Core源码(九)List
Core里面的List沿用的framework的结构,整个core的体系是把项目的组织方式改变了,变得更灵活,更可配置,不像framework那么死板。但底层的数据结构和中间代码CLR并没有很大的改变。
在framework源码中的位置

无参构造函数和变量
首先我们来看构造函数和一些内部的变量,然后默认的_defaultCapacity数组长度是4,构造函数上也有说明,一旦加入元素,capacity会增加到16,然后以2倍的乘数增长。
List的内部是一个私有的T[] _items对象,在无参的构造函数中,可以看到_items = _emptyArray,也就是被赋值了静态的空数组,这算是个小技巧,List实例的很多方法都涉及到空数组参数,这样设置一个静态只读的空数组,大家都可以共用这个对象。如果一旦被插入数据,或者修改数组的Capacity就会进行再次实例化到对应Capacity。
_size记录的是当前数组内,有赋值的数量,也就是我们用的Count属性,数组的实际容量肯定是大于等于_size的。
public class List<T> : IList<T>, System.Collections.IList, IReadOnlyList<T> { private const int _defaultCapacity = 4; private T[] _items; [ContractPublicPropertyName("Count")] private int _size; private int _version; [NonSerialized] private Object _syncRoot; static readonly T[] _emptyArray = new T[0]; // Constructs a List. The list is initially empty and has a capacity // of zero. Upon adding the first element to the list the capacity is // increased to 16, and then increased in multiples of two as required. public List() { _items = _emptyArray; } }
IEnumerable<T>的构造函数
// Constructs a List, copying the contents of the given collection. The // size and capacity of the new list will both be equal to the size of the // given collection. public List(IEnumerable<T> collection) { if (collection==null) ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.collection); ICollection<T> c = collection as ICollection<T>; if( c != null) { int count = c.Count; if (count == 0) { _items = _emptyArray; } else { _items = new T[count]; c.CopyTo(_items, 0); _size = count; } } else { _size = 0; _items = _emptyArray; // This enumerable could be empty. Let Add allocate a new array, if needed. // Note it will also go to _defaultCapacity first, not 1, then 2, etc. using(IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator()) { while(en.MoveNext()) { Add(en.Current); } } } }
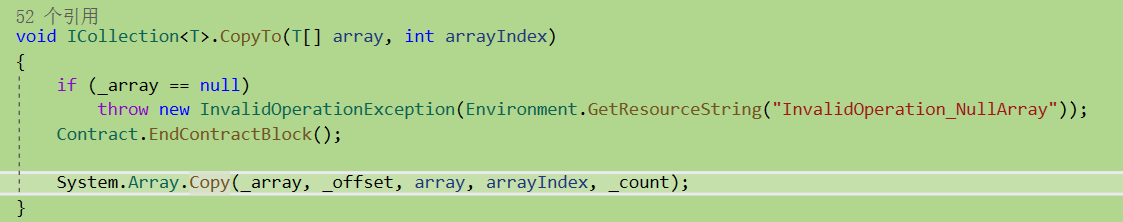
这里如果集合不为空,设置对应_size变量为目标集合的数量,然后调用CopyTo 方法进行拷贝,CopyTo 内部调用System.Array.Copy,此方法等效于标准 C/C++ 函数 memmove,而不是 memcpy。此方法的运算复杂度为 O(n),其中 n 是 length。
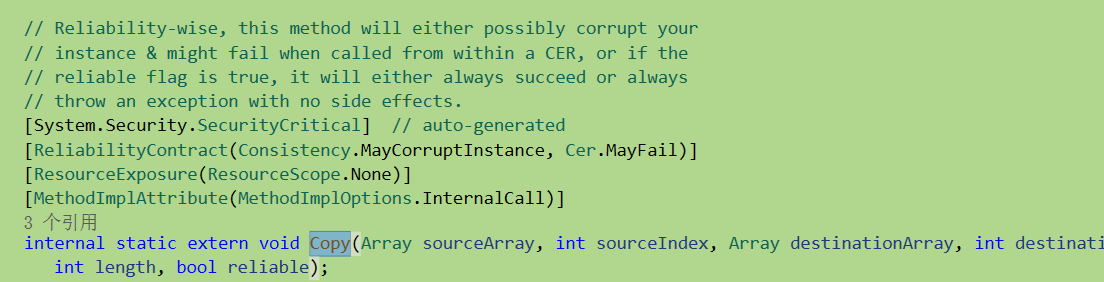
MethodImplAttribute(MethodImplOptions.InternalCall)]用于说明该方法的具体实现可以从CLR内部找到。也就是代码到了这个程度已经脱离了C#范围,是clr内部的实现了。
Capacity属性和Count
Capacity的属性如果用户不手动设置,一般会使用EnsureCapacity来自动的根据集合大小进行调整。
public int Capacity { get { return _items.Length; } set { if (value < _size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.value, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_SmallCapacity); } Contract.EndContractBlock(); if (value != _items.Length) { if (value > 0) { T[] newItems = new T[value]; if (_size > 0) { Array.Copy(_items, 0, newItems, 0, _size); } _items = newItems; } else { _items = _emptyArray; } } } } // Read-only property describing how many elements are in the List. public int Count { get { Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() >= 0); return _size; } } private void EnsureCapacity(int min) { if (_items.Length < min) { int newCapacity = _items.Length == 0? _defaultCapacity : _items.Length * 2; // Allow the list to grow to maximum possible capacity (~2G elements) before encountering overflow. // Note that this check works even when _items.Length overflowed thanks to the (uint) cast if ((uint)newCapacity > Array.MaxArrayLength) newCapacity = Array.MaxArrayLength; if (newCapacity < min) newCapacity = min; Capacity = newCapacity; } }
EnsureCapacity方法的参数min是目前能接受的最小容量,就是操作后数组的长度。
如果目前的数组长度小于min就返回,如果新的newCapacity大于最大数组允许的长度就为最大长度。如果翻倍后还是小于min,那么就把newCapacity设置为min。
按索引获取和修改
从代码可知,使用索引获取和设置都是O(1)的复杂度
public T this[int index] { get { // Following trick can reduce the range check by one if ((uint) index >= (uint)_size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(); } Contract.EndContractBlock(); return _items[index]; } set { if ((uint) index >= (uint)_size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(); } Contract.EndContractBlock(); _items[index] = value; _version++; } } public void Add(T item) { if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1); _items[_size++] = item; _version++; } // Inserts an element into this list at a given index. The size of the list // is increased by one. If required, the capacity of the list is doubled // before inserting the new element. // public void Insert(int index, T item) { // Note that insertions at the end are legal. if ((uint) index > (uint)_size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.index, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_ListInsert); } Contract.EndContractBlock(); if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1); if (index < _size) { Array.Copy(_items, index, _items, index + 1, _size - index); } _items[index] = item; _size++; _version++; }
