shiro源码(四)-角色和权限验证过滤器原理以及基于注解验证原理
有时候我们在接口会进行权限鉴定,下面研究其鉴权原理。也就是研究基于角色的鉴权和基于权限码的鉴权。
1. 前置配置
1. shiro 配置
/** * 路径 -> 过滤器名称1[参数1,参数2,参数3...],过滤器名称2[参数1,参数2...]... * 自定义配置(前面是路径, 后面是具体的过滤器名称加参数,多个用逗号进行分割,过滤器参数也多个之间也是用逗号分割)) * 有的过滤器不需要参数,比如anon, authc, shiro 在解析的时候接默认解析一个数组为 [name, null] */ FILTER_CHAIN_DEFINITION_MAP.put("/test2", "anon"); // 测试地址 FILTER_CHAIN_DEFINITION_MAP.put("/login2", "anon"); // 登陆地址 FILTER_CHAIN_DEFINITION_MAP.put("/login3", "anon"); // 登陆地址 FILTER_CHAIN_DEFINITION_MAP.put("/user/**", "roles[系统管理员,用户管理员],perms[user:manager:*]"); FILTER_CHAIN_DEFINITION_MAP.put("/dept/**", "perms[dept:manage:*]"); FILTER_CHAIN_DEFINITION_MAP.put("/**", "authc"); // 所有资源都需要经过验证
2. com.zd.bx.config.shiro.CustomRealm 自定义realm
package com.zd.bx.config.shiro; import com.beust.jcommander.internal.Lists; import com.zd.bx.bean.user.User; import com.zd.bx.utils.permission.PermissionUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.*; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomRealm.class); /** * 鉴权 * * @param principalCollection * @return */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { // getPrimaryPrincipal获取到的是doGetAuthenticationInfo方法最后存进去的user对象 Object primaryPrincipal = principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal(); if (primaryPrincipal == null) { return null; } SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); User currentUser = (User) primaryPrincipal; // 添加角色 authorizationInfo.addRoles(Lists.newArrayList("管理员")); // 添加权限 authorizationInfo.addStringPermissions(Lists.newArrayList("user:manage:*", "dept:manage:*")); log.debug("authorizationInfo roles: {}, permissions: {}", authorizationInfo.getRoles(), authorizationInfo.getStringPermissions()); return authorizationInfo; } /** * 认证 */ @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { if (authenticationToken == null || !(authenticationToken instanceof UsernamePasswordToken)) { return null; } User user = new User(); user.setPassword("111222"); return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPassword(), this.getName()); } @Override public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) { log.info("token: {}", token); return token != null && UsernamePasswordToken.class.isAssignableFrom(token.getClass()); } }
2. 基于角色的校验原理
1. 访问地址: http://localhost:8081/user/test
2. 入口是 SpringShiroFilter, 请求到达 org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.OncePerRequestFilter#doFilter
3. 然后到达:org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.AbstractShiroFilter#doFilterInternal 创建Subject、 绑定到ThreadLocal 对象内部、构造FilterChain (Shiro 环境需要经过的Filter)
protected void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, final FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException { Throwable t = null; try { final ServletRequest request = prepareServletRequest(servletRequest, servletResponse, chain); final ServletResponse response = prepareServletResponse(request, servletResponse, chain); final Subject subject = createSubject(request, response); //noinspection unchecked subject.execute(new Callable() { public Object call() throws Exception { updateSessionLastAccessTime(request, response); executeChain(request, response, chain); return null; } }); } catch (ExecutionException ex) { t = ex.getCause(); } catch (Throwable throwable) { t = throwable; } if (t != null) { if (t instanceof ServletException) { throw (ServletException) t; } if (t instanceof IOException) { throw (IOException) t; } //otherwise it's not one of the two exceptions expected by the filter method signature - wrap it in one: String msg = "Filtered request failed."; throw new ServletException(msg, t); } }
4. 到达 org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.AbstractShiroFilter#executeChain
protected void executeChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain origChain) throws IOException, ServletException { FilterChain chain = getExecutionChain(request, response, origChain); chain.doFilter(request, response); }
1》 org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.AbstractShiroFilter#getExecutionChain 获取过滤器链
protected FilterChain getExecutionChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain origChain) { FilterChain chain = origChain; FilterChainResolver resolver = getFilterChainResolver(); if (resolver == null) { log.debug("No FilterChainResolver configured. Returning original FilterChain."); return origChain; } FilterChain resolved = resolver.getChain(request, response, origChain); if (resolved != null) { log.trace("Resolved a configured FilterChain for the current request."); chain = resolved; } else { log.trace("No FilterChain configured for the current request. Using the default."); } return chain; }
- 调用 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.mgt.PathMatchingFilterChainResolver#getChain
