【SpringBoot】SpringBoot事务
导读
本文尝试着围绕以下几个问题来讲解spring-boot事务:
- 内部调用的方法上声明@Transactional为何会失效?
- spring-boot自动装配就事务管理做了哪些工作?
- spring-boot事务的传播行为是如何控制的?
- spring-boot如何实现编程式事务?
- 什么是分布式事务?
- spring-boot中如何实现分布式事务?
文章的 代码演示
1 spring-boot事务自动装配
spring-boot autoconfigure 自动装配模块会自动注册spring-tx相关的bean,以便在我们需要的时候仅需要通过@Transactional进行声明,就可以实现事务管理。
spring tx自动装配路线:
- Spring Boot Auto Configure 引入自动装配类TransactionAutoConfiguration
TransactionAutoConfiguration中引入@EnableTransactionManagement@EnableTransactionManagement中引入TransactionManagementConfigurationSelectorTransactionManagementConfigurationSelector中引入ProxyTransactionManagementConfigurationProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration中引入BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor、TransactionAttributeSource、TransactionInterceptor、- 自动装配完成
下面尝试对这几个关键类进行讲解。
1.1 TransactionAutoConfiguration
该类是spring-tx自动装配类,所有的spring-tx相关的类都是直接或间接地通过这个类进行注册的。
@Configuration
// spring ioc中存在PlatformTransactionManager对象时生效
@ConditionalOnClass(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
// 当前配置在指定的几个配置类自动装配完之后再执行()
@AutoConfigureAfter({
JtaAutoConfiguration.class,
HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class,
// 数据源自动装配时会注册PlatformTransactionManager对象。默认使用DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器。
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class,
Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration.class })
// 解析spring env中的属性并获取TransactionProperties对象
@EnableConfigurationProperties(TransactionProperties.class)
public class TransactionAutoConfiguration {
// 【bean作用】:对TM进行一些定制化的处理
@Bean
// spring ioc中缺失TransactionManagerCustomizers 对象时,注册一个这样的bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public TransactionManagerCustomizers platformTransactionManagerCustomizers(
ObjectProvider<PlatformTransactionManagerCustomizer<?>> customizers) {
return new TransactionManagerCustomizers(customizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
// 【bean作用】:编程式事务的时候会用到这个TransactionTemplate 对象
// 如果项目中只有一个数据源,可以不进行手动注册TransactionTemplate ,直接使用当前这个自动装配的对象就好
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
public static class TransactionTemplateConfiguration {
// 如果存在多个数据源,这里注入的时主数据源
private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
public TransactionTemplateConfiguration(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate() {
return new TransactionTemplate(this.transactionManager);
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)
public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {
// 【bean作用】:主要是启用spring-tx可拔插注解@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false)
// 当spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false的时候生效
// matchIfMissing = false,表示如果不配置该属性则默认不匹配
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false",
matchIfMissing = false)
public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
// 【bean作用】:同上
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
// 当spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true的时候生效
// matchIfMissing = ture,表示如果不配置该属性则默认匹配
// 可见,如果不进行配置,动态代理默认采用Cglib方案
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
}1.2 TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector
public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> {
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
//导入ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类。
//导入AutoProxyRegistrar猜测是为确保支持aop功能,这里不深入了解。
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}
private String determineTransactionAspectClass() {
return (ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", getClass().getClassLoader()) ?
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.JTA_TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME :
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
}
}1.3 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
“代理事务管理配置”,顾名思义是用于注册spring-tx AOP要素的配置类。
@Configuration
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
// 【bean作用】:一个aop需要有advice和pointCut两个组件。transactionAdvisor就是spring事务aop中,管理advice和pointCut的bean。
// spring事务的advice实现就是下面的TransactionInterceptor
// spring事务的pointCut实现是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut(改对象在BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor中创建)
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
// 标注当前bean是spring框架内部的bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
// 依赖transactionAttributeSource对象
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
// 【bean作用】:改bean是注解数据属性源,用于管理从@Transactional注解中解析得到的TransactionAttribute对象。
// 其内部维护两个集合:
// Set<TransactionAnnotationParser> annotationParsers;==>@Transactional注解解析器集合。
// Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache;==>@Transactional注解属性映射表。key根据@Transactional注解所在类以及所标注方法名称生成。
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
// 【bean作用】:spring tx的aop advice实现类。在try-catch中提交事务或进行回滚
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
