Core源码(一) ConcurrentDictionary
先贴源码地址
.NET CORE很大一个好处就是代码的开源,你可以详细的查看你使用类的源代码,并学习微软的写法和实现思路。
这里我对.net core中ConcurrentDictionary源码进行了分析,里面采用了Volatile.Read和write(volatile作用:确保本条指令不会因编译器的优化而省略,且要求每次直接从内存地址读值,而不走寄存器),然后也使用了lock这种混合锁,而且还定义了更细颗粒度的锁。所以多线程使用ConcurrentDictionary集合还是比较好的选择。
本来想把本篇放到我的《C#异步编程系列》,不过后来感觉那个系列写的已经算是收尾了,而且以后还会有写更多core源码分析的文字,所以就单独新增一个系列把。
ConcurrentDictionary内部私有类
先上源码,再仔细聊
/// <summary> /// Tables that hold the internal state of the ConcurrentDictionary /// /// Wrapping the three tables in a single object allows us to atomically /// replace all tables at once. /// </summary> private sealed class Tables { // A singly-linked list for each bucket. // 单链表数据结构的桶,里面的节点就是对应字典值 internal readonly Node[] _buckets; // A set of locks, each guarding a section of the table. //锁的数组 internal readonly object[] _locks; // The number of elements guarded by each lock. internal volatile int[] _countPerLock; internal Tables(Node[] buckets, object[] locks, int[] countPerLock) { _buckets = buckets; _locks = locks; _countPerLock = countPerLock; } } /// <summary> /// A node in a singly-linked list representing a particular hash table bucket. /// 由Dictionary里的Entry改成Node,并且把next放到Node里 /// </summary> private sealed class Node { internal readonly TKey _key; internal TValue _value; internal volatile Node _next; internal readonly int _hashcode; internal Node(TKey key, TValue value, int hashcode, Node next) { _key = key; _value = value; _next = next; _hashcode = hashcode; } } private volatile Tables _tables; // Internal tables of the dictionary private IEqualityComparer<TKey> _comparer; // Key equality comparer // The maximum number of elements per lock before a resize operation is triggered // 每个锁对应的元素最大个数,如果超过,要重新进行resize tables private int _budget;
首先,内部类定义为私有且密封,这样就保证了无法从外部进行篡改,而且注意volatile关键字的使用,这确保了我们多线程操作的时候,最终都是去内存中读取对应地址的值和操作对应地址的值。
internal readonly object[] _locks; internal volatile int[] _countPerLock;
以上两个类是为了高性能及并发锁所建立的对象,实际方法上锁时,使用如下语句
lock (tables._locks[lockNo]) Monitor.Enter(tables._locks[lockNo], ref lockTaken);
以上两种调用方式是等价的,都会阻塞执行,直到获取到锁(对于Monitor我很多时候会尽可能使用TryEnter,毕竟不阻塞,不过这个类的实现一定要使用阻塞式的,这样程序逻辑才能继续往下走。更多关于Monitor我在 《C#异步编程(四)混合模式线程同步》里面有详细介绍)
这样,实现了颗粒化到每个单独的键值的锁,最大限度的保证了并发。
这里lockNo参数是通过GetBucketAndLockNo方法获取的,方法通过out变量返回值。
/// <summary> /// Computes the bucket and lock number for a particular key. ///这里获取桶的索引和锁的索引,注意,锁的索引和桶未必是同一个值。 /// </summary> private static void GetBucketAndLockNo(int hashcode, out int bucketNo, out int lockNo, int bucketCount, int lockCount) { bucketNo = (hashcode & 0x7fffffff) % bucketCount; lockNo = bucketNo % lockCount; }
上面方法中
hashcode 是通过private IEqualityComparer<TKey> _comparer对象的GetHashCode方法通过key获取到的。
bucketCount是整个table的长度。
lockCount是现有的锁的数组
TryAdd方法
我们从最简单的TryAdd方法开始介绍,这里ConcurrentDictionary类的封装非常合理,暴露出来的方法,很多是通过统一的内部方法进行执行,比如更新删除等操作等,都有类内部唯一的私有方法进行执行,然后通过向外暴漏各种参数不同的方法,来实现不同行为。
public bool TryAdd(TKey key, TValue value) { if (key == null) ThrowKeyNullException(); TValue dummy; return TryAddInternal(key, _comparer.GetHashCode(key), value, false, true, out dummy); }
上面TryAddInternal的参数对应如下
