各大框架都在使用注解,浅谈注解的使用及原理以及类加载器
一、类加载器
1.什么是类加载器,作用是什么?
类加载器就加载字节码文件(.class)
2.类加载器的种类
类加载器有三种,不同类加载器加载不同的
1)BootStrap:引导类加载器:加载都是最基础的文件
2)ExtClassLoader:扩展类加载器:加载都是基础的文件
3)AppClassLoader:应用类加载器:三方jar包和自己编写java文件
怎么获得类加载器?(重点)
ClassLoader 字节码对象.getClassLoader();
package cn.qlq; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { //获得Demo字节码文件的类加载器 Class clazz = Demo.class;//获得Demo的字节码对象 ClassLoader classLoader = clazz.getClassLoader();//获得类加载器 //getResource的参数路径相对classes(src) //获得classes(src)下的任何的资源 String path = classLoader.getResource("cn/qlq/jdbc.properties").getPath(); //classLoader.getResourceAsStream(""); System.out.println(path); } }
二、注解 @xxx
注解在目前而言最主流的应用:代替配置文件
关于配置文件与注解开发的优缺点:
注解优点:开发效率高 成本低
注解缺点:耦合性大 并且不利于后期维护
1.jdk5提供的注解
@Override:告知编译器此方法是覆盖父类的
@Deprecated:标注过时
@SuppressWarnings:压制警告
发现的问题:
不同的注解只能在不同的位置使用(方法上、字段上、类上)
2.自定义注解:
1.注解是给机器看的,注释是给程序员看的,这是两者的区别。现在各大框架都在使用注解,而我们程序员需要做的就是知道如何使用注解,而对其底层原理却不清楚,今天看了一段视频,现在浅谈一下注解的使用。
2.注解的使用:
大体分为三部分: 定义注解、使用注解、解析注解。在框架中定义与解析框架都已经为我们做好了。
(1)定义注解:定义一个简单的注解:
1 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 2 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 3 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 4 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 5 6 7 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) 8 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 9 public @interface MyAnnotation { 10 //定义注解的属性,这不是方法 11 String name();//必选注解 12 int value() default 20;//有属性就是可选属性 13 }
做一个解释吧:定义前面的@Target,与@Retention又称为元注解,限制定义的注解的特性:
@Target定义注解使用的位置,值有:看名字一般就很明显了吧
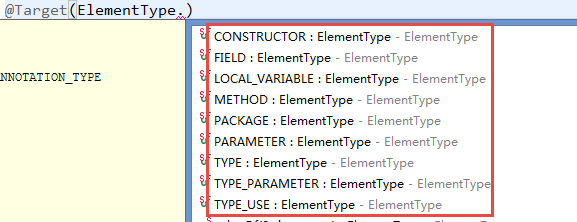
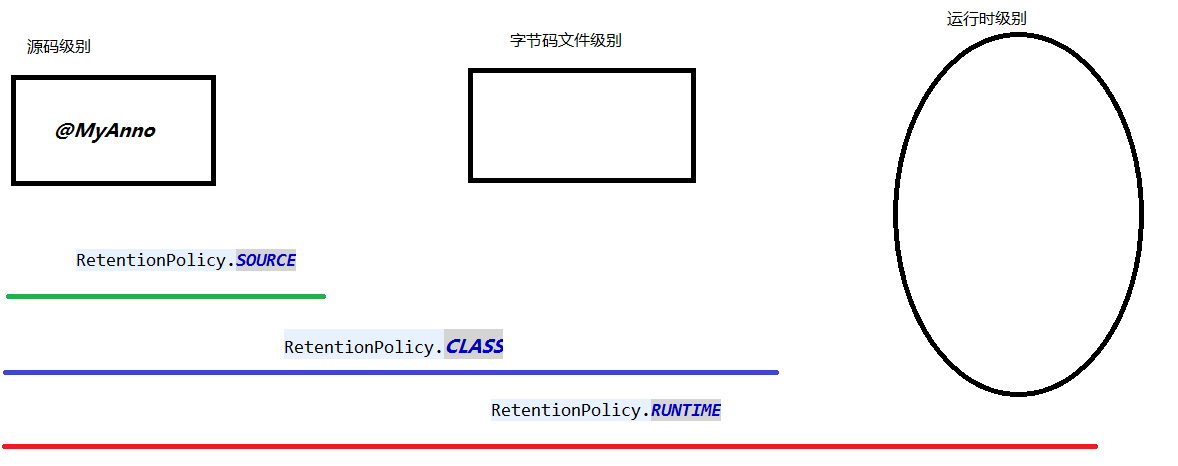
@Retention:限定注解的可见范围:值有

一个图解释上面的可见范围:
(2)注解的使用:
1 package annotation; 2 3 public class UseMyAnnotion { 4 5 // 这里只用一个属性,另一个value属性有默认值不用设置 6 @MyAnnotation(name = "QizoZhi") 7 public void show(String str){ 8 System.out.println(str); 9 } 10 }
(3)解析注解:这里使用了底层的映射原理
1 package annotation; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 5 6 public class MyAnnotationParser { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException { 9 // 获取字节码对象 10 Class clazz = UseMyAnnotion.class; 11 Method method = clazz.getMethod("show", String.class); 12 // 获取方法上面的注解 13 MyAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); 14 // 获取注解属性值 15 System.out.println(annotation.name()+"\t"+annotation.value()); 16 17 // 取到值就可以根据业务处理数据 18 19 //激活方法,也就是让方法执行 20 method.invoke(new UseMyAnnotion(), "HH"); 21 } 22 }
到这里注解基本上就完了,我们需要了解底层实现原理,真正开发的时候定义注解以及解析注解一般不用我们写,我们只需要学会使用框架提供的注解,但是使用注解的开发也有缺点。对后期的维护增加了困难。
Java注解之Retention、Documented、Target介绍参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/qlqwjy/p/8516551.html
补充:关于注解继承
有关Annotation的继承说明:
1. 方法上的注解可以被继承,如果方法被重写将不会被继承。(接口和类上的方法都是如此)
1、类和抽象类上的注解可以被继承,而且注解加上@Inherited才可以被继承
3、接口上的注解不能被继承
测试如下:
注解:
package annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { // 定义注解的属性,这不是方法 String name();// 必选注解 int value() default 20;// 有属性就是可选属性 }
(1)类和方法的注解测试
父类:
package annotation; @MyAnnotation(name = "类注解") public class ParentClass { @MyAnnotation(name = "show方法上面") public void show(String str) { } @MyAnnotation(name = "show2方法上面") public void show2(String str) { } }
子类:
package annotation; public class SubClass extends ParentClass { @Override public void show2(String str) { } }
测试:
package annotation; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MyAnnotationParser { public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException { // 获取类上的注解 MyAnnotation annotationsByType = SubClass.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); printAnnotation(annotationsByType); // 获取方法上面的注解 Method method = SubClass.class.getMethod("show", String.class); MyAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); printAnnotation(annotation); Method method2 = SubClass.class.getMethod("show2", String.class); MyAnnotation annotation2 = method2.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); printAnnotation(annotation2); } private static void printAnnotation(MyAnnotation annotation) { if (annotation != null) { System.out.println(annotation.name() + "\t" + annotation.value()); } else { System.out.println("null"); } } }
结果: 类上的注解没继承到,方法show1的注解继承到了,方法show2被重写了所以没有获取到继承的注解。
null
show方法上面 20
null
修改注解加上@Inherited
package annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited public @interface MyAnnotation { // 定义注解的属性,这不是方法 String name();// 必选注解 int value() default 20;// 有属性就是可选属性 }
再次测试结果: 类上的注解也可以获取到
类注解 20 show方法上面 20 null
(2)测试接口的注解:接口上的注解不能被继承,接口中抽象方法的注解可以继承(与类中方法一样)
package annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited public @interface MyAnnotation { // 定义注解的属性,这不是方法 String name();// 必选注解 int value() default 20;// 有属性就是可选属性 }
package annotation; @MyAnnotation(name = "类注解") public interface ParentInterface { @MyAnnotation(name = "show方法上面") public void show(String str); @MyAnnotation(name = "show2方法上面") public void show2(String str); }
package annotation; public interface SubInterface extends ParentInterface { @Override public void show2(String str); }
package annotation; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MyAnnotationParser { public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException { // 获取类上的注解 MyAnnotation annotationsByType = SubInterface.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); printAnnotation(annotationsByType); // 获取方法上面的注解 Method method = SubInterface.class.getMethod("show", String.class); MyAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); printAnnotation(annotation); Method method2 = SubInterface.class.getMethod("show2", String.class); MyAnnotation annotation2 = method2.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); printAnnotation(annotation2); } private static void printAnnotation(MyAnnotation annotation) { if (annotation != null) { System.out.println(annotation.name() + "\t" + annotation.value()); } else { System.out.println("null"); } } }
结果:
null
show方法上面 20
null
补充:@Target({}) 用于组合复杂的注解,例如:
@Target({})修饰的Index注解
package javax.persistence; import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface Index { String name() default ""; String columnList(); boolean unique() default false; }
Table注解中使用上述注解:
/** <a href="http://www.cpupk.com/decompiler">Eclipse Class Decompiler</a> plugin, Copyright (c) 2017 Chen Chao. */ package javax.persistence; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE; import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME; @Target(TYPE) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface Table { String name() default ""; String catalog() default ""; String schema() default ""; UniqueConstraint[] uniqueConstraints() default {}; Index[] indexes() default {}; }
使用方法如下:
@Entity @Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true) @ToString(callSuper = true) @Table(indexes = { @Index(name = "type", columnList = "type"), @Index(name = "enable", columnList = "enable") }) public class Dictionary extends AbstractSequenceEntity { private static final long serialVersionUID = 581214652229924448L; private String value; private String type; private Boolean enable; }