// 依赖transactionAttributeSource()对象
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}1.4 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
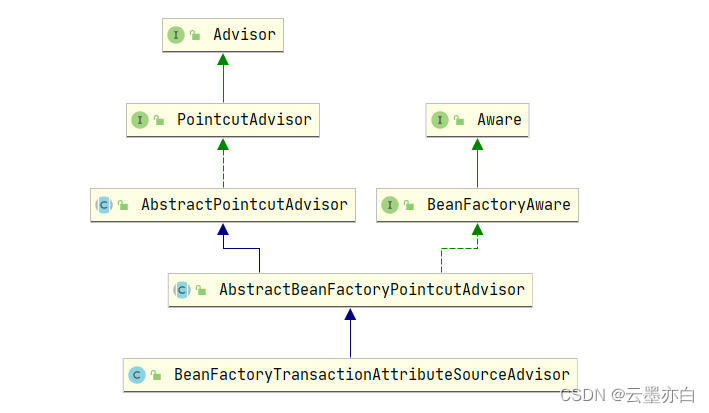
AOP有两个组成要素:PointCut(切入点)和Advice(增强逻辑)。Advisor一般用于管理PointCut和Advice。
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor管理spring tx相关的aop对象:
- PointCut对象:具体实现类是
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut。在BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor中初始化的 - Advice对象:具体实现类是
TransactionInterceptor。在ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 配置类创建BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor对象的时候,通过set方法进行设置。
1.5 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
注解事务属性源,根据名称进行猜测,该类估计是用于管理注解事务属性对象的(@Transactional标注的属性)。我们先梳理该类的类图关系,看看它定义了哪些成员变量,通过这些成员变量可以验证我们的猜想。
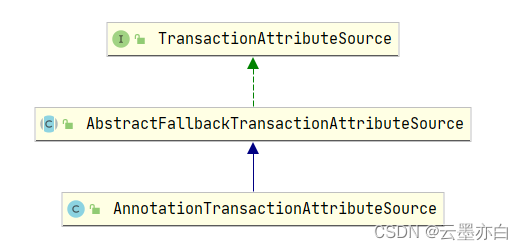
public interface TransactionAttributeSource {
// 获取TransactionAttribute事务属性对象
TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass);
}public abstract class AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource implements TransactionAttributeSource {
……
// 维护TransactionAttribute映射表
private final Map<Object, TransactionAttribute> attributeCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(1024);
// 根据所在类和方法创建TransactionAttribute映射表的key
protected Object getCacheKey(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
return new MethodClassKey(method, targetClass);
}
……
// 查找指定方法上的事务属性配置
protected abstract TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method);
// 查找指定类上的事务属性配置
protected abstract TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Class<?> clazz);
//判断事务注解是否只能在puplic方法上生效。
//子类实现中均设置为true,即要求只能在在puplic方法上生效
protected boolean allowPublicMethodsOnly() {
return false;
}
}public class AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource extends AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource
implements Serializable {
// 表明当前类文件是否存在javax.transaction.Transactional
private static final boolean jta12Present;
// 表明当前类文件是否存在javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute
private static final boolean ejb3Present;
// 静态代码块,初始化对象之前执行,用于设置jta12Present和ejb3Present两个属性
static {
ClassLoader classLoader = AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.class.getClassLoader();
jta12Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", classLoader);
ejb3Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute", classLoader);
}
// 表明事务注解是否只能在public方法上生效
private final boolean publicMethodsOnly;
// 可用的事务注解解析器集合
private final Set<TransactionAnnotationParser> annotationParsers;
// 初始化AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource对象,事务注解只能在public方法上生效
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource() {
this(true);
}
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;
if (jta12Present || ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
if (jta12Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
if (ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
// 默认情况下,使用的是org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional注解
// 只需要引入SpringTransactionAnnotationParser注解解析器
else {
this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}通过梳理类图,我们可以看到AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource维护了两个对象集合
TransactionAttribute映射表: key根据方法信息和类信息生成。(添加元素的时机是在spring事务aop执行PointCut判断时,即TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#matches()。下文会提到)TransactionAnnotationParser集合: 默认情况下,只有一个主机解析器SpringTransactionAnnotationParser用于解析org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional注解。当前类文件中导入了javax.transaction.Transactional或者javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute的时候,则导入对应注解的解析器。(调用AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource构造函数的时候初始化该集合)
1.6 TransactionInterceptor
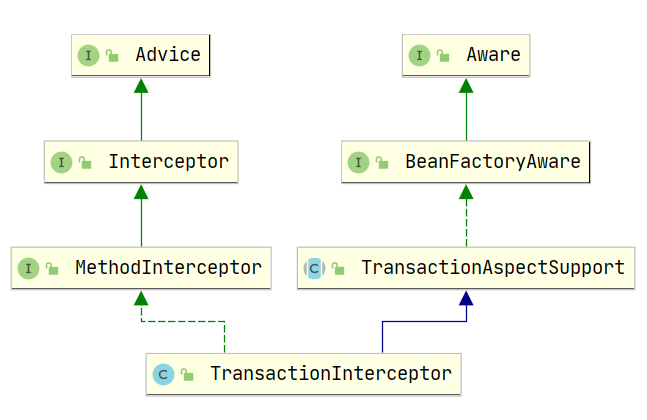
实现MethodInterceptor接口可以具备aop动态代理的能力。实现可以具备获取spring context的能力(处理的过程中可能需要从spring工厂中获取bean对象,比如获取PlatformTransactionManager事务管理器对象)
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
// 构造函数
public TransactionInterceptor() {
}
// 构造函数适配1
public TransactionInterceptor(PlatformTransactionManager ptm, Properties attributes) {
setTransactionManager(ptm);
setTransactionAttributes(attributes);
}
// 构造函数适配2
public TransactionInterceptor(PlatformTransactionManager ptm, TransactionAttributeSource tas) {
setTransactionManager(ptm);
setTransactionAttributeSource(tas);
}
// 动态代理逻辑实现
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
// 具体的逻辑在父类TransactionAspectSupport中实现
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Serialization support
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
//……
} 可以看到TransactionInterceptor中并没有太多的处理逻辑,事务advice逻辑主要是在其父类中进行实现
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
// NOTE: This class must not implement Serializable because it serves as base
// class for AspectJ aspects (which are not allowed to implement Serializable)!