public FilterChain getChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain originalChain) { FilterChainManager filterChainManager = getFilterChainManager(); if (!filterChainManager.hasChains()) { return null; } String requestURI = getPathWithinApplication(request); // in spring web, the requestURI "/resource/menus" ---- "resource/menus/" bose can access the resource // but the pathPattern match "/resource/menus" can not match "resource/menus/" // user can use requestURI + "/" to simply bypassed chain filter, to bypassed shiro protect if(requestURI != null && !DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR.equals(requestURI) && requestURI.endsWith(DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR)) { requestURI = requestURI.substring(0, requestURI.length() - 1); } //the 'chain names' in this implementation are actually path patterns defined by the user. We just use them //as the chain name for the FilterChainManager's requirements for (String pathPattern : filterChainManager.getChainNames()) { if (pathPattern != null && !DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR.equals(pathPattern) && pathPattern.endsWith(DEFAULT_PATH_SEPARATOR)) { pathPattern = pathPattern.substring(0, pathPattern.length() - 1); } // If the path does match, then pass on to the subclass implementation for specific checks: if (pathMatches(pathPattern, requestURI)) { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Matched path pattern [" + pathPattern + "] for requestURI [" + Encode.forHtml(requestURI) + "]. " + "Utilizing corresponding filter chain..."); } return filterChainManager.proxy(originalChain, pathPattern); } } return null; }
这里根据路径进行正则匹配,如果满足条件调用 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.mgt.DefaultFilterChainManager#proxy 生成代理FilterChain。
public FilterChain proxy(FilterChain original, String chainName) { NamedFilterList configured = getChain(chainName); if (configured == null) { String msg = "There is no configured chain under the name/key [" + chainName + "]."; throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg); } return configured.proxy(original); }
最后生成的代理FilterChain 如下:

2》调用org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.ProxiedFilterChain#doFilter 开始执行代理FilterChain 逻辑
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException { if (this.filters == null || this.filters.size() == this.index) { //we've reached the end of the wrapped chain, so invoke the original one: if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Invoking original filter chain."); } this.orig.doFilter(request, response); } else { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Invoking wrapped filter at index [" + this.index + "]"); } this.filters.get(this.index++).doFilter(request, response, this); } }
5. 权限过滤器开始过滤:
模板模式, 会调用到: org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.AdviceFilter#doFilterInternal
public void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException { Exception exception = null; try { boolean continueChain = preHandle(request, response); if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Invoked preHandle method. Continuing chain?: [" + continueChain + "]"); } if (continueChain) { executeChain(request, response, chain); } postHandle(request, response); if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Successfully invoked postHandle method"); } } catch (Exception e) { exception = e; } finally { cleanup(request, response, exception); } }
preHandle(request, response); 调用到 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.PathMatchingFilter#preHandle
protected boolean preHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (this.appliedPaths == null || this.appliedPaths.isEmpty()) { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("appliedPaths property is null or empty. This Filter will passthrough immediately."); } return true; } for (String path : this.appliedPaths.keySet()) { // If the path does match, then pass on to the subclass implementation for specific checks //(first match 'wins'): if (pathsMatch(path, request)) { log.trace("Current requestURI matches pattern '{}'. Determining filter chain execution...", path); Object config = this.appliedPaths.get(path); return isFilterChainContinued(request, response, path, config); } } //no path matched, allow the request to go through: return true; }
这里先是进行路径匹配,然后 this.appliedPaths.get(path); 获取相关的配置, 获取到的信息如下:

然后调用 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.PathMatchingFilter#isFilterChainContinued
private boolean isFilterChainContinued(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, String path, Object pathConfig) throws Exception { if (isEnabled(request, response, path, pathConfig)) { //isEnabled check added in 1.2 if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Filter '{}' is enabled for the current request under path '{}' with config [{}]. " + "Delegating to subclass implementation for 'onPreHandle' check.", new Object[]{getName(), path, pathConfig}); } //The filter is enabled for this specific request, so delegate to subclass implementations //so they can decide if the request should continue through the chain or not: return onPreHandle(request, response, pathConfig); } if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Filter '{}' is disabled for the current request under path '{}' with config [{}]. " + "The next element in the FilterChain will be called immediately.", new Object[]{getName(), path, pathConfig}); } //This filter is disabled for this specific request, //return 'true' immediately to indicate that the filter will not process the request //and let the request/response to continue through the filter chain: return true; }