补充:@Inherited注解的使用
如果注解声明的时候加上此元注解,则该注解可以被子类继承(只对类上的注解生效);字段以及方法声明的注解无效。测试如下:
源码如下:
/** <a href="http://www.cpupk.com/decompiler">Eclipse Class Decompiler</a> plugin, Copyright (c) 2017 Chen Chao. */ package java.lang.annotation; /** * Indicates that an annotation type is automatically inherited. If * an Inherited meta-annotation is present on an annotation type * declaration, and the user queries the annotation type on a class * declaration, and the class declaration has no annotation for this type, * then the class's superclass will automatically be queried for the * annotation type. This process will be repeated until an annotation for this * type is found, or the top of the class hierarchy (Object) * is reached. If no superclass has an annotation for this type, then * the query will indicate that the class in question has no such annotation. * * <p>Note that this meta-annotation type has no effect if the annotated * type is used to annotate anything other than a class. Note also * that this meta-annotation only causes annotations to be inherited * from superclasses; annotations on implemented interfaces have no * effect. * * @author Joshua Bloch * @since 1.5 * @jls 9.6.3.3 @Inherited */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Inherited { }
源码都解释了,只对类有效。对实现接口也无效。
注解如下:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD }) //@Inherited @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { // 定义注解的属性,这不是方法 String name();// 必选注解 int value() default 20;// 有属性就是可选属性 }
1. 测试接口继承:
父接口
@MyAnnotation(name = "Parent") public interface ParentInterface { @MyAnnotation(name = "ParentInterface method1") void method1(); }
子接口
public interface SubInterface extends ParentInterface { }
测试代码:
import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.apache.commons.lang3.ClassUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.FieldUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.MethodUtils; public class PlainTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { // 获取类上注解 Class<?> class1 = ClassUtils.getClass("SubInterface"); MyAnnotation annotation = class1.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===类==="); System.out.println(class1); System.out.println(annotation); // 获取方法上注解 Method matchingAccessibleMethod = MethodUtils.getMatchingAccessibleMethod(class1, "method1"); MyAnnotation annotation2 = matchingAccessibleMethod.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===方法==="); System.out.println(matchingAccessibleMethod); System.out.println(annotation2); } }
(1)注解未声明@Inherited,结果如下:
===类===
interface SubInterface
null
===方法===
public abstract void ParentInterface.method1()
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=ParentInterface method1)
(2)注解声明@Inherited,结果如下:
===类===
interface SubInterface
null
===方法===
public abstract void ParentInterface.method1()
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=ParentInterface method1)
结果:
| 未声明@Inherited | 声明@Inherited | |
| 父接口类上注解能否被继承 | 否 | 否 |
| 父接口方法上注解能否被继承 | 能 | 能 |
2. 测试接口实现
(1)父接口:
@MyAnnotation(name = "Parent") public interface ParentInterface { @MyAnnotation(name = "ParentInterface method1") void method1(); }
(2)实现类
public class Children implements ParentInterface { @Override public void method1() { } }
测试代码:
import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.apache.commons.lang3.ClassUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.FieldUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.MethodUtils; public class PlainTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { // 获取类上注解 Class<?> class1 = ClassUtils.getClass("Children"); MyAnnotation annotation = class1.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===类==="); System.out.println(class1); System.out.println(annotation); // 获取方法上注解 Method matchingAccessibleMethod = MethodUtils.getMatchingAccessibleMethod(class1, "method1"); MyAnnotation annotation2 = matchingAccessibleMethod.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===方法==="); System.out.println(matchingAccessibleMethod); System.out.println(annotation2); } }
(1)注解未声明@Inherited,结果如下:
===类===
class Children
null
===方法===
public void Children.method1()
null
(2)注解声明@Inherited,结果如下:
===类===
class Children
null
===方法===
public void Children.method1()
null
结果:
| 注解未声明@Inherited | 注解声明@Inherited | |
| 实现类类能否继承接口注解 | 否 | 否 |
| 实现类方法能否继承接口注解 | 否 | 否 |
3.测试类继承:
父类:
import lombok.Data; @MyAnnotation(name = "Parent") @Data public class Parent { @MyAnnotation(name = "Parent name") private String name; @MyAnnotation(name = "ParentInterface method1") public void method1() { } @MyAnnotation(name = "ParentInterface method2") public void method2() { } }
子类:
public class Children extends Parent { @Override public void method2() { } }
测试代码:
import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.apache.commons.lang3.ClassUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.FieldUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect.MethodUtils; public class PlainTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { // 获取类上注解 Class<?> class1 = ClassUtils.getClass("Children"); MyAnnotation annotation = class1.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===类==="); System.out.println(class1); System.out.println(annotation); // 获取方法上注解 Method matchingAccessibleMethod = MethodUtils.getMatchingAccessibleMethod(class1, "method1"); MyAnnotation annotation2 = matchingAccessibleMethod.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===方法==="); System.out.println(matchingAccessibleMethod); System.out.println(annotation2); // 获取重写的方法上注解 Method method2 = MethodUtils.getMatchingAccessibleMethod(class1, "method2"); MyAnnotation method2Anno = method2.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===override方法==="); System.out.println(method2); System.out.println(method2Anno); // 获取字段上注解 Field field = FieldUtils.getField(class1, "name", true); if (field != null) { MyAnnotation annotation3 = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("===属性==="); System.out.println(field); System.out.println(annotation3); } } }
测试结果如下:
(1)注解未声明@Inherited,结果如下:
===类===
class Children
null
===方法===
public void Parent.method1()
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=ParentInterface method1)
===override方法===
public void Children.method2()
null
===属性===
private java.lang.String Parent.name
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=Parent name)
(2)注解声明@Inherited,结果如下:
===类===
class Children
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=Parent)
===方法===
public void Parent.method1()
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=ParentInterface method1)
===override方法===
public void Children.method2()
null
===属性===
private java.lang.String Parent.name
@MyAnnotation(value=20, name=Parent name)
结果:
| 注解未声明@Inherited | 注解声明@Inherited | |
| 子类能否继承父类类上注解 | 否 | 能 |
| 子类继承的属性能否继承注解 | 能 | 能 |
| 子类继承的方法(未覆盖)能否继承注解 | 能 | 能 |
| 子类继承的方法(覆盖)能否继承注解 | 否 | 否 |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号