/**
* Key to use to store the default transaction manager.
*/
private static final Object DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY = new Object();
/**
1、transactionInfoHolder是当前事务aop对象持有的TransactionInfo对象。
2、使用ThreadLocal修饰,表明每个线程各自绑定一个TransactionInfo对象。
3、TransactionInfo对象有四个主要的成员变量:
- transactionManager:某个数据源的事务管理器对象
- trantransactionAttribute:解析@Transactional注解获取到的事务属性对象
- joinpointIdentification:作为切入点的当前方法的信息描述。(由类、方法、参数等信息组合构建)
- transactionStatus:当前事务的状态信息,用于描述当前事务的行为(回滚还是提交、使用哪个事务管理器进行操作等)。
4、
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<TransactionInfo> transactionInfoHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current aspect-driven transaction");
protected static TransactionInfo currentTransactionInfo() throws NoTransactionException {
return transactionInfoHolder.get();
}
@Nullable
private String transactionManagerBeanName;
@Nullable
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
@Nullable
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource;
@Nullable
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, PlatformTransactionManager> transactionManagerCache =
new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(4);
// ……
/**
* Set the BeanFactory to use for retrieving PlatformTransactionManager beans.
* 获取BeanFactory,用于获取PlatformTransactionManager对象
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
// 具体的Advice逻辑
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
// TransactionAttributeSource对象是在ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration中创建并设置的
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 决定使用哪个事务管理器。
// 如果有多个数据源的事务管理器,且@Transactional中没有指定哪个事务管理器,则这里会使用主数据源的事务管理器(这时如果没有指定主数据原,会报错)。
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 根据方法、所在类、方法参数构建切入点描述
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 1、如果TransactionAttribute为空,或事务管理器不是CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager类型==>即,使用的是声明式事务
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建TransactionInfo对象。其中的关键步骤是创建TransactionStatus对象(涉及到事务传播行为的实现)
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 执行事务回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 清理TransactionInfo对象
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 执行事务提交
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
// 2、如果是编程式事务,执行下面的逻辑
else {
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
// 获取TransactionInfo对象(该对象包括transactionManager、trantransactionAttribute和joinpointIdentification)
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
// 执行原方法逻辑
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
// 捕获异常,进行事务回滚
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
/**
* Determine the specific transaction manager to use for the given transaction.
* 判断使用哪个事务管理器
*/
@Nullable
protected PlatformTransactionManager determineTransactionManager(@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
// Do not attempt to lookup tx manager if no tx attributes are set
if (txAttr == null || this.beanFactory == null) {
return getTransactionManager();
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, qualifier);
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.transactionManagerBeanName)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, this.transactionManagerBeanName);
}
else {
PlatformTransactionManager defaultTransactionManager = getTransactionManager();
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY);
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.beanFactory.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(
DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY, defaultTransactionManager);
}
}
return defaultTransactionManager;
}
}
/**
* Create a transaction if necessary based on the given TransactionAttribute.
* <p>Allows callers to perform custom TransactionAttribute lookups through
* the TransactionAttributeSource.
* @param txAttr the TransactionAttribute (may be {@code null})
* @param joinpointIdentification the fully qualified method name
* (used for monitoring and logging purposes)
* @return a TransactionInfo object, whether or not a transaction was created.
* The {@code hasTransaction()} method on TransactionInfo can be used to
* tell if there was a transaction created.
* @see #getTransactionAttributeSource()
*/
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 1、这一步是关键。
// 2、TransactionStatus status;==>可以看作是当前事务的状态视图,描述了当前事务的行为。
// 3、传播事务中,下一个事务依据上一个事务的status来设置自己的行为。
// 4、具体逻辑在AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#getTransaction()中实现
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
// 创建TransactionInfo对象
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification,
@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
if (txAttr != null) {
// We need a transaction for this method...