继续向下调用到 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.AccessControlFilter#onPreHandle :
public boolean onPreHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception { return isAccessAllowed(request, response, mappedValue) || onAccessDenied(request, response, mappedValue); }
这里和之前一样有两个逻辑: isAccessAllowed 请求允许直接返回, 则进行下一个过滤器链的调用;返回true表示继续执行后面的过滤器链,返回false表示不执行后面过滤器链 (好像和方法名称有点歧义...)。
(1) org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.RolesAuthorizationFilter#isAccessAllowed 判断请求是否允许,开始权限校验:
public boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws IOException { Subject subject = getSubject(request, response); String[] rolesArray = (String[]) mappedValue; if (rolesArray == null || rolesArray.length == 0) { //no roles specified, so nothing to check - allow access. return true; } Set<String> roles = CollectionUtils.asSet(rolesArray); return subject.hasAllRoles(roles); }
参数解释:
mappedValue 就是解析到的配置的角色名称,上面传递的是: ["系统管理员", "用户管理员"]
代码解释:
校验之后调用到: org.apache.shiro.subject.support.DelegatingSubject#hasAllRoles 请求转交给subject
public boolean hasAllRoles(Collection<String> roleIdentifiers) { return hasPrincipals() && securityManager.hasAllRoles(getPrincipals(), roleIdentifiers); }
1》 org.apache.shiro.subject.support.DelegatingSubject#hasPrincipals 实际是判断是否认证,认证之后这里会存放认证信息
protected boolean hasPrincipals() { return !isEmpty(getPrincipals()); }
这里做个简单的认证,也就是认证信息存到session 中,然后研究下面第二步。

2》 org.apache.shiro.mgt.AuthorizingSecurityManager#hasAllRoles 判断是否有权限, 请求转交给授权器
public boolean hasAllRoles(PrincipalCollection principals, Collection<String> roleIdentifiers) { return this.authorizer.hasAllRoles(principals, roleIdentifiers); }
然后请求调用到: org.apache.shiro.authz.ModularRealmAuthorizer#hasAllRoles
public boolean hasAllRoles(PrincipalCollection principals, Collection<String> roleIdentifiers) { assertRealmsConfigured(); for (String roleIdentifier : roleIdentifiers) { if (!hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier)) { return false; } } return true; } protected void assertRealmsConfigured() throws IllegalStateException { Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); if (realms == null || realms.isEmpty()) { String msg = "Configuration error: No realms have been configured! One or more realms must be " + "present to execute an authorization operation."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } } public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String roleIdentifier) { assertRealmsConfigured(); for (Realm realm : getRealms()) { if (!(realm instanceof Authorizer)) continue; if (((Authorizer) realm).hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier)) { return true; } } return false; }
可以看到是遍历所有的角色,然后调用hasRole 单个进行判断。 hasRole 内部获取到realm, 然后请求转交给realm 判断是否有角色。请求到达:org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm#hasRole(org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection, java.lang.String)
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principal, String roleIdentifier) { AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal); return hasRole(roleIdentifier, info); } protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { if (principals == null) { return null; } AuthorizationInfo info = null; if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Retrieving AuthorizationInfo for principals [" + principals + "]"); } Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthorizationCache(); if (cache != null) { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Attempting to retrieve the AuthorizationInfo from cache."); } Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals); info = cache.get(key); if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { if (info == null) { log.trace("No AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]"); } else { log.trace("AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]"); } } } if (info == null) { // Call template method if the info was not found in a cache info = doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals); // If the info is not null and the cache has been created, then cache the authorization info. if (info != null && cache != null) { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Caching authorization info for principals: [" + principals + "]."); } Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals); cache.put(key, info); } } return info; } protected boolean hasRole(String roleIdentifier, AuthorizationInfo info) { return info != null && info.getRoles() != null && info.getRoles().contains(roleIdentifier); }
到这里可以看出其逻辑, 调用 getAuthorizationInfo 获取其授权信息,然后从授权角色信息中判断其是否包含指定的角色。
getAuthorizationInfo 获取授权信息和获取认证信息逻辑一样,先从缓存拿,缓存拿步到就调用realm 实时获取。 这里没有缓存,所以直接调用 com.zd.bx.config.shiro.CustomRealm#doGetAuthorizationInfo 实时获取。
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { // getPrimaryPrincipal获取到的是doGetAuthenticationInfo方法最后存进去的user对象 Object primaryPrincipal = principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal(); if (primaryPrincipal == null) { return null; } SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); User currentUser = (User) primaryPrincipal; // 添加角色 authorizationInfo.addRoles(PermissionUtils.listUserRolenames(currentUser)); // 添加权限 authorizationInfo.addStringPermissions(PermissionUtils.listUserPermissionCodes(currentUser)); log.debug("authorizationInfo roles: {}, permissions: {}", authorizationInfo.getRoles(), authorizationInfo.getStringPermissions()); return authorizationInfo; }
