Spring中@Async注解使用及配置
Spring中@Async注解使用及配置
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42272869/article/details/123082657
一、@Async注解的使用
在使用spring框架中,可以非常简单方便的实现一个异步执行方法,具体只需要在启动类添加@EnableAsync注解开启支持异步,然后在需要进行异步处理的方法上使用@Async注解即可进行异步执行。
注意:想要异步执行,不能在一个类中直接调用本类中被@Async注解标记的方法,本类中直接调用会同步执行,不会进行异步执行
主启动类
@EnableAsync//开启异步支持,也可以标记在被@Configuration注解标注的类上,效果一致 @SpringBootApplication public class ApplicationTest{ .... }
使用实例:需要交给spring容器管理bean
@Component public class MyAsyncService { @Async//直接使用异步注解即可,默认使用的线程池就是自定义实现的线程池 public void testAsync(){ System.out.println("==== 我执行了 ===="); System.out.println("MyAsyncService.testAsync() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
测试执行:
/* 使用SpringBoot执行测试 */ @SpringBootTest(classes = ApplicationTest.class) public class ApplicationTest1 { @Resource MyAsyncService myAsyncService; @Test void testTread(){ myAsyncService.testAsync(); System.out.println("结束.... " ); } }
测试结果:
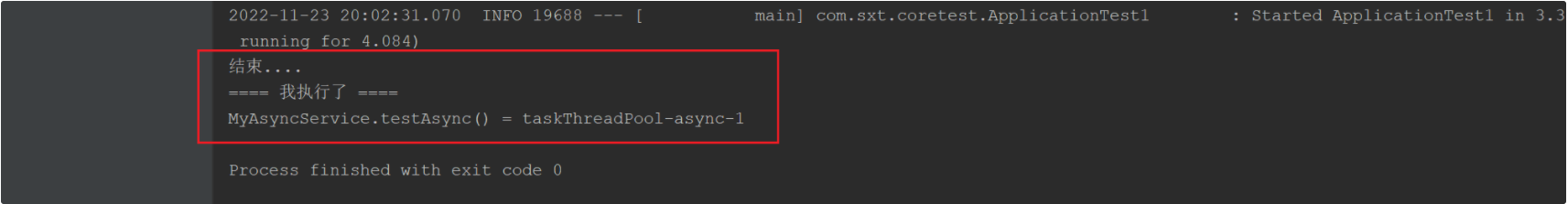
二、@Async注解线程池的配置及使用
1、@Async默认线程池修改
对于修改@Async使用的默认线程池,我们可以使用实现AsyncConfigurer接口,并重写getAsyncExecutor()方法,为其提供我们自己定义的线程池即可
具体示例:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurer; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; /** * 描述:线程池配置类,修改@Async注解默认使用的线程池 * * @author SXT * @version 1.0 * @date 2022/11/22 */ //开启自动启用异步注解,与配置类放在一起,方便管理 @EnableAsync @Configuration @Slf4j public class AsyncTaskPoolConfig implements AsyncConfigurer { /** * 用于@Async注解获取默认线程连接池 * @return */ @Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor() { //此类由Spring提供,org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent包下,是线程池的封装类 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); //线程池中线程的名字前缀 taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("taskThreadPool-async-"); //线程池核心线程数量 taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(5); //线程池最大线程数量 taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(10); //线程池空闲线程存活时间,单位秒 taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(100); //线程池拒绝策略 taskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()); //线程池任务队容量,如果不设置则默认 Integer.MAX_VALUE, // 队列默认使用LinkedBlockingQueue 若queueCapacity的值 <= 0,则使用SynchronousQueue taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(1000); //线程池中核心线程是否允许超时,默认为false taskExecutor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); //线程池中的超时处理时间,单位秒,有一个对应方法为毫秒,默认为不超时 taskExecutor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60); //初始化线程池,不可以少,否者会抛出 线程池没有初始化 taskExecutor.initialize(); return taskExecutor; } /** * 线程未处理异常的统一处理机制,即线程池异常处理器,简单示例 * @return */ @Override public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() { // 异常处理器函数接口类 return new AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() { @Override public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... objects) { log.error("============ " + throwable.getMessage() + " ===========", throwable); log.error("============ " + method.getName() + " ===========", objects); } }; } }
实现AsyncConfigurer类中的getAsyncExecutor()方法后,在使用@Async注解进行异步执行时,默认使用的线程池就是实现提供的线程池,具体使用示例如下:
/** * 描述:异步方法调用 * * @author SXT * @version 1.0 * @date 2022/11/23 */ @Component public class MyAsyncService { @Async//直接使用异步注解即可,默认使用的线程池就是自定义实现的线程池 public void testAsync(){ System.out.println("==== 我执行了 ===="); System.out.println("MyAsyncService.testAsync() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } /* 使用SpringBoot执行测试 */ @SpringBootTest(classes = ApplicationTest.class) public class ApplicationTest1 { @Resource MyAsyncService myAsyncService; @Test void testTread(){ myAsyncService.testAsync(); System.out.println("结束.... " ); } }
测试执行结果如下:如实使用实现提供的线程池
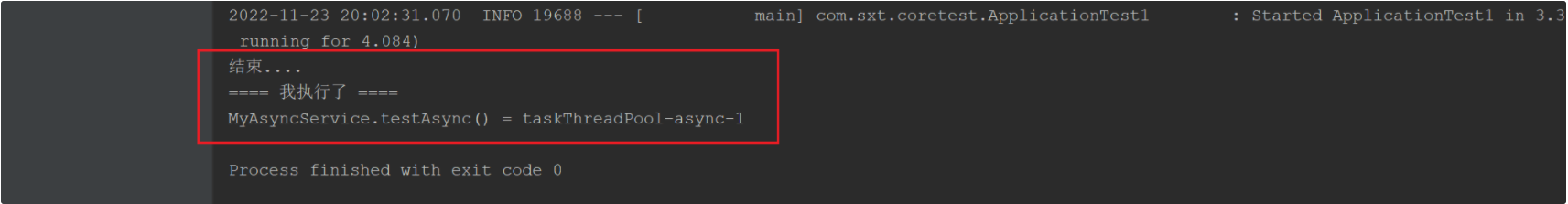
2、自定义线程池(@Async指定使用自定义线程池)
无论是修改@Async默认提供的线程池还是不修改,都可以对某些使用@Async标注的异步执行方法为其指定使用具体的某一个线程池,若想要使用指定的线程池需要明确的为@Async注解指定使用的线程池名称(自定义的线程池需要交给Spring管理),也就是bean的名称
自定义线程池示例:可以看到与修改@Async默认线程池中提供线程池的内容一样,线程池具体的配置可以根据需求进行设置
@Configuration public class CommentConfig { /** * 自定义异步线程池,bean的名字如果不显示的指定,则默认使用方法的名称作为bean的名称 * @return */ @Bean("asyncTaskPool") public Executor asyncTaskPool(){ //此类由Spring提供,org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent包下,是线程池的封装类 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); //线程池中线程的名字前缀 executor.setThreadNamePrefix("asyncTaskPool-task-"); //线程池核心线程数量 executor.setCorePoolSize(5); //线程池最大线程数量 executor.setMaxPoolSize(10); //线程池空闲线程存活时间,单位秒 executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(100); //线程池拒绝策略 executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //线程池任务队容量,如果不设置则默认 Integer.MAX_VALUE, // 队列默认使用LinkedBlockingQueue 若queueCapacity的值 <= 0,则使用SynchronousQueue executor.setQueueCapacity(1000); //线程池中核心线程是否允许超时,默认为false executor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); //线程池中的超时处理时间,单位秒,有一个对应方法为毫秒,默认为不超时 executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60); //初始化线程池,不可以少,否者会抛出 线程池没有初始化 executor.initialize(); return executor; } }
使用自定义线程池示例:
/** * 描述:异步方法调用 * * @author SXT * @version 1.0 * @date 2022/11/23 */ @Component public class MyAsyncService { //指定使用线程池的bean的名称,不指定的话使用的是默认提供的线程池 //asyncTaskPool就是被Spring管理的线程池实例的对象名称 @Async("asyncTaskPool") public void testAsync2(){ System.out.println("==== 我执行了 ===="); System.out.println("MyAsyncService.testAsync2() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } /* 使用SpringBoot执行测试 */ @SpringBootTest(classes = ApplicationTest.class) public class ApplicationTest1 { @Resource MyAsyncService myAsyncService; @Test void testTread2(){ myAsyncService.testAsync2(); System.out.println("结束.... " ); } }
测试结果如下:
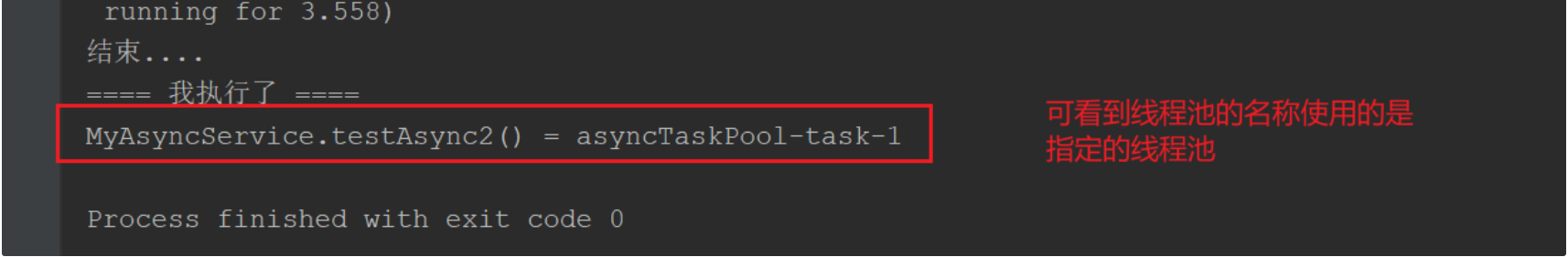
拓展:
若想要根据配置文件进行动态的配置自定义线程池,则可以使用如下方式
配置文件properties文件或yml文件
#这里使用properties文件进行配置,yml文件同样的方式,只是格式不同 #也可以将驼峰命名改成core-size ,keep-alive-seconds,对应的实体类依旧是驼峰命名 asyncTask.pool.coreSize=5 asyncTask.pool.maxPoolSize=10 asyncTask.pool.keepAliveSeconds=60 asyncTask.pool.queueCapacity=1000 asyncTask.pool.timeOutSeconds=60
定义获取配置文件对应配置的类
/** * 描述:线程池配置文件实体类 * * @author SXT * @version 1.0 * @date 2022/11/23 */ //使用@ConfigurationProperties注解,其类必须交给Spring管理 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "async-task.pool") @Component @ToString @Data public class ThreadConfig { private int coreSize; private int maxPoolSize; private long keepAliveSeconds; private int queueCapacity; private long timeOutSeconds; } @SpringBootTest(classes = ApplicationTest.class) public class ApplicationTest1 { @Autowired ThreadConfig threadConfig; @Test void testProperties1(){ System.out.println("threadConfig = " + threadConfig); } }
测试结果:
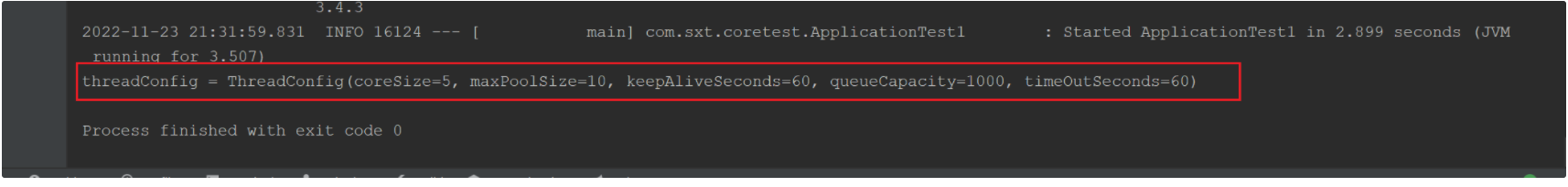
提示:配置的key不要写错,不然获取不到值
三、@Async注解的原理
待完善




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)