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Getting transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
// The transaction manager will flag an error if an incompatible tx already exists.
txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status);
}
else {
// The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only
// to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No need to create transaction for [" + joinpointIdentification +
"]: This method is not transactional.");
}
}
// We always bind the TransactionInfo to the thread, even if we didn't create
// a new transaction here. This guarantees that the TransactionInfo stack
// will be managed correctly even if no transaction was created by this aspect.
// 将txInfo与当前线程绑定
txInfo.bindToThread();
return txInfo;
}
/**
* Execute after successful completion of call, but not after an exception was handled.
* Do nothing if we didn't create a transaction.
* @param txInfo information about the current transaction
*/
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
/**
* Handle a throwable, completing the transaction.
* We may commit or roll back, depending on the configuration.
* @param txInfo information about the current transaction
* @param ex throwable encountered
*/
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
/**
* Reset the TransactionInfo ThreadLocal.
* <p>Call this in all cases: exception or normal return!
* @param txInfo information about the current transaction (may be {@code null})
*/
protected void cleanupTransactionInfo(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null) {
txInfo.restoreThreadLocalStatus();
}
}
/**
* Opaque object used to hold transaction information. Subclasses
* must pass it back to methods on this class, but not see its internals.
*/
protected final class TransactionInfo {
private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
private final TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute;
private final String joinpointIdentification;
private TransactionStatus transactionStatus;
private TransactionInfo oldTransactionInfo;
public TransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute, String joinpointIdentification) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
this.transactionAttribute = transactionAttribute;
this.joinpointIdentification = joinpointIdentification;
}
public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
Assert.state(this.transactionManager != null, "No PlatformTransactionManager set");
return this.transactionManager;
}
private void bindToThread() {
// Expose current TransactionStatus, preserving any existing TransactionStatus
// for restoration after this transaction is complete.
this.oldTransactionInfo = transactionInfoHolder.get();
transactionInfoHolder.set(this);
}
private void restoreThreadLocalStatus() {
// Use stack to restore old transaction TransactionInfo.
// Will be null if none was set.
transactionInfoHolder.set(this.oldTransactionInfo);
}
}
/**
* Simple callback interface for proceeding with the target invocation.
* Concrete interceptors/aspects adapt this to their invocation mechanism.
*/
@FunctionalInterface
protected interface InvocationCallback {
Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable;
}
}重要的对象TransactionInfo,包含了事务执行的全部信息。其关键的成员属性如下
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager:当前事务的事务管理器对象,对应某一个数据源。TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute:解析@Transactional注解获取到的事务属性对象String joinpointIdentification:作为切入点的当前方法的信息描述。(由类、方法、参数等信息组合构建)TransactionStatus transactionStatus:当前事务的状态信息,用于描述当前事务的行为(回滚还是提交、使用哪个事务管理器进行操作等)。几个关键属性如下TransactionInfo oldTransactionInfo:事务传播时候,用于记录上一个事务信息。Object transaction:事务对象。不同的数据源有不同的实现。jdbc事务对象实现类是DataSourceTransactionObjectboolean newTransaction:当前事务是否是新建事务(事务传播的时候,不同的行为策略有的需要新建事务,有的则是复用上一个事务)boolean readOnly:当前事务是否是只读事务。boolean rollbackOnly:当前事务是否立即回滚。boolean completed:当前事务是否完成。事务提交或执行回滚方可视为“已完成”。Object savepoint:顾名思义“保存点”,是数据库提供的事务管理的一种功能。可以参考SQL事务——SAVEPOINT 命令
1.7 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
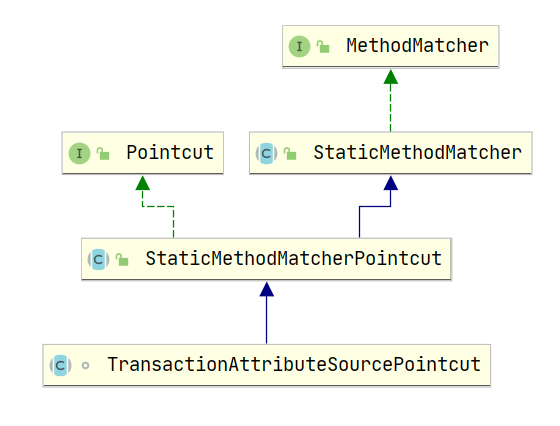
一个Pointcut对象主要包含两个方法:
public interface Pointcut {
// 获取类过滤器
ClassFilter getClassFilter();
// 获取方法匹配器
MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();
}ClassFilter是一个函数式接口,用于对类进行“切入点”资格判断。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ClassFilter {
/**
* Should the pointcut apply to the given interface or target class?