可以看到该方法就是调用到自己的realm 获取授权, 获取一个Authorizationinfo 对象。然后拿该AuthorizationInfo 对象调用org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm#hasRole(java.lang.String, org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo) 进行判断是否有角色, 这个方法对授权信息Authorizationinfo 进行非空判断、角色集合判断、是否包含指定角色判断后返回。
(2) 上面返回false 之后调用 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.AccessControlFilter#onAccessDenied(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, java.lang.Object) 进行 onAccessDenied 判断,如果这个方法返回 true 则可以下一个链条的执行; 如果返回false 则步进行链条的执行。
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception { return onAccessDenied(request, response); }
继续请求调用到 org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.AuthorizationFilter#onAccessDenied:
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException { Subject subject = getSubject(request, response); // If the subject isn't identified, redirect to login URL if (subject.getPrincipal() == null) { saveRequestAndRedirectToLogin(request, response); } else { // If subject is known but not authorized, redirect to the unauthorized URL if there is one // If no unauthorized URL is specified, just return an unauthorized HTTP status code String unauthorizedUrl = getUnauthorizedUrl(); //SHIRO-142 - ensure that redirect _or_ error code occurs - both cannot happen due to response commit: if (StringUtils.hasText(unauthorizedUrl)) { WebUtils.issueRedirect(request, response, unauthorizedUrl); } else { WebUtils.toHttp(response).sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED); } } return false; }
这里判断未认证的话送到重定向到登录地址; 如果是认证之后,权限不足。 如果有未授权页面就重定向到未授权页面; 如果没有未授权页面就调用WebUtils.toHttp(response).sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED); 发送未授权信息。然后返回false, 返回false 则步进行后续流程。
调用到: org.apache.catalina.connector.ResponseFacade#sendError(int) 发送错误响应码
public void sendError(int sc) throws IOException { if (this.isCommitted()) { throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("coyoteResponse.sendError.ise")); } else { this.response.setAppCommitted(true); this.response.sendError(sc); } }
上面就是基于角色鉴权流程。 都是以org.apache.shiro.web.filter.AccessControlFilter#onPreHandle 为入口, 里面两个方法: isAccessAllowed 判断是否允许执行, 返回true则继续后续的过滤器的执行, 返回false则继续调用onAccessDenied 。 onAccessDenied 中处理一些拒绝处理后的逻辑, 返回true 表示可以继续执行,返回false 表示后续过滤器也不执行。
3. 权限校验原理
1. 访问连接 : http://localhost:8081/dept/test
2. 前面步骤和基于角色校验一样,断点下在org.apache.shiro.web.filter.AccessControlFilter#onPreHandle 进行查看:
public boolean onPreHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception { return isAccessAllowed(request, response, mappedValue) || onAccessDenied(request, response, mappedValue); }
参数: mappedValue 传递的是 ["dept:manage:*"]
1》 isAccessAllowed 方法: org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.PermissionsAuthorizationFilter#isAccessAllowed
public boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws IOException { Subject subject = getSubject(request, response); String[] perms = (String[]) mappedValue; boolean isPermitted = true; if (perms != null && perms.length > 0) { if (perms.length == 1) { if (!subject.isPermitted(perms[0])) { isPermitted = false; } } else { if (!subject.isPermittedAll(perms)) { isPermitted = false; } } } return isPermitted; }
这里可以理解, 过程和上面一样转交给Subject,
(1) 调用org.apache.shiro.subject.support.DelegatingSubject#isPermitted(java.lang.String)
public boolean isPermitted(String permission) { return hasPrincipals() && securityManager.isPermitted(getPrincipals(), permission); }
首先校验是否认证,然后转交给securityManager。
(2) org.apache.shiro.mgt.AuthorizingSecurityManager#isPermitted(org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection, java.lang.String)
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permissionString) { return this.authorizer.isPermitted(principals, permissionString); }
继续转交给授权器
(3) org.apache.shiro.authz.ModularRealmAuthorizer#isPermitted(org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection, java.lang.String)
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission) { assertRealmsConfigured(); for (Realm realm : getRealms()) { if (!(realm instanceof Authorizer)) continue; if (((Authorizer) realm).isPermitted(principals, permission)) { return true; } } return false; }
可以看到是获取到realm, 遍历然后进行鉴权。
(4) org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm#isPermitted(org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection, java.lang.String)
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission) { Permission p = getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permission); return isPermitted(principals, p); }
这里将权限码解析成Permission 对象。 org.apache.shiro.authz.permission.WildcardPermissionResolver#resolvePermission:
public Permission resolvePermission(String permissionString) { return new WildcardPermission(permissionString, caseSensitive); }
org.apache.shiro.authz.permission.WildcardPermission#WildcardPermission(java.lang.String, boolean):