/// <summary> /// Shared internal implementation for inserts and updates. /// If key exists, we always return false; and if updateIfExists == true we force update with value; /// If key doesn't exist, we always add value and return true; /// </summary> private bool TryAddInternal(TKey key, int hashcode, TValue value, bool updateIfExists, bool acquireLock, out TValue resultingValue)
也就说说,updateIfExists为false,存在值的情况下,TryAdd不会更新原有值,而是直接返回false。我的多线程并发写库就是利用了这个特性,这个案例我会在本文最后介绍。现在我们来看TryAddInternal内部,废话不多说,上源码(大部分都注释过了,所以直接阅读即可)
//while包在外面,为了continue,如果发生了_tables私有变量在操作过程被其他线程修改的情况 while (true) { int bucketNo, lockNo; //变量复制到方法本地变量 判断tables是否在操作过程中被其他线程修改。 Tables tables = _tables; //提到过的获取桶的索引和锁的索引 GetBucketAndLockNo(hashcode, out bucketNo, out lockNo, tables._buckets.Length, tables._locks.Length); //是否要扩大tables bool resizeDesired = false; //是否成功获取锁,成功的话会在final块中进行退出 bool lockTaken = false; try { if (acquireLock) Monitor.Enter(tables._locks[lockNo], ref lockTaken); // If the table just got resized, we may not be holding the right lock, and must retry. // This should be a rare occurrence. if (tables != _tables) { continue; } // Try to find this key in the bucket Node prev = null; //这里如果找到对应地址为空,会直接跳出循环,说明对应的key没有添加锅 //不为空的时候,会进行返回false(具体是否更新根据updateIfExists)(当然也存在会有相同_hashcode值的情况,所以还要对key进行判定,key不同,继续往后找,直到找到相同key) for (Node node = tables._buckets[bucketNo]; node != null; node = node._next) { Debug.Assert((prev == null && node == tables._buckets[bucketNo]) || prev._next == node); //对hashcode和key进行判定,确保找到的就是要更新的 if (hashcode == node._hashcode && _comparer.Equals(node._key, key)) { // The key was found in the dictionary. If updates are allowed, update the value for that key. // We need to create a new node for the update, in order to support TValue types that cannot // be written atomically, since lock-free reads may be happening concurrently. if (updateIfExists) { if (s_isValueWriteAtomic) { node._value = value; } else { Node newNode = new Node(node._key, value, hashcode, node._next); if (prev == null) { Volatile.Write(ref tables._buckets[bucketNo], newNode); } else { prev._next = newNode; } } resultingValue = value; } else { resultingValue = node._value; } return false; } prev = node; } // The key was not found in the bucket. Insert the key-value pair. Volatile.Write<Node>(ref tables._buckets[bucketNo], new Node(key, value, hashcode, tables._buckets[bucketNo])); checked { tables._countPerLock[lockNo]++; } // // If the number of elements guarded by this lock has exceeded the budget, resize the bucket table. // It is also possible that GrowTable will increase the budget but won't resize the bucket table. // That happens if the bucket table is found to be poorly utilized due to a bad hash function. // if (tables._countPerLock[lockNo] > _budget) { resizeDesired = true; } } finally { if (lockTaken) Monitor.Exit(tables._locks[lockNo]); } // // The fact that we got here means that we just performed an insertion. If necessary, we will grow the table. // // Concurrency notes: // - Notice that we are not holding any locks at when calling GrowTable. This is necessary to prevent deadlocks. // - As a result, it is possible that GrowTable will be called unnecessarily. But, GrowTable will obtain lock 0 // and then verify that the table we passed to it as the argument is still the current table. // if (resizeDesired) { GrowTable(tables); } resultingValue = value; return true; }