* @param clazz the candidate target class
* @return whether the advice should apply to the given target class
* 判断当前切入点是否可以应用于clazz所示的接口或者类
*/
boolean matches(Class<?> clazz);
/**
* Canonical instance of a ClassFilter that matches all classes.
* TrueClassFilter是ClassFilter的典型的实例,其matches()方法始终返回true.
*/
ClassFilter TRUE = TrueClassFilter.INSTANCE;
}MethodMatcher的作用与ClassFilter类似,不过它是对方法进行校验:
public interface MethodMatcher {
//执行静态检查,以判断当前方法是否满足切入点条件。
boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass);
//标识当前MethodMatcher是否是动态的
boolean isRuntime();
//执行动态检查,以判断当前方法是否满足切入点条件。
//只有 matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass)返回true,且isRuntime返回true的时候会执行动态检查。
boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, Object... args);
//TrueMethodMatcher是MethodMatcher的典型实现,其matches()方法始终返回true.
MethodMatcher TRUE = TrueMethodMatcher.INSTANCE;
}TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut中ClassFilter使用的是TrueClassFilter(在父类StaticMethodMatcherPointcut中定义)。MethodMatcher使用的就是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut本身(MethodMatcherexception中重写了MethodMatcher#matches()方法)。
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PlatformTransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) 的过程中,会先调用注解解析器解析获取事务属性对象,解析成功之后将其保存到TransactionAttributeSource对象的事务属性映射表中
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
//……
//抽象方法。BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor中创建TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut对象的时候进行了继承实现
protected abstract TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource();
}2 spring-boot事务流程串讲
1、spring-boot-autoconfigure触发TransactionAutoConfiguration自动装配
2、TransactionAutoConfiguration自动装配类中使用了@EnableTransactionManagement注解,该注解引入TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector
3、TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector向spring工厂中注册ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration配置类
4、ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration向spring工厂中注册BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor、 TransactionAttributeSource、和TransactionInterceptor三个bean
(1)BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor中主要有以下几个属性
- pointCut:是
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut的实例- advice:是
TransactionInterceptor的实例- transactionAttributeSource:是
TransactionAttributeSource的实例Set<TransactionAnnotationParser>annotationParsers: spring事务注解解析器集合Map<Object, TransactionAttribute>attributeCache:spring事务配置属性集合。key根据事务注解所在类以及所标注方法名称进行创建 。(2)TransactionInterceptor:是spring事务的aop逻辑实现。
(3)TransactionAttributeSourcePointcutPointcut:实现了Pointcut接口,其中
- TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut中的
getClassFilter(), 返回的是TrueClassFilter实例,TrueClassFilter#matches() 对所有类都不进行过滤,统一返回true。- TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut的
getMethodMatcher(),返回的就是它本身的实例 (TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut是MethodMatcher的实现类)。其中的TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#matches逻辑大致是:如果当前targetClass、method在BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSource 的attributeCache中存在事务配置属性,则说明当前方法是匹配的。
5、至此,spring事务自动装配完毕
6、对于如下代码:
@Service
Public class TestService{
@AutoWrite
ServiceA serviceA;
@Tansactional
public void test(){
serviceA.insert();
}
}(1)spring创建serviceA的过程简述:
- 初始化 serviceA 完毕,调用BeanPostProcessor系列接口进行初始化后置处理,会调用
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization。 - 接着会调用
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary判断是否需要为serviceA创建aop代理对象。 - 会调用
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#getClassFilter()#matches(),TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#getMethodMatcher()#matches()依次进行判断,最后得出结论,需要为serviceA创建aop代理对象。 - serviceA创建完毕,得到serviceA代理对象serviceAProxy。
(2)spring创建testService的的过程简述
- 初始化 testService完毕
- 为testService的成员属性ServiceA自动注入serviceAProxy对象(ps:如果serviceA 还没被创建怎么办?==>spring三级缓存策略会确保最终注入的是serviceAProxy,而不是serviceA本身)。
- 调用BeanPostProcessor系列接口进行初始化后置处理,没有找到关联testService的Advice对象,所以不需要为testService创建aop代理
(3)TestService.test()中执行 ServiceA.insert() 的过程简述
- 首先执行
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept()方法, - 接着会调用
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#getClassFilter()#matches(),TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#getMethodMatcher()#matches()再次进行判断当前方法是否需要进行aop代理。如果当前方法确实与TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut匹配,则执行spring 事务管理流程TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction。
3 spring-boot 事务传播机制
spring事务的七种传播行为:
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:外部方法存在事务,则当前方法加入该事务;外部方法没有事务,则当前方法创建一个新事物(默认)。
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW:无论外部方法是否存在事务,当前方法均会创建一个新的事务且独立执行(外部存在事务则将外部事务悬停,确保内部事务不受影响)。
- PROPAGATION_NESTED(nested嵌套):效果上与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似。不同在于PROPAGATION_REQUIRED会确保使用同一个事务,而PROPAGATION_NESTED会新建事务,并通过savepoint命令实现回滚。
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:如果外部方法存在事务,则加入该事务;如果外部方法没有事务,则以非事务的方式继续运行。
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果外部方法存在事务,则把外部方法事务挂起。
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY(mandatory强制性的):如果外部方法存在事务,则加入该事务;如果外部方法没有事务,则抛出异常。
- PROPAGATION_NEVER(never从不):以非事务方式运行,如果外部方法存在事务,则抛出异常
实现事务传播控制很关键的一个类就是上文提到的TransactionStatus,用于描述当前事务的行为(回滚还是提交、使用哪个事务管理器进行操作等),其关键属性如下:
TransactionInfo oldTransactionInfo:事务传播时候,用于记录上一个事务信息。Object transaction:事务对象。不同的数据源有不同的实现。jdbc事务对象实现类是DataSourceTransactionObjectboolean newTransaction:当前事务是否是新建事务(事务传播的时候,不同的行为策略有的需要新建事务,有的则是复用上一个事务)boolean readOnly:当前事务是否是只读事务。boolean rollbackOnly:当前事务是否立即回滚。boolean completed:当前事务是否完成。事务提交或执行回滚方可视为“已完成”。Object savepoint:顾名思义“保存点”,是数据库提供的事务管理的一种功能。可以参考SQL事务——SAVEPOINT 命令
获取TransactionStatus对象的代码是 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#getTransaction()
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
// 判断是否已经存在事务(外部方法是否存在事务)
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// 已经存在事务,则处理当前事务的传播行为
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.(外部方法没有事务,根据事务传播行为创建DefaultTransactionStatus对象)
// 1、传播行为是PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,但外部方法没有事务,所以抛出异常
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// 2、如果是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED、PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW、PROPAGATION_NESTED三种传播行为中的一种,则创建DefaultTransactionStatus对象时需要新建事务
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
// 3、其他传播行为会报错
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}已经存在事务(外部方法存在事务),当前事务的处理逻辑在AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#handleExistingTransaction()中:
/**
* Create a TransactionStatus for an existing transaction.
*/
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
//1、传播行为是PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED。执行到这里说明外部肯定存在事务,不符合PROPAGATION_NEVER行为规范,所以抛出异常
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
//2、传播行为是PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED。如果外面有事务则暂停该事务,创建TransactionStatus的时候不创建新事务。
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
// Suspending current transaction,悬停当前事务
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(
// 第三个参数为false,表示不新建事务
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
//3、传播行为是PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW。如果外部有事务,则悬停该事务,创建TransactionStatus的时候需要创建新事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
// 第三个参数为true,表示需要新建事务
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// doBegin()中会获取新的数据库连接
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
//4、传播行为是PROPAGATION_NESTED。
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
// 如果事务管理器不支持SAVEPOINT命令,如JtaTransactionManager
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
// 如果事务管理器支持SAVEPOINT命令,如一般使用的DataSourceTransactionManager
else {
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
// doBegin()中会获取新的数据库连接
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
}
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
// 5、传播行为是PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}4 spring-boot编程式事务
编程式事务和声明式事务唯一的别就是TransactionAttribute的来源而已,前者是编程式创建而后者是通过注解自动解析创建。
流程上最终都会调用TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction,
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// 执行声明式事务
}
else {
// 编程式事务
}
}实现编程式事务的两种方法如下所示:
RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = {TransactionApplication.class})
public class TransactionTest {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* TransactionAutoConfiguration自动装配的时候会使用主数据原自动注册TransactionTemplate对象,所以直接拿来用即可
*/
@Autowired
TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
/**
* 这个同理,是DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration自动装配的时候使用主数据原自动注册的
*/
@Autowired
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager;
/**
* 方式一:使用TransactionTemplate(spring官方推荐)
*/
@Test
public void programTransactionTest1() {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("张三");
user.setUserId("999");
userMapper.insert(user);
// 模拟异常
System.out.println(1 / 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("异常回滚");
status.setRollbackOnly();
throw e;
}
}
});
}
/**
* 方式二:使用TransactionManager
*/
@Test
public void programTransactionTest2() {
// 1.新建一个默认的事务对象
DefaultTransactionDefinition definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 2.自定义事务属性
// ……
// 3.获取事务状态
TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(definition);
try {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("张三");
user.setUserId("999");
userMapper.insert(user);
// 模拟异常
System.out.println(1 / 0);
// 提交事务
transactionManager.commit(status);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 事务回滚
transactionManager.rollback(status);
throw e;
}
}
}5 spring-boot分布式事务
参考连接:分布式事务及常见解决方案
分布式事务术语:
- 分布式事务:简单理解,分布式事务是跨数据源或者跨连接的事务。
- AP:应用程序,用于定义事务开始和结束的边界. 说人话就是我们开启事务的代码所以的应用.