/*-------------------------------------------- | C O N S T A N T S | ============================================*/ protected static final String WILDCARD_TOKEN = "*"; protected static final String PART_DIVIDER_TOKEN = ":"; protected static final String SUBPART_DIVIDER_TOKEN = ","; protected static final boolean DEFAULT_CASE_SENSITIVE = false; public WildcardPermission(String wildcardString, boolean caseSensitive) { setParts(wildcardString, caseSensitive); } protected void setParts(String wildcardString, boolean caseSensitive) { wildcardString = StringUtils.clean(wildcardString); if (wildcardString == null || wildcardString.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wildcard string cannot be null or empty. Make sure permission strings are properly formatted."); } if (!caseSensitive) { wildcardString = wildcardString.toLowerCase(); } List<String> parts = CollectionUtils.asList(wildcardString.split(PART_DIVIDER_TOKEN)); this.parts = new ArrayList<Set<String>>(); for (String part : parts) { Set<String> subparts = CollectionUtils.asSet(part.split(SUBPART_DIVIDER_TOKEN)); if (subparts.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wildcard string cannot contain parts with only dividers. Make sure permission strings are properly formatted."); } this.parts.add(subparts); } if (this.parts.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wildcard string cannot contain only dividers. Make sure permission strings are properly formatted."); } }
可以看到是按照传的权限码按照 ":" 切割,然后再按照"," 进行分割。 最后放到parts 集合内部。
(5) 继续调用:org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm#isPermitted(org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection, org.apache.shiro.authz.Permission)
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, Permission permission) { AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principals); return isPermitted(permission, info); } protected boolean isPermitted(Permission permission, AuthorizationInfo info) { Collection<Permission> perms = getPermissions(info); if (perms != null && !perms.isEmpty()) { for (Permission perm : perms) { if (perm.implies(permission)) { return true; } } } return false; } //visibility changed from private to protected per SHIRO-332 protected Collection<Permission> getPermissions(AuthorizationInfo info) { Set<Permission> permissions = new HashSet<Permission>(); if (info != null) { Collection<Permission> perms = info.getObjectPermissions(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) { permissions.addAll(perms); } perms = resolvePermissions(info.getStringPermissions()); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) { permissions.addAll(perms); } perms = resolveRolePermissions(info.getRoles()); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) { permissions.addAll(perms); } } if (permissions.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptySet(); } else { return Collections.unmodifiableSet(permissions); } } private Collection<Permission> resolvePermissions(Collection<String> stringPerms) { Collection<Permission> perms = Collections.emptySet(); PermissionResolver resolver = getPermissionResolver(); if (resolver != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(stringPerms)) { perms = new LinkedHashSet<Permission>(stringPerms.size()); for (String strPermission : stringPerms) { if (StringUtils.clean(strPermission) != null) { Permission permission = resolver.resolvePermission(strPermission); perms.add(permission); } } } return perms; }
getAuthorizationInfo 同上面角色校验一样获取授权信息,会调用realm 的 doGetAuthorizationInfo () 方法。 然后从这个方法返回的参数内部获取到permission 权限码集合和权限码对象,然后构造成Collection<Permission>, 代表当前用户具有的权限。 然后遍历当前用户具有的权限, 调用org.apache.shiro.authz.permission.WildcardPermission#implies 判断权限码是否匹配:
public boolean implies(Permission p) { // By default only supports comparisons with other WildcardPermissions if (!(p instanceof WildcardPermission)) { return false; } WildcardPermission wp = (WildcardPermission) p; List<Set<String>> otherParts = wp.getParts(); int i = 0; for (Set<String> otherPart : otherParts) { // If this permission has less parts than the other permission, everything after the number of parts contained // in this permission is automatically implied, so return true if (getParts().size() - 1 < i) { return true; } else { Set<String> part = getParts().get(i); if (!part.contains(WILDCARD_TOKEN) && !part.containsAll(otherPart)) { return false; } i++; } } // If this permission has more parts than the other parts, only imply it if all of the other parts are wildcards for (; i < getParts().size(); i++) { Set<String> part = getParts().get(i); if (!part.contains(WILDCARD_TOKEN)) { return false; } } return true; }
可以看到其匹配规则是对 权限码 拆分后的各个权限部分进行匹配, * 代表任意权限, 则可以下一个part 的匹配。
- getParts().size() - 1 < i 是当前权限码的part 部分少于需要匹配的部分,则返回true。
比如: user:manage -》user:manage:1。 这种情况返回true。 理解为, 比完user、manage 两部分之后, i 变为2, getParts().size() - 1 是1。 也就是当前的Permisson(user:manage) 没有剩余可比的part 部分,则返回true。
- 如果当前比对的不包含*, 则认为是等值匹配。 两个part 必须一样,如果不一样则返回false。 否则认为一样,就继续下个part 部分比对。
- 继续进行判断是处理当前对象权限码大于被比对的情况,比如: user:manage:* -》user:manage 。那么多出的部分只能是包含*, 否则会返回false。
也就是下面几种情况可以返回true:(前面是当前用户拥有的权限码, 后面是需要验证的权限)
user:manage -》user:manage:1:2:....
