接受数据,也可以使用pojo接收数据。
要求:pojo对象中的属性名和表单中input的name属性一致。(与pojo对象名字无关)
页面定义如下图:
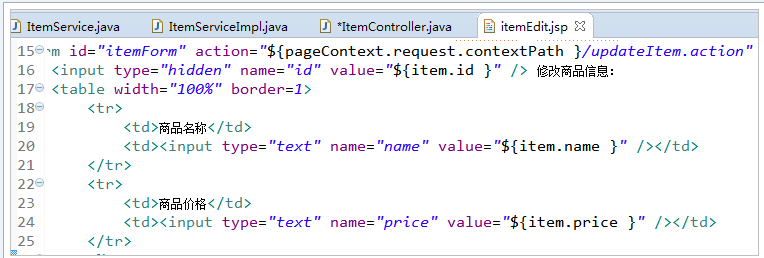
Pojo(逆向工程生成)如下图:
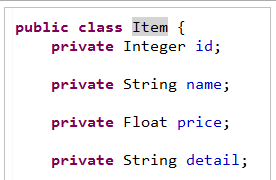
请求的参数名称和pojo的属性名称一致,会自动将请求参数赋值给pojo的属性。
Controller层代码:
@RequestMapping("/updateItem")
public String updateItem(Item item) {
// 调用服务更新商品
this.itemService.updateItemById(item);
// 返回逻辑视图(存在success.jsp)
return "success";
}
注意:
提交的表单中不要有日期类型的数据,否则会报400错误。如果想提交日期类型的数据需要用到后面的自定义参数绑定的内容。
补充:如果提交的参数太多可以封装到map中:(表单的name自动映射为key)
@RequestMapping("/getCourseBaseInfosByCondition")
public @ResponseBody List<Map<String,Object>> getCourseBaseInfosByCondition(@RequestParam Map<String,Object> condition){
System.out.println(condition.get("username"));
return null;
}
4. 解决post乱码问题
提交发现,保存成功,但是保存的是乱码
在web.xml中加入:
<!-- 解决post乱码问题 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!-- 设置编码参是UTF8 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
对于get请求中文参数出现乱码解决方法有两个:
修改tomcat配置文件添加编码与工程编码一致,如下:
<Connector URIEncoding="utf-8" connectionTimeout="20000" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443"/>
另外一种方法对参数进行重新编码:
String userName = new String(request.getParamter("userName").getBytes("ISO8859-1"),"utf-8")
ISO8859-1是tomcat默认编码,需要将tomcat编码后的内容按utf-8编码
5 绑定包装pojo
(1)需求
使用包装的pojo接收商品信息的查询条件。
(2)需求分析:
包装对象定义如下:
public class QueryVo { private Item item; set/get。。。 }
页面定义如下图:

(3)接收查询条件:
// 绑定包装数据类型 @RequestMapping("/queryItem") public String queryItem(QueryVo queryVo) { System.out.println(queryVo.getItem().getId()); System.out.println(queryVo.getItem().getName()); return "success"; }
6. 自定义参数绑定(自定义日期转换器以及绑定)
(1) 需求
在商品修改页面可以修改商品的生产日期,并且根据业务需求自定义日期格式。
(2) 需求分析
由于日期数据有很多种格式,springmvc没办法把字符串转换成日期类型。所以需要自定义参数绑定。
前端控制器接收到请求后,找到注解形式的处理器适配器,对RequestMapping标记的方法进行适配,并对方法中的形参进行参数绑定。可以在springmvc处理器适配器上自定义转换器Converter进行参数绑定。
一般使用<mvc:annotation-driven/>注解驱动加载处理器适配器,可以在此标签上进行配置。
(3). 修改jsp页面
如下图修改itemEdit.jsp页面,显示时间
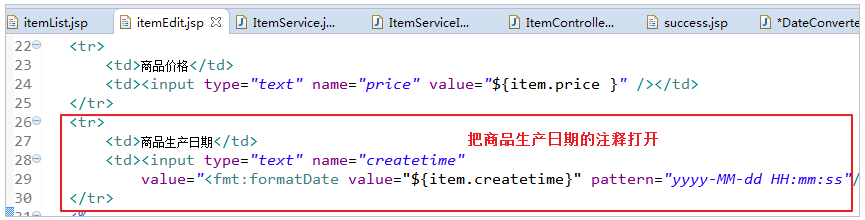
(4)自定义Converter
//Converter<S, T> //S:source,需要转换的源的类型 //T:target,需要转换的目标类型 public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> { @Override public Date convert(String source) { try { // 把字符串转换为日期类型 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); Date date = simpleDateFormat.parse(source); return date; } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 如果转换异常则返回空 return null; } }
(5). 配置Converter
我们同时可以配置多个的转换器。
类似下图的usb设备,可以接入多个usb设备

<!-- 配置注解驱动 --> <!-- 如果配置此标签,可以不用配置... --> <mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService" /> <!-- 转换器配置 --> <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean"> <property name="converters"> <set> <bean class="cn.itcast.springmvc.converter.DateConverter" /> </set> </property> </bean>
(6). 配置方式2(了解)
<!--注解适配器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <property name="webBindingInitializer" ref="customBinder"></property> </bean> <!-- 自定义webBinder --> <bean id="customBinder" class="org.springframework.web.bind.support.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer"> <property name="conversionService" ref="conversionService" /> </bean> <!-- 转换器配置 --> <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean"> <property name="converters"> <set> <bean class="cn.itcast.springmvc.convert.DateConverter" /> </set> </property> </bean>
注意:此方法需要独立配置处理器映射器、适配器,
不再使用<mvc:annotation-driven/>
代码