ContainsKey和TryGetValue
ContainsKey和TryGetValue其实内部最后调用的都是私有TryGetValueInternal,这里ContainsKey调用TryGetValue。
ContainsKey方法
/// <summary> /// Determines whether the ConcurrentDictionary{TKey, TValue} contains the specified key. /// </summary> /// <param name="key">The key to locate in the</param> /// <returns>true if the ConcurrentDictionary{TKey, TValue} contains an element withthe specified key; otherwise, false.</returns> public bool ContainsKey(TKey key) { if (key == null) ThrowKeyNullException(); TValue throwAwayValue; return TryGetValue(key, out throwAwayValue); }
TryGetValue方法
/// <summary> /// Attempts to get the value associated with the specified key from the ConcurrentDictionary{TKey,TValue}. /// </summary> /// <param name="key">The key of the value to get.</param> /// <param name="value">When this method returns, <paramref name="value"/> contains the object from /// the ConcurrentDictionary{TKey,TValue} with the specified key or the default value of /// <returns>true if the key was found in the <see cref="ConcurrentDictionary{TKey,TValue}"/>; /// otherwise, false.</returns> public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value) { if (key == null) ThrowKeyNullException(); return TryGetValueInternal(key, _comparer.GetHashCode(key), out value); }
TryGetValueInternal方法
private bool TryGetValueInternal(TKey key, int hashcode, out TValue value) { //用本地变量保存这个table的快照。 // We must capture the _buckets field in a local variable. It is set to a new table on each table resize. Tables tables = _tables; //获取key对应的桶位置 int bucketNo = GetBucket(hashcode, tables._buckets.Length); // We can get away w/out a lock here. // The Volatile.Read ensures that we have a copy of the reference to tables._buckets[bucketNo]. // This protects us from reading fields ('_hashcode', '_key', '_value' and '_next') of different instances. Node n = Volatile.Read<Node>(ref tables._buckets[bucketNo]); //如果key相符 ,赋值,不然继续寻找下一个。 while (n != null) { if (hashcode == n._hashcode && _comparer.Equals(n._key, key)) { value = n._value; return true; } n = n._next; } value = default(TValue);//没找到就赋默认值 return false; }
TryRemove
TryRemove方法
public bool TryRemove(TKey key, out TValue value) { if (key == null) ThrowKeyNullException(); return TryRemoveInternal(key, out value, false, default(TValue)); }
这个方法会调用内部私用的TryRemoveInternal
/// <summary> /// Removes the specified key from the dictionary if it exists and returns its associated value. /// If matchValue flag is set, the key will be removed only if is associated with a particular /// value. /// </summary> /// <param name="key">The key to search for and remove if it exists.</param> /// <param name="value">The variable into which the removed value, if found, is stored.</param> /// <param name="matchValue">Whether removal of the key is conditional on its value.