Cache整合Ehcache
项目创建
首先,来创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,引入 Cache 依赖:
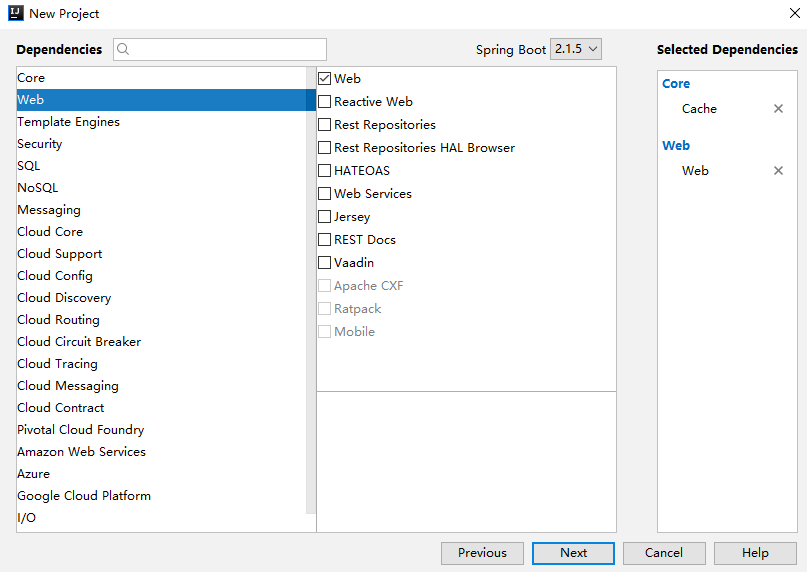
工程创建完成后,引入 Ehcache 的依赖,Ehcache 目前有两个版本:

这里采用第二个,在 pom.xml 文件中,引入 Ehcache 依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
添加 Ehcache 配置
在 resources 目录下,添加 ehcache 的配置文件 ehcache.xml ,文件内容如下:
<ehcache>
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/shiro-spring-sample"/>
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
/>
<cache name="user"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="true"
overflowToDisk="true"
diskPersistent="true"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="600"/>
</ehcache>
配置含义:
1. name:缓存名称。
2. maxElementsInMemory:缓存最大个数。
3. eternal:对象是否永久有效,一但设置了,timeout将不起作用。
4. timeToIdleSeconds:设置对象在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒)。仅当eternal=false对象不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大。
5. timeToLiveSeconds:设置对象在失效前允许存活时间(单位:秒)。最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间。仅当eternal=false对象不是永久有效时使用,默认是0.,也就是对象存活时间无穷大。
6. overflowToDisk:当内存中对象数量达到maxElementsInMemory时,Ehcache将会对象写到磁盘中。
7. diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区。
8. maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘最大缓存个数。
9. diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据。
10. diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒。
11. memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为FIFO(先进先出)或是LFU(较少使用)。
12. clearOnFlush:内存数量最大时是否清除。
13. diskStore 则表示临时缓存的硬盘目录。
注意
默认情况下,这个文件名是固定的,必须叫 ehcache.xml ,如果一定要换一个名字,那么需要在 application.properties 中明确指定配置文件名,配置方式如下:
spring.cache.ehcache.config=classpath:aaa.xml
开启缓存
开启缓存的方式,也和 Redis 中一样,如下添加 @EnableCaching 依赖即可:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class EhcacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EhcacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
缓存使用
@CachaConfig
这个注解在类上使用,用来描述该类中所有方法使用的缓存名称,当然也可以不使用该注解,直接在具体的缓存注解上配置名称,示例代码如下:
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "c1")
public class UserService {
}
@Cacheable
这个注解一般加载查询方法上,表示将一个方法的返回值缓存起来,默认情况下,缓存的key就是方法的参数,缓存的value就是方法的返回值,示例代码如下:
@Cacheable(key = "#id")
public User getUserById(Integer id,String username) {
System.out.println("getUserById");
return getUserFromDBById(id);
}
当有多个参数时,默认就使用多个参数来做key,如果只需要其中某一个参数做key,则可以在@Cacheable注解中,通过key属性来指定key,如上代码就表示只使用id作为缓存的key,如果对key有复杂的要求,可以自定义keyGenerator。当然,Spring Cache中提供了root对象,可以在不定义keyGenerator的情况下实现一些复杂的效果:
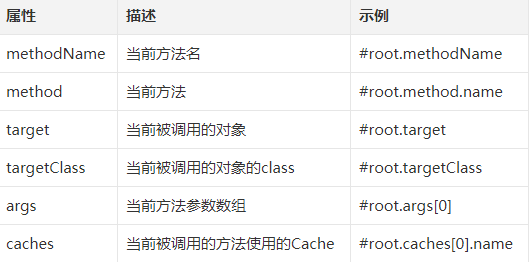
@CachePut
这个注解一般加在更新方法上,当数据库中的数据更新后,缓存中的数据也要跟着更新,使用该注解,可以将方法的返回值自动更新到已经存在的key上,示例代码如下:
@CachePut(key = "#user.id")
public User updateUserById(User user) {
return user;
}
@CacheEvict
这个注解一般加在删除方法上,当数据库中的数据删除后,相关的缓存数据也要自动清除,该注解在使用的时候也可以配置按照某种条件删除(condition属性)或者或者配置清除所有缓存(allEntries属性),示例代码如下:
@CacheEvict()
public void deleteUserById(Integer id) {
//在这里执行删除操作, 删除是去数据库中删除
}
总结
在Spring
Boot中,使用Redis缓存,既可以使用RedisTemplate自己来实现,也可以使用使用这种方式,这种方式是Spring
Cache提供的统一接口,实现既可以是Redis,也可以是Ehcache或者其他支持这种规范的缓存框架。从这个角度来说,Spring
Cache和Redis、Ehcache的关系就像JDBC与各种数据库驱动的关系。