user:manage:1 -》 user:manage:1
user:manage:*:* -》user:manage
2》 onAccessDenied 方法和上面基于角色校验逻辑一样。
4. 基于注解进行权限校验原理
我们也可以基于注解对方法进行校验。 这种大体思路就是基于AOP实现。
1. 开启:
@Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(SecurityManager securityManager) { AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; }
2. 测试代码
@RequiresPermissions(value = {"test"})
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return "test";
}
3. 测试
访问报错
org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthorizedException: Subject does not have permission [test] at org.apache.shiro.authz.ModularRealmAuthorizer.checkPermission(ModularRealmAuthorizer.java:323) ~[shiro-core-1.5.3.jar:1.5.3] at org.apache.shiro.mgt.AuthorizingSecurityManager.checkPermission(AuthorizingSecurityManager.java:137) ~[shiro-core-1.5.3.jar:1.5.3] at org.apache.shiro.subject.support.DelegatingSubject.checkPermission(DelegatingSubject.java:209) ~[shiro-core-1.。。。
4. 原理
基于 PointcutAdvisor 接口实现AOP。
1. AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor类图
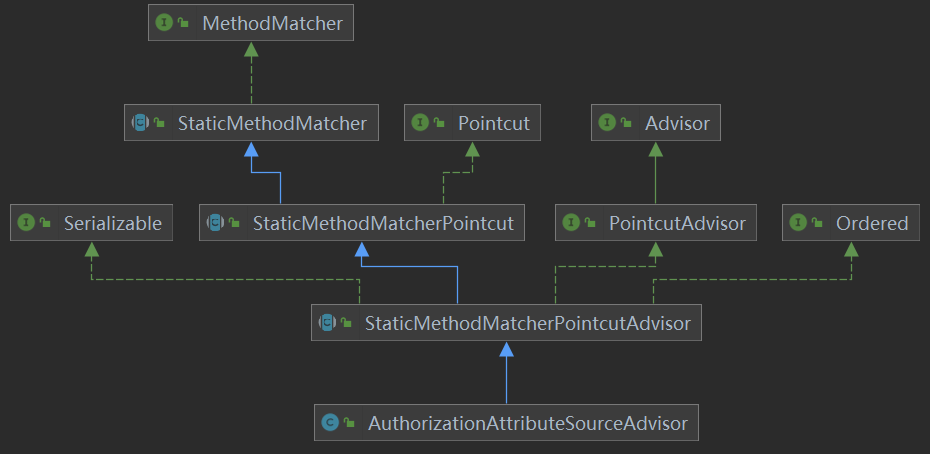
2. 源码:
package org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor; import org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.*; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.aop.support.StaticMethodMatcherPointcutAdvisor; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * TODO - complete JavaDoc * * @since 0.1 */ @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"}) public class AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcutAdvisor { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.class); private static final Class<? extends Annotation>[] AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES = new Class[] { RequiresPermissions.class, RequiresRoles.class, RequiresUser.class, RequiresGuest.class, RequiresAuthentication.class }; protected SecurityManager securityManager = null; /** * Create a new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor. */ public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor() { setAdvice(new AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor()); } public SecurityManager getSecurityManager() { return securityManager; } public void setSecurityManager(org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager) { this.securityManager = securityManager; } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if the method or the class has any Shiro annotations, false otherwise. * The annotations inspected are: * <ul> * <li>{@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresAuthentication RequiresAuthentication}</li> * <li>{@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresUser RequiresUser}</li> * <li>{@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresGuest RequiresGuest}</li> * <li>{@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresRoles RequiresRoles}</li> * <li>{@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresPermissions RequiresPermissions}</li> * </ul> * * @param method the method to check for a Shiro annotation * @param targetClass the class potentially declaring Shiro annotations * @return <tt>true</tt> if the method has a Shiro annotation, false otherwise. * @see org.springframework.aop.MethodMatcher#matches(java.lang.reflect.Method, Class) */ public boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass) { Method m = method; if ( isAuthzAnnotationPresent(m) ) { return true; } //The 'method' parameter could be from an interface that doesn't have the annotation. //Check to see if the implementation has it. if ( targetClass != null) { try { m = targetClass.getMethod(m.getName(), m.getParameterTypes()); return isAuthzAnnotationPresent(m) || isAuthzAnnotationPresent(targetClass); } catch (NoSuchMethodException ignored) { //default return value is false. If we can't find the method, then obviously //there is no annotation, so just use the default return value. } } return false; } private boolean isAuthzAnnotationPresent(Class<?> targetClazz) { for( Class<? extends Annotation> annClass : AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES ) { Annotation a = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(targetClazz, annClass); if ( a != null ) { return true; } } return false; } private boolean isAuthzAnnotationPresent(Method method) { for( Class<? extends Annotation> annClass : AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES ) { Annotation a = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, annClass); if ( a != null ) { return true; } } return false; } }
3. 解释:
(1) 判断是否匹配是: org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor#matches 方法。 实际是判断是否携带有org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor#AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES 指定的相关注解。
(2) org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor#AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor 是MethodInteceptor 的处理类:
package org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; import org.apache.shiro.aop.AnnotationResolver; import org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.*; import org.apache.shiro.spring.aop.SpringAnnotationResolver; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * Allows Shiro Annotations to work in any <a href="http://aopalliance.sourceforge.net/">AOP Alliance</a> * specific implementation environment (for example, Spring). * * @since 0.2 */ public class AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor extends AnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { public AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor() { List<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor>(5); //use a Spring-specific Annotation resolver - Spring's AnnotationUtils is nicer than the //raw JDK resolution process. AnnotationResolver resolver = new SpringAnnotationResolver(); //we can re-use the same resolver instance - it does not retain state: interceptors.add(new RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new AuthenticatedAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new UserAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new GuestAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); setMethodInterceptors(interceptors); } /** * Creates a {@link MethodInvocation MethodInvocation} that wraps an * {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation} instance, * enabling Shiro Annotations in <a href="http://aopalliance.sourceforge.net/">AOP Alliance</a> environments * (Spring, etc). * * @param implSpecificMethodInvocation AOP Alliance {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation MethodInvocation} * @return a Shiro {@link MethodInvocation MethodInvocation} instance that wraps the AOP Alliance instance. */ protected org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation createMethodInvocation(Object implSpecificMethodInvocation) { final MethodInvocation mi = (MethodInvocation) implSpecificMethodInvocation; return new org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation() { public Method getMethod() { return mi.getMethod(); } public Object[] getArguments() { return mi.getArguments(); } public String toString() { return "Method invocation [" + mi.getMethod() + "]"; } public Object proceed() throws Throwable { return mi.proceed(); } public Object getThis() { return mi.getThis(); } }; } /** * Simply casts the method argument to an * {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation} and then * calls <code>methodInvocation.{@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation#proceed proceed}()</code> * * @param aopAllianceMethodInvocation the {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation} * @return the {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation#proceed() org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation.proceed()} method call result. * @throws Throwable if the underlying AOP Alliance <code>proceed()</code> call throws a <code>Throwable</code>. */ protected Object continueInvocation(Object aopAllianceMethodInvocation) throws Throwable { MethodInvocation mi = (MethodInvocation) aopAllianceMethodInvocation; return mi.proceed(); } /** * Creates a Shiro {@link MethodInvocation MethodInvocation} instance and then immediately calls * {@link org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.AuthorizingMethodInterceptor#invoke super.invoke}. * * @param methodInvocation the AOP Alliance-specific <code>methodInvocation</code> instance. * @return the return value from invoking the method invocation. * @throws Throwable if the underlying AOP Alliance method invocation throws a <code>Throwable</code>. */ public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation mi = createMethodInvocation(methodInvocation); return super.invoke(mi); } }
methodInterceptors 维护了五个相关的Handler。
org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.AuthorizingMethodInterceptor:
public abstract class AuthorizingMethodInterceptor extends MethodInterceptorSupport { /** * Invokes the specified method (<code>methodInvocation.{@link org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation#proceed proceed}()</code> * if authorization is allowed by first * calling {@link #assertAuthorized(org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation) assertAuthorized}. */ public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { assertAuthorized(methodInvocation); return methodInvocation.proceed(); } /** * Asserts that the specified MethodInvocation is allowed to continue by performing any necessary authorization * (access control) checks first. * @param methodInvocation the <code>MethodInvocation</code> to invoke. * @throws AuthorizationException if the <code>methodInvocation</code> should not be allowed to continue/execute. */ protected abstract void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws AuthorizationException; }
invoke 执行AOP时 有assertAuthorized 逻辑。这个方法的逻辑也就是调用上面五个Handler, 然后调用其 supports 方法判断是否支持,然后调用其assertAuthorized 方法。
(3) 以org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor#RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor() 角色校验为例子
public class RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor extends AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor { /** * Default no-argument constructor that ensures this interceptor looks for * {@link RequiresRoles RequiresRoles} annotations in a method declaration. */ public RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor() { super( new RoleAnnotationHandler() ); } /** * @param resolver * @since 1.1 */ public RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor(AnnotationResolver resolver) { super(new RoleAnnotationHandler(), resolver); } }
org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor 源码如下:
public abstract class AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor extends AnnotationMethodInterceptor { /** * Constructor that ensures the internal <code>handler</code> is set which will be used to perform the * authorization assertion checks when a supported annotation is encountered. * @param handler the internal <code>handler</code> used to perform authorization assertion checks when a * supported annotation is encountered. */ public AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor( AuthorizingAnnotationHandler handler ) { super(handler); } /** * * @param handler * @param resolver * @since 1.1 */ public AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor( AuthorizingAnnotationHandler handler, AnnotationResolver resolver) { super(handler, resolver); } /** * Ensures the <code>methodInvocation</code> is allowed to execute first before proceeding by calling the * {@link #assertAuthorized(org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation) assertAuthorized} method first. * * @param methodInvocation the method invocation to check for authorization prior to allowing it to proceed/execute. * @return the return value from the method invocation (the value of {@link org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation#proceed() MethodInvocation.proceed()}). * @throws org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException if the <code>MethodInvocation</code> is not allowed to proceed. * @throws Throwable if any other error occurs. */ public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { assertAuthorized(methodInvocation); return methodInvocation.proceed(); } /** * Ensures the calling Subject is authorized to execute the specified <code>MethodInvocation</code>. * <p/> * As this is an AnnotationMethodInterceptor, this implementation merely delegates to the internal * {@link AuthorizingAnnotationHandler AuthorizingAnnotationHandler} by first acquiring the annotation by * calling {@link #getAnnotation(MethodInvocation) getAnnotation(methodInvocation)} and then calls * {@link AuthorizingAnnotationHandler#assertAuthorized(java.lang.annotation.Annotation) handler.assertAuthorized(annotation)}. * * @param mi the <code>MethodInvocation</code> to check to see if it is allowed to proceed/execute. * @throws AuthorizationException if the method invocation is not allowed to continue/execute. */ public void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation mi) throws AuthorizationException { try { ((AuthorizingAnnotationHandler)getHandler()).assertAuthorized(getAnnotation(mi)); } catch(AuthorizationException ae) { // Annotation handler doesn't know why it was called, so add the information here if possible. // Don't wrap the exception here since we don't want to mask the specific exception, such as // UnauthenticatedException etc. if (ae.getCause() == null) ae.initCause(new AuthorizationException("Not authorized to invoke method: " + mi.getMethod())); throw ae; } } }
可以看到上面(2) 执行AOP时调用 assertAuthorized 调用到 org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor#assertAuthorized。 这个调用到具体Handler的assertAuthorized 方法。
org.apache.shiro.authz.aop.RoleAnnotationHandler:
public class RoleAnnotationHandler extends AuthorizingAnnotationHandler { /** * Default no-argument constructor that ensures this handler looks for * {@link org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation.RequiresRoles RequiresRoles} annotations. */ public RoleAnnotationHandler() { super(RequiresRoles.class); } /** * Ensures that the calling <code>Subject</code> has the Annotation's specified roles, and if not, throws an * <code>AuthorizingException</code> indicating that access is denied. * * @param a the RequiresRoles annotation to use to check for one or more roles * @throws org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException * if the calling <code>Subject</code> does not have the role(s) necessary to * proceed. */ public void assertAuthorized(Annotation a) throws AuthorizationException { if (!(a instanceof RequiresRoles)) return; RequiresRoles rrAnnotation = (RequiresRoles) a; String[] roles = rrAnnotation.value(); if (roles.length == 1) { getSubject().checkRole(roles[0]); return; } if (Logical.AND.equals(rrAnnotation.logical())) { getSubject().checkRoles(Arrays.asList(roles)); return; } if (Logical.OR.equals(rrAnnotation.logical())) { // Avoid processing exceptions unnecessarily - "delay" throwing the exception by calling hasRole first boolean hasAtLeastOneRole = false; for (String role : roles) if (getSubject().hasRole(role)) hasAtLeastOneRole = true; // Cause the exception if none of the role match, note that the exception message will be a bit misleading if (!hasAtLeastOneRole) getSubject().checkRole(roles[0]); } } }
可以看到核心逻辑也是解析注解上的value。 然后调用 org.apache.shiro.subject.support.DelegatingSubject#checkRoles(java.util.Collection<java.lang.String>) 检查是否有相应权限。 最终和上面校验角色和权限一样。比如checkRoles 最终调用到:org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm#checkRole(java.lang.String, org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo)
protected void checkRole(String role, AuthorizationInfo info) { if (!hasRole(role, info)) { String msg = "User does not have role [" + role + "]"; throw new UnauthorizedException(msg); } }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 一个奇形怪状的面试题:Bean中的CHM要不要加volatile?
· 分享4款.NET开源、免费、实用的商城系统
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· Obsidian + DeepSeek:免费 AI 助力你的知识管理,让你的笔记飞起来!
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了
2017-10-29 [JSP]自定义EL函数以及使用
2017-10-29 【zTree】zTree根据后台数据生成树并动态设置前面的节点复选框的选中状态
2017-10-29 如何改变linux系统的只读文件的权限