</param> /// <param name="oldValue">The conditional value to compare against if <paramref name="matchValue"/> is true</param> /// <returns></returns> private bool TryRemoveInternal(TKey key, out TValue value, bool matchValue, TValue oldValue) { int hashcode = _comparer.GetHashCode(key); while (true) { Tables tables = _tables; int bucketNo, lockNo; //这里获取桶的索引和锁的索引,注意,锁的索引和桶未必是同一个值,具体算法看源码。 GetBucketAndLockNo(hashcode, out bucketNo, out lockNo, tables._buckets.Length, tables._locks.Length); //这里锁住的只是对应这个index指向的锁,而不是所有锁。 lock (tables._locks[lockNo]) { //这里table可能被重新分配,所以这里再次获取,看得到的是不是同一个table // If the table just got resized, we may not be holding the right lock, and must retry. // This should be a rare occurrence. if (tables != _tables) { continue; } Node prev = null; //这里同一个桶,可能因为连地址,有很多值,所以要对比key for (Node curr = tables._buckets[bucketNo]; curr != null; curr = curr._next) { Debug.Assert((prev == null && curr == tables._buckets[bucketNo]) || prev._next == curr); //对比是不是要删除的的那个元素 if (hashcode == curr._hashcode && _comparer.Equals(curr._key, key)) { if (matchValue) { bool valuesMatch = EqualityComparer<TValue>.Default.Equals(oldValue, curr._value); if (!valuesMatch) { value = default(TValue); return false; } } //执行删除,判断有没有上一个节点。然后修改节点指针或地址。 if (prev == null) { Volatile.Write<Node>(ref tables._buckets[bucketNo], curr._next); } else { prev._next = curr._next; } value = curr._value; tables._countPerLock[lockNo]--; return true; } prev = curr; } } value = default(TValue); return false; } }
我的使用实例
之前做项目时候,有个奇怪的场景,就是打电话的时候回调接口保存通话记录,这里通过CallId来唯一识别每次通话,但是前端程序是通过websocket跟通话服务建立连接(通话服务是另外一个公司做的)。客户是呼叫中心,一般在网页端都是多个页面操作,所以会有多个websocket连接,这时候每次通话,每个页面都会回调接口端,保存相同的通话记录,并发是同一时间的。
我们最早考虑使用消息队列来过滤重复的请求,但是我仔细考虑了下,发现使用ConcurrentDictionary方式的实现更简单,具体实现如下(我精简了下代码):
private static ConcurrentDictionary<string,string> _strDic=new ConcurrentDictionary<string, string>(); public async Task<BaseResponse> AddUserByAccount(string callId) { if ( _strDic.ContainsKey(callId)) { return BaseResponse.GetBaseResponse(BusinessStatusType.Failed,"键值已存在"); } //成功写入 if (_strDic.TryAdd(callId,callId)) { var recordExist =await _userRepository.FirstOrDefaultAsync(c => c.CallId == callId); if (recordExist ==null) { Record record=new Record { CallId = callId, ………… ………… IsVerify=1 }; _userRepository.Insert(record); _userRepository.SaveChanges(); } return BaseResponse.GetBaseResponse(BusinessStatusType.OK); } //尝试竞争线程,写入失败 return BaseResponse.GetBaseResponse(BusinessStatusType.Failed,"写入失败"); }
这里如果进行同时的并发请求,最后请求都可以通过if ( _strDic.ContainsKey(callId))的判定,因为所有线程同时读取,都是未写入状态。但是多个线程会在TryAdd时有竞争,而且ConcurrentDictionary的实现保证了只有一个线程可以成功更新,其他的都返回失败。
GetOrAdd方法线程不安全的探秘
这个是我写完本篇文字,无意浏览博客园时候看到的(文字地址https://www.cnblogs.com/CreateMyself/p/6086752.html),自己试了下,确实会出现线程不安全。原本实例如下
基本程序
class Program { private static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, string> _dictionary = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, string>(); private static int _runCount = 0; public static void Main(string[] args) { var task1 = Task.Run(() => PrintValue("JeffckWang")); var task2 = Task.Run(() => PrintValue("cnblogs")); Task.WaitAll(task1, task2); PrintValue("JeffckyWang from cnblogs"); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("运行次数为:{0}", _runCount)); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void PrintValue(string valueToPrint) { var valueFound = _dictionary.GetOrAdd("key", x => { Interlocked.Increment(ref _runCount); return valueToPrint; }); Console.WriteLine(valueFound); } }