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import java.util.UUID; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; import org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import com.itheima.springmvc.exception.MessageException; import com.itheima.springmvc.pojo.Items; import com.itheima.springmvc.pojo.QueryVo; import com.itheima.springmvc.service.ItemService; /** * 商品管理 * * */ @Controller public class ItemController { @Autowired private ItemService itemService; //入门程序 第一 包类 + 类包 + 方法名 /** * 1.ModelAndView 无敌的 带着数据 返回视图路径 不建议使用 * 2.String 返回视图路径 model带数据 官方推荐此种方式 解耦 数据 视图 分离 MVC 建议使用 * 3.void ajax 请求 合适 json格式数据 (response 异步请求使用 * @return * @throws MessageException */ @RequestMapping(value = {"/item/itemlist.action","/item/itemlisthaha.action"}) public String itemList(Model model,HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws MessageException{ // Integer i = 1/0; //从Mysql中查询 List<Items> list = itemService.selectItemsList(); // if(null == null){ // throw new MessageException("商品信息不能为空"); // } model.addAttribute("itemList", list); return "itemList"; } //去修改页面 入参 id @RequestMapping(value = "/itemEdit.action") // public ModelAndView toEdit(@RequestParam(value = "id",required = false,defaultValue = "1") Integer idaaq, public ModelAndView toEdit(Integer id, HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response ,HttpSession session,Model model){ //Servlet时代开发 // String id = request.getParameter("id"); //查询一个商品 // Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(Integer.parseInt(id)); Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(id); ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); //数据 mav.addObject("item", items); mav.setViewName("editItem"); return mav; } //提交修改页面 入参 为 Items对象 @RequestMapping(value = "/updateitem.action") // public ModelAndView updateitem(Items items){ public String updateitem(QueryVo vo,MultipartFile pictureFile) throws Exception{ //保存图片到 String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""); //jpg String ext = FilenameUtils.getExtension(pictureFile.getOriginalFilename()); pictureFile.transferTo(new File("D:\\upload\\" + name + "." + ext)); vo.getItems().setPic(name + "." + ext); //修改 itemService.updateItemsById(vo.getItems()); // ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); // mav.setViewName("success"); return "redirect:/itemEdit.action?id=" + vo.getItems().getId(); // return "forward:/item/itemlist.action"; } //删除多个 @RequestMapping(value = "/deletes.action") public ModelAndView deletes(QueryVo vo){ ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); mav.setViewName("success"); return mav; } //修改 @RequestMapping(value = "/updates.action",method = {RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET}) public ModelAndView updates(QueryVo vo){ ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); mav.setViewName("success"); return mav; } //json数据交互 @RequestMapping(value = "/json.action") public @ResponseBody Items json(@RequestBody Items items){ // System.out.println(items); return items; } //RestFul风格的开发 @RequestMapping(value = "/itemEdit/{id}.action") public ModelAndView toEdit1(@PathVariable Integer id, HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response ,HttpSession session,Model model){ //Servlet时代开发 // String id = request.getParameter("id"); //查询一个商品 // Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(Integer.parseInt(id)); Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(id); ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); //数据 mav.addObject("item", items); mav.setViewName("editItem"); return mav; } //去登陆的页面 @RequestMapping(value = "/login.action",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String login(){ return "login"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/login.action",method = RequestMethod.POST) public String login(String username ,HttpSession httpSession){ httpSession.setAttribute("USER_SESSION", username); return "redirect:/item/itemlist.action"; } }