AddRange
AddRange分为默认的和指定索引的AddRange,
// Adds the elements of the given collection to the end of this list. If // required, the capacity of the list is increased to twice the previous // capacity or the new size, whichever is larger. // public void AddRange(IEnumerable<T> collection) { Contract.Ensures(Count >= Contract.OldValue(Count)); InsertRange(_size, collection); } // Inserts the elements of the given collection at a given index. If // required, the capacity of the list is increased to twice the previous // capacity or the new size, whichever is larger. Ranges may be added // to the end of the list by setting index to the List's size. // public void InsertRange(int index, IEnumerable<T> collection) { if (collection==null) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.collection); } if ((uint)index > (uint)_size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.index, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_Index); } ICollection<T> c = collection as ICollection<T>; if( c != null ) { // if collection is ICollection<T> int count = c.Count; if (count > 0) { EnsureCapacity(_size + count); if (index < _size) { Array.Copy(_items, index, _items, index + count, _size - index); } // If we're inserting a List into itself, we want to be able to deal with that. if (this == c) { // Copy first part of _items to insert location Array.Copy(_items, 0, _items, index, index); // Copy last part of _items back to inserted location Array.Copy(_items, index+count, _items, index*2, _size-index); } else { T[] itemsToInsert = new T[count]; c.CopyTo(itemsToInsert, 0); itemsToInsert.CopyTo(_items, index); } _size += count; } } else { using(IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator()) { while(en.MoveNext()) { Insert(index++, en.Current); } } } _version++; }
这里的步骤是先确保容量足够,然后调用Array.Copy为将要插入的数据余出空间。然后再次调用把新插入的数组赋值到_items。
List中的Remove
Remove和RemoveRange实际都是调用Array.Copy方法,这里removeAll的循环判断稍微有点绕,但是仔细研究下就能懂。
public bool Remove(T item) { int index = IndexOf(item); if (index >= 0) { RemoveAt(index); return true; } return false; } void System.Collections.IList.Remove(Object item) { if(IsCompatibleObject(item)) { Remove((T) item); } }
RemoveAt
// Removes the element at the given index. The size of the list is // decreased by one. public void RemoveAt(int index) { if ((uint)index >= (uint)_size) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(); } _size--; if (index < _size) { Array.Copy(_items, index + 1, _items, index, _size - index); //相当于把数组index后面的元素都向前赋值 } _items[_size] = default(T); _version++; } // Removes a range of elements from this list. // public void RemoveRange(int index, int count) { if (index < 0) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.index, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum); } if (count < 0) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.count, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum); } if (_size - index < count) ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_InvalidOffLen); Contract.EndContractBlock(); if (count > 0) { int i = _size; _size -= count; if (index < _size) { Array.Copy(_items, index + count, _items, index, _size - index); } Array.Clear(_items, _size, count); _version++; } }
RemoveAll
// This method removes all items which matches the predicate. // The complexity is O(n). public int RemoveAll(Predicate<T> match) { if( match == null) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.match); } int freeIndex = 0; // the first free slot in items array // Find the first item which needs to be removed. while( freeIndex < _size && !match(_items[freeIndex])) freeIndex++; if( freeIndex >= _size) return 0; int current = freeIndex + 1; while( current < _size) { // Find the first item which needs to be kept. while( current < _size && match(_items[current])) current++; if( current < _size) { // copy item to the free slot. _items[freeIndex++] = _items[current++]; } } Array.Clear(_items, freeIndex, _size - freeIndex); int result = _size - freeIndex; _size = freeIndex; _version++; return result; }


