opencv学习之路(24)、轮廓查找与绘制(三)——凸包
一、简介
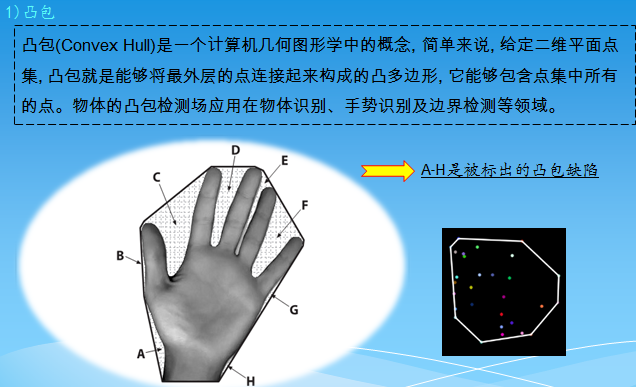


二、绘制点集的凸包
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace cv; void main() { //---绘制点集的凸包 Mat img(400, 400, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0)); //定义绘制图像 RNG rng; //定义随机数对象 while(1) { char key; int count = (unsigned int)rng % 100; //定义点的个数 vector<Point> points; //定义点集 for(int i=0; i<count; i++) { Point pt; pt.x = rng.uniform(img.cols/4, img.cols*3/4); //设定点的x范围 pt.y = rng.uniform(img.rows/4, img.rows*3/4); //设定点的y范围 points.push_back(pt); } //检测凸包 vector<int> hull; convexHull(Mat(points), hull, true); img = Scalar::all(0); for(int i = 0; i < count; i++ ) circle(img, points[i], 3, Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255)), CV_FILLED, CV_AA); //准备参数 int hullcount = (int)hull.size(); //凸包的边数 Point point0 = points[hull[hullcount-1]]; //连接凸包边的坐标点 //绘制凸包的边 for(int i = 0; i < hullcount; i++ ) { Point point = points[hull[i]]; circle(img, point, 8, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); line(img, point0, point, Scalar(255, 255, 255), 2, CV_AA); point0 = point; } //显示效果图 imshow("img", img); //按下ESC,Q,或者q,程序退出 key = (char)waitKey(); if( key == 27 || key == 'q' || key == 'Q' ) break; } 51}
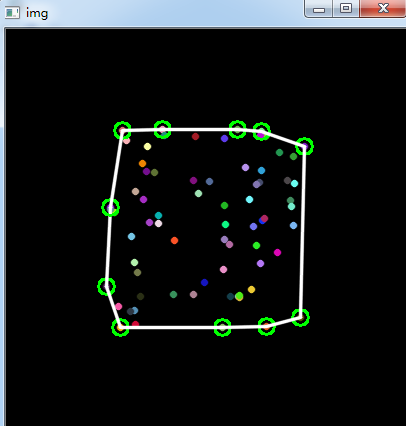
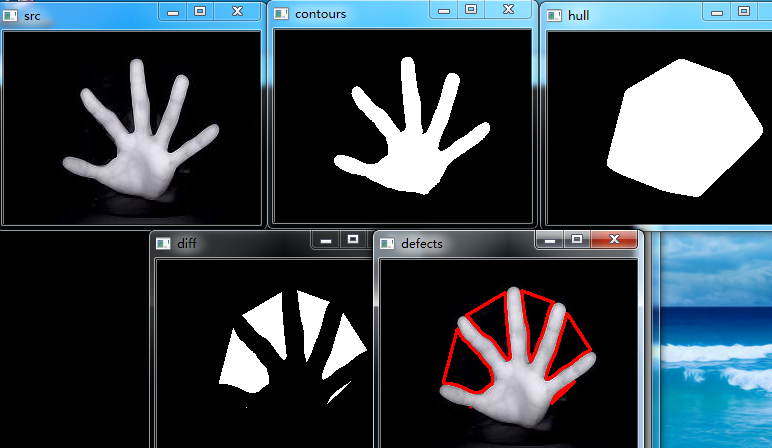
三、绘制轮廓的凸包
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace cv; void main() { Mat srcImg = imread("E://12.jpg"); imshow("src", srcImg); Mat dstImg2 = srcImg.clone(); Mat tempImg(srcImg.rows, srcImg.cols, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0)); //用于绘制凸包 Mat dstImg(srcImg.rows, srcImg.cols, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0)); //用于绘制轮廓 cvtColor(srcImg, srcImg, CV_BGR2GRAY); threshold(srcImg, srcImg, 100, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); //二值化 vector<vector<Point>> contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarcy; findContours(srcImg, contours, hierarcy, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); vector<vector<Point>> hull(contours.size()); for(int i=0; i<contours.size(); i++) { convexHull(Mat(contours[i]), hull[i], true); //查找凸包 drawContours(dstImg, contours, i, Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, 8); //绘制轮廓 //drawContours(dstImg, hull, i, Scalar(rand()%255, rand()%255, rand()%255), 2, 8); drawContours(tempImg, hull, i, Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, 8); } imshow("hull", tempImg); imshow("contours", dstImg); Mat diffImg; absdiff(tempImg, dstImg, diffImg); //图像相减 Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3), Point(-1, -1)); erode(diffImg, diffImg, element); imshow("diff", diffImg); vector<vector<Point>> contours2; vector<Vec4i> hierarcy2; cvtColor(diffImg, diffImg, CV_BGR2GRAY); //转为灰度图 threshold(diffImg, diffImg, 100, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); //二值化 findContours(diffImg, contours2, hierarcy2, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); drawContours(dstImg2, contours2, -1, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8); //红色绘制缺陷轮廓 imshow("defects", dstImg2); waitKey(0); }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/little-monkey/p/7424951.html
---
作者:柒月
Q群 :2122210(嵌入式/机器学习)

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号