- RM:资源管理器. 理论上一切支持持久化的数据库资源都可以是一个资源管理器.
- TM: 事务管理器, 负责对事务进行协调,监控. 并负责事务的提交和回滚.
- TC (Transaction Coordinator) - 事务协调者
- 两阶段提交(Two-phase Commit,2PC)
- 两阶段补偿型提交(TCC)
- 三阶段提交(3PC)
分布式事务概况地说可以分为两种场景:
- 单机多数据源:一个微服务上有多个数据源,要对处理过程中涉及到的所有数据源上的事务进行原子性操作。==>使用spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos可以满足场景要求(代码示例)。
- 多机多数据源:每个微服务有自己地数据源,要对处理过程中涉及到的所有微服务进行原子性操作。==>使用spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos无法满足场景要求,需要引入第三方组件,比如阿里的seata。
6 问题回顾
文章开头提到的6个问题,除了第1个问题其他问题文中都有提到,这里仅对问题1进行补充。
场景描述:
@Service
public class ServiceA {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public void insertWrapper() throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setId(999L);
user.setUserName("张三");
user.setUserId("999");
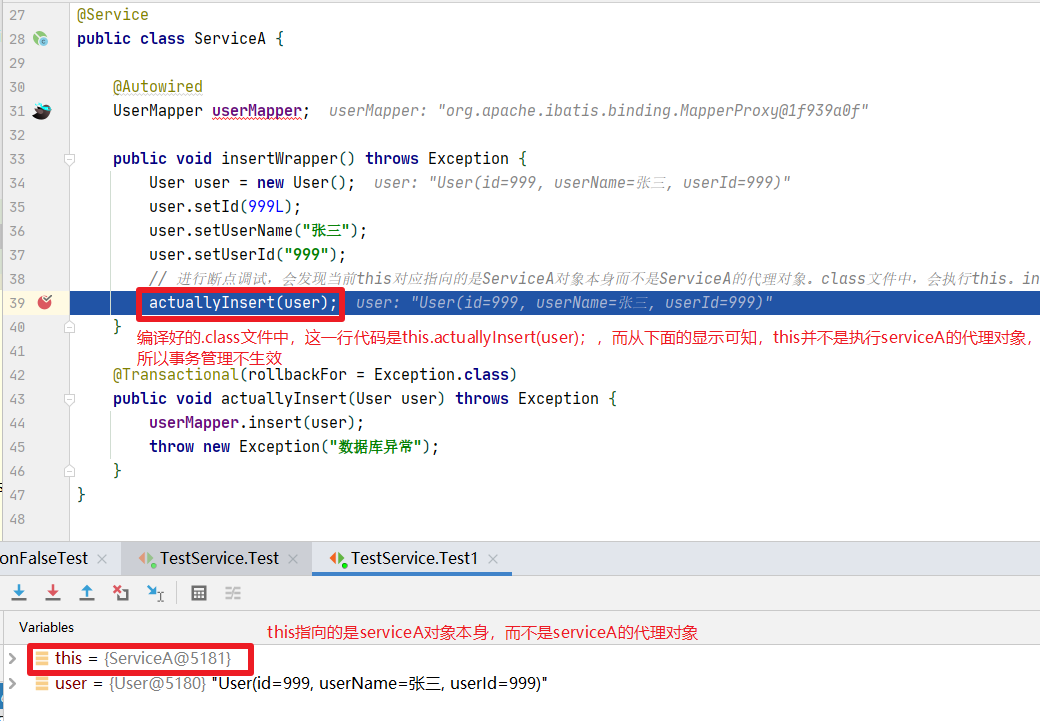
// 进行断点调试,会发现当前this对应指向的是ServiceA对象本身而不是ServiceA的代理对象。class文件中,会执行this。insert(user),所以不会触发aop增强逻辑
actuallyInsert(user);
