数据结构算法及应用——二叉树
一、二叉树性质
特性1 包含n (n> 0 )个元素的二叉树边数为n-1
特性2 二叉树的高度(height)或深度(depth)是指该二叉树的层数(有几层元素,而不是有层的元素间隔)
特性3 若二叉树的高度为h,h≥0,则该二叉树最少有h个元素,最多有(2^h – 1)个元素。
特性4 包含n 个元素的二叉树的高度最大为n,最小[log2 (n+1)]
二、满二叉树:
当高度为h 的二叉树恰好有2^h - 1个元素时,称其为满二叉树.
三、完全二叉树
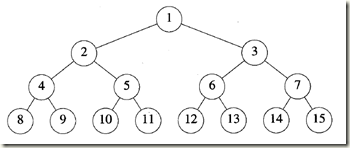
假设对高度为h 的满二叉树中的元素按从第上到下,从左到右的顺序从1到2^h- 1进行编号(如图8 - 6所示)。假设从满二叉树中删除k个元素,其编号为2^h -i, 1≤i≤k,所得到的二叉树被称为完全二叉树.
注意满二叉树是完全二叉树的一个特例,并且,注意有n个元素的完全二叉树的深度为[log2 (n+1)]
特性5 设完全二叉树中一元素的序号为i, 1≤i≤n。则有以下关系成立:
1) 当i = 1时,该元素为二叉树的根。若i > 1,则该元素父节点的编号为 下取整【i/2】
2) 当2i >n时,该元素无左孩子。否则,其左孩子的编号为2i。
3) 若2i + 1 >n,该元素无右孩子。否则,其右孩子编号为2i + 1。
四、二叉树的遍历
• 前序遍历。
• 中序遍历。
• 后序遍历。
• 逐层遍历。
在进行前序遍历时,每个节点是在其左右子树被访问之前进行访问的;
在中序遍历时,首先访问左子树,然后访问子树的根节点,最后访问右子树。
在后序遍历时,当左右子树均访问完之后才访问子树的根节点。
五、源码
1.InterfaceBinaryTree 类
#pragma once
/*
T为BinaryTreeNode<U>类型的数据
*/
template<class T>
class InterfaceBinaryTree {
//如果二叉树为空,则返回true ,否则返回false
virtual bool IsEmpty() const=0;
//返回二叉树的大小
virtual int Size()const = 0;
//前序遍历
virtual void PreOrder(void (*)(T *))const=0; //参数是一个指向 void Func(T*)类型的函数指针
//中序遍历
virtual void InOrder(void(*)(T *))const=0;
//后序遍历
virtual void PostOrder(void(*)(T *))const=0;
//逐层遍历
virtual void LevelOrder(void(*)(T *))const=0;
};
2.BinaryTreeNode类
#pragma once
template<class T>
class BinaryTreeNode{
public:
template<class T> friend class BinaryTree;
BinaryTreeNode() {
leftChild = rightChild = 0;
}
BinaryTreeNode(const T &data) {
this->data = data;
leftChild = rightChild = 0;
}
BinaryTreeNode(const T &data, BinaryTreeNode<T> *leftSubTree, BinaryTreeNode<T> *rightSubTree) {
this->data = data;
leftChild = leftSubTree;
rightChild = rightSubTree;
}
private:
T data;
BinaryTreeNode<T> *leftChild;
BinaryTreeNode<T> *rightChild;
};
3.BinaryTree类
#pragma once
#include"BinaryTreeNode.h"
#include"InterfaceBinaryTree.h"
#include"MyException.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class BinaryTree:public InterfaceBinaryTree<BinaryTreeNode<T>> {
public:
BinaryTree() { root = 0; }
~BinaryTree() {};
//如果二叉树为空,则返回true ,否则返回false
bool IsEmpty() const {
return (root == 0) ? true : false;
}
//取根节点的数据域放入x;如果操作失败,则返回false,否则返回true
bool Root(T &x)const;
//创建一个二叉树,root作为根节点, left作为左子树,right作为右子树
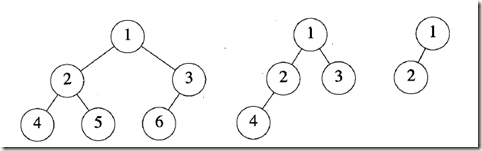
void MakeTree(const T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right);
//拆分二叉树
void BreakTree(T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right);
void PreOrderOutput() const {
PreOrder(output);
}
void InOrderOutput()const {
InOrder(output);
}
void PostOrderOutput()const {
PostOrder(output);
}
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _preOrder(root);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _inOrder(root);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _postOrder(root);
}
//逐层遍历
void LevelOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _levelOrder(root);
}
void Delete() {
PostOrder(free);
root = 0;
}
int Height()const {
return height(root);
}
int Size()const {
count = 0;
InOrder(addCount);
return count;
}
protected:
static void _preOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void _inOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void _postOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void _levelOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void(*visit)(BinaryTreeNode<T> *); //函数指针,用于遍历时的函数访问
static void output(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
cout << t->data << " ";
}
static void free(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
delete t;
}
static void addCount(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
count++;
}
static int height(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t);
private:
BinaryTreeNode<T> *root;
static int count;
};
//访问函数的函数指针
template<class T>
void(*BinaryTree<T>::visit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*);
template<class T>
int BinaryTree<T>::count = 0;
//前序遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_preOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
if (root != 0) {
BinaryTree<T>::visit(root);
_preOrder(root->leftChild);
_preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
//中序遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_inOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
if (root != 0) {
_inOrder(root->leftChild);
BinaryTree<T>::visit(root);
_inOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
//后序遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_postOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
if (root != 0) {
_postOrder(root->leftChild);
_postOrder(root->rightChild);
BinaryTree<T>::visit(root);
}
}
//逐层遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_levelOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
}
//取根节点的数据域放入x;如果操作失败,则返回false,否则返回true
template<class T>
bool BinaryTree<T>::Root(T &x)const {
if (root == 0) {
return false;
}
x = root->data;
return true;
}
/*生成一个二叉树,新建一个BinaryTreeNode节点,使其值为element,左子树为left,右子树为right*/
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::MakeTree(const T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right) {
root = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element, left.root, right.root);
left.root = right.root = 0;
}
/*将一个二叉树拆分成左子树和右子树两部分,根节点的值保存到element*/
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::BreakTree(T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right) {
if (root == 0)
throw BadInput();
element = root->data;
left.root = root->leftChild;
right.root = root->rightChild;
delete root; //删除原来根节点的内存
root = 0;
}
/*求二叉树的高度*/
template<class T>
int BinaryTree<T>::height(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
if (t == 0)
return 0;
int leftHeight = height(t->leftChild); //左子树的高度
int rightHeight = height(t->rightChild); //右子树的高度
//返回左右子树中的最大值加一
if (leftHeight > rightHeight)
return ++leftHeight;
else
return ++rightHeight;
}
4.MyException类
#pragma once
#pragma once
// exception classes for various error types
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class NoMem {
public:
NoMem() {
this->message = "内存不足";
}
NoMem(string msg) {
this->message = msg;
}
void OutputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;
}
private:
string message;
};
class OutOfBounds {
public:
OutOfBounds() {
this->message = "输入超过了数组的界";
}
OutOfBounds(string msg) {
this->message = msg;
}
void OutputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;
}
private:
string message;
};
class BadInput {
public:
BadInput() {
this->message = "输入有误";
}
BadInput(string msg) {
this->message = msg;
}
void OutputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;
}
private:
string message;
};
henry