运行结果
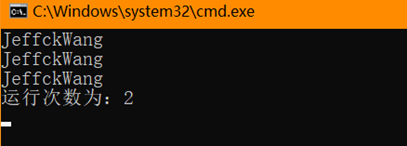
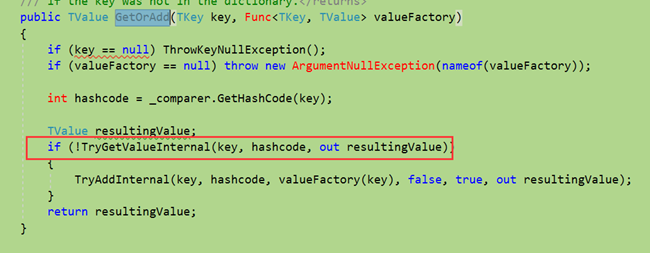
我截图了下GetOrAdd的源码,问题出现在红框部位。多线程同时运行的情况下,这个判断都会为true,因为同时都拿不到值,然后2个线程就同时进行新增,最后就导致可能出现的结果不一致。
对于这个问题,其实windows团队也是知道的,目前已开源的 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Core ,我们可以查看中间件管道源代码如下:
/// <summary> /// Builds a middleware pipeline after receiving the pipeline from a pipeline provider /// </summary> public class MiddlewareFilterBuilder { // 'GetOrAdd' call on the dictionary is not thread safe and we might end up creating the pipeline more // once. To prevent this Lazy<> is used. In the worst case multiple Lazy<> objects are created for multiple // threads but only one of the objects succeeds in creating a pipeline. private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Lazy<RequestDelegate>> _pipelinesCache = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Lazy<RequestDelegate>>(); private readonly MiddlewareFilterConfigurationProvider _configurationProvider; public IApplicationBuilder ApplicationBuilder { get; set; } }
通过ConcurrentDictionary类调用上述方法无法保证委托调用的次数,在对于mvc中间管道只能初始化一次所以ASP.NET Core团队使用Lazy<>来初始化,此时我们将上述也进行上述对应的修改,如下:
class Program { private static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, Lazy<string>> _lazyDictionary = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, Lazy<string>>(); private static int _runCount = 0; public static void Main(string[] args) { var task1 = Task.Run(() => PrintValue("JeffckWang")); var task2 = Task.Run(() => PrintValue("cnblogs")); Task.WaitAll(task1, task2); PrintValue("JeffckyWang from cnblogs"); Console.WriteLine(_runCount); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void PrintValue(string valueToPrint) { var valueFound = _lazyDictionary.GetOrAdd("key", x => new Lazy<string>( () => { Interlocked.Increment(ref _runCount); return valueToPrint; })); Console.WriteLine(valueFound.Value); } }
运行结果如下
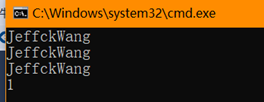
我们将第二个参数修改为Lazy<string>,最终调用valueFound.value将调用次数输出到控制台上。此时我们再来解释上述整个过程发生了什么。
(1)线程1调用GetOrAdd方法时,此键不存在,此时会调用valueFactory这个委托。
(2)线程2也调用GetOrAdd方法,此时线程1还未完成,此时也会调用valueFactory这个委托。
(3)线程1完成调用,返回一个未初始化的Lazy<string>对象,此时在Lazy<string>对象上的委托还未进行调用,此时检查未存在键key的值,于是将Lazy<striing>插入到字典中,并返回给调用者。
(4)线程2也完成调用,此时返回一个未初始化的Lazy<string>对象,在此之前检查到已存在键key的值通过线程1被保存到了字典中,所以会中断创建(因为方法的updateIfExists为false),于是其值会被线程1中的值所代替并返回给调用者。
(5)线程1调用Lazy<string>.Value,委托的调用以线程安全的方式运行,所以如果被两个线程同时调用则只运行一次。
(6)线程2调用Lazy<string>.Value,此时相同的Lazy<string>刚被线程1初始化过,此时则不会再进行第二次委托调用,如果线程1的委托初始化还未完成,此时线程2将被阻塞,直到完成为止,线程2才进行调用。(也就是Lazy写法强制使相同的委托同一时间只能执行一个,不知道我这个理解对不对)
(7)线程3调用GetOrAdd方法,此时已存在键key则不再调用委托,直接返回键key保存的结果给调用者。
上述使用Lazy来强迫我们运行委托只运行一次,如果调用委托比较耗时此时不利用Lazy来实现那么将调用多次,结果可想而知,现在我们只需要运行一次,虽然二者结果是一样的。我们通过调用Lazy<string>.Value来促使委托以线程安全的方式运行,从而保证在某一个时刻只有一个线程在运行,其他调用Lazy<string>.Value将会被阻塞直到第一个调用执行完,其余的线程将使用相同的结果。
问题是解决了,但是内部原理是什么呢?