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void actuallyInsert(User user) throws Exception {
userMapper.insert(user);
throw new Exception("数据库异常");
}
}@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = {TransactionApplication.class})
public class TestService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
ServiceA serviceA;
@Test
public void Test1() throws Exception {
serviceA.insertWrapper();
}
@Test
public void Test2() throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setId(999L);
user.setUserName("张三");
user.setUserId("999");
serviceA.actuallyInsert(user);
}
}1、TestService#Test1
调试截图1:
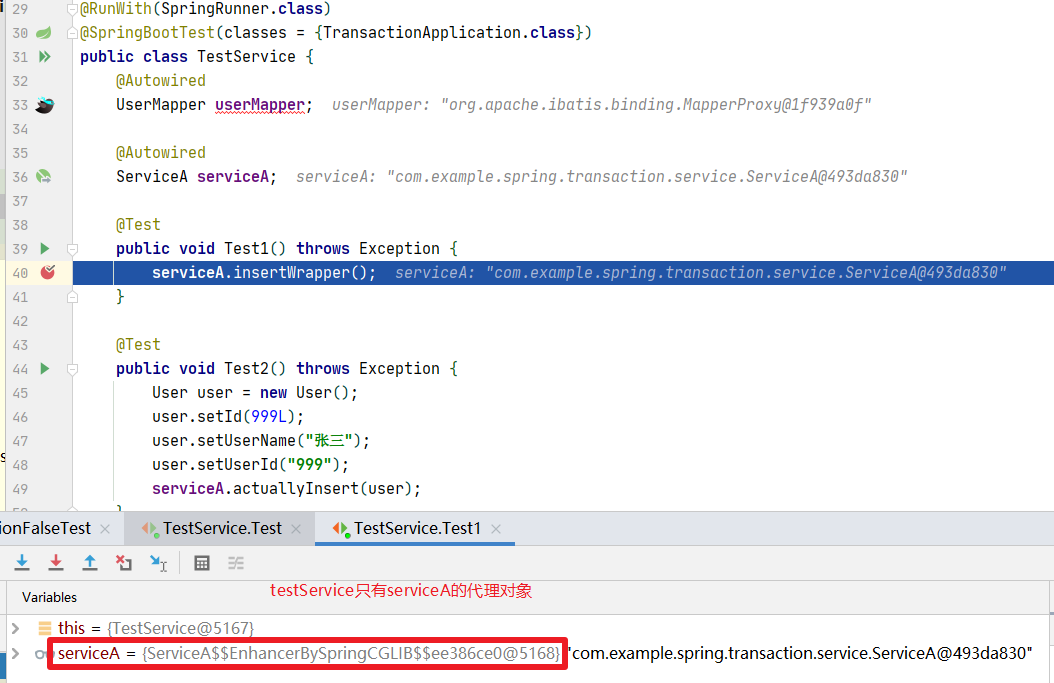
调试截图2:
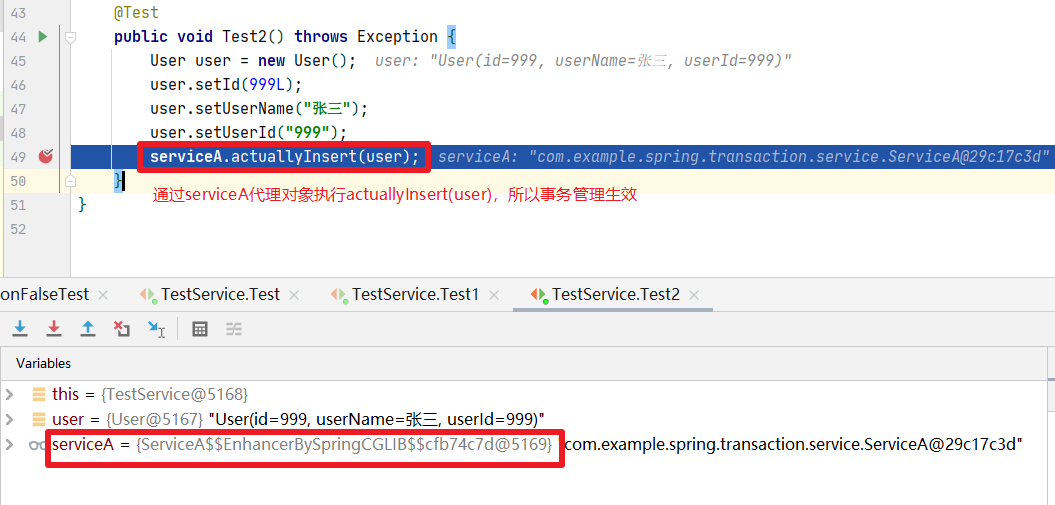
2、TestService#Test1
如果如类似TestService#test2()中的调用方式,最终是通过serviceA的代理对象来调用actuallyInsert(user),所以事务管理会生效。
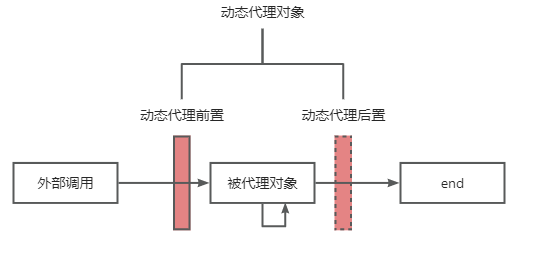
3、小结
内部方法上标注@Transactional导致事务管理失效,根本原因是动态代理失效。如图所示,被代理对象调用自身方法不会触达动态代理地增强逻辑。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号