我们接下来看看Lazy对象。方便演示我们定义一个博客类
public class Blog { public string BlogName { get; set; } public Blog() { Console.WriteLine("博客构造函数被调用"); BlogName = "JeffckyWang"; } }
接下来在控制台进行调用:
var blog = new Lazy<Blog>(); Console.WriteLine("博客对象被定义"); if (!blog.IsValueCreated) Console.WriteLine("博客对象还未被初始化"); Console.WriteLine("博客名称为:" + (blog.Value as Blog).BlogName); if (blog.IsValueCreated) Console.WriteLine("博客对象现在已经被初始化完毕");
打印如下:

通过上述打印我们知道当调用blog.Value时,此时博客对象才被创建并返回对象中的属性字段的值,上述布尔属性即IsValueCreated显示表明Lazy对象是否已经被初始化,上述初始化对象过程可以简述如下:
var lazyBlog = new Lazy<Blog> ( () => { var blogObj = new Blog() { BlogName = "JeffckyWang" }; return blogObj; } );
打印结果和上述一致。上述运行都是在非线程安全的模式下进行,要是在多线程环境下对象只被创建一次我们需要用到如下构造函数:
public Lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode mode); public Lazy(Func<T> valueFactory, LazyThreadSafetyMode mode);
通过指定LazyThreadSafetyMode的枚举值来进行。
(1)None = 0【线程不安全】
(2)PublicationOnly = 1【针对于多线程,有多个线程运行初始化方法时,当第一个线程完成时其值则会设置到其他线程】
(3)ExecutionAndPublication = 2【针对单线程,加锁机制,每个初始化方法执行完毕,其值则相应的输出】
默认的模式为 LazyThreadSafetyMode.ExecutionAndPublication【针对单线程,加锁机制,每个初始化方法执行完毕,其值则相应的输出】保证委托只执行一次。为了不破坏原生调用ConcurrentDictionary的GetOrAdd方法,但是又为了保证线程安全,我们封装一个方法来方便进行调用。
封装线程安全方法
public class LazyConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue> { private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, Lazy<TValue>> concurrentDictionary; public LazyConcurrentDictionary() { this.concurrentDictionary = new ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, Lazy<TValue>>(); } public TValue GetOrAdd(TKey key, Func<TKey, TValue> valueFactory) { var lazyResult = this.concurrentDictionary.GetOrAdd(key, k => new Lazy<TValue>(() => valueFactory(k), LazyThreadSafetyMode.ExecutionAndPublication)); return lazyResult.Value; } }
原封不动的进行方法调用:
private static int _runCount = 0; private static readonly LazyConcurrentDictionary<string, string> _lazyDictionary = new LazyConcurrentDictionary<string, string>(); public static void Main(string[] args) { var task1 = Task.Run(() => PrintValue("JeffckyWang")); var task2 = Task.Run(() => PrintValue("cnblogs")); Task.WaitAll(task1, task2); PrintValue("JeffckyWang from cnblogs"); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("运行次数为:{0}", _runCount)); Console.Read(); } public static void PrintValue(string valueToPrint) { var valueFound = _lazyDictionary.GetOrAdd("key", x => { Interlocked.Increment(ref _runCount); Thread.Sleep(100); return valueToPrint; }); Console.WriteLine(valueFound); }
最终正确打印只运行一次的结果,如下:



