Linux系统之SSH端口转发
ssh端口转发也叫ssh隧道,我们知道ssh客户端与服务端之间的通讯会自动加密和解密,除此以外,ssh为其他tcp连接提供了一个安全的通道进行数据传输,并提供了一系列相应的加密和解密服务,这一过程被称之为“隧道”。例如,Telnet,SMTP,LDAP这些tcp应用均能够从中得益,避免了用户名,密码以及隐私信息的铭文传输。与此同时,如果工作环境的防火墙限制了一些网络端口的使用,只要允许ssh连接,也能够通过将TCP端口转发,来使用ssh进行通讯。
通过以上的阐述,不难发现SSH端口转发给我们提供了两大功能,一是加密ssh客户端至ssh服务端之间的通讯数据;二是突破防火墙的限制完成之前无法建立的TCP连接;
ssh端口转发分三大类:
1、本地端口转发:把本地主机端口通过待登录主机端口转发到远程主机端口上去。本地端口转发通过选项-L指定,其格式为
ssh -L <local port>:<remote host>:<remote port> <SSH hostname>
选项:
-f:后台启用
-N:不打开远程shell,处于等待状态
-g:启用网关功能(这个选项需要把sshd_config配置文件中的GatewayPorts 参数配置成yes )
实验环境:
通过上述得知,我们需要三台主机,一台是本地主机(A),一台是中间待登录主机(B),一台是远程主机(C)。这三台主机分别是这样的,本地主机可以通过ssh连接至中间主机,中间主机能够通过ssh连接至远程主机,但是本地主机不能直接通过ssh连接至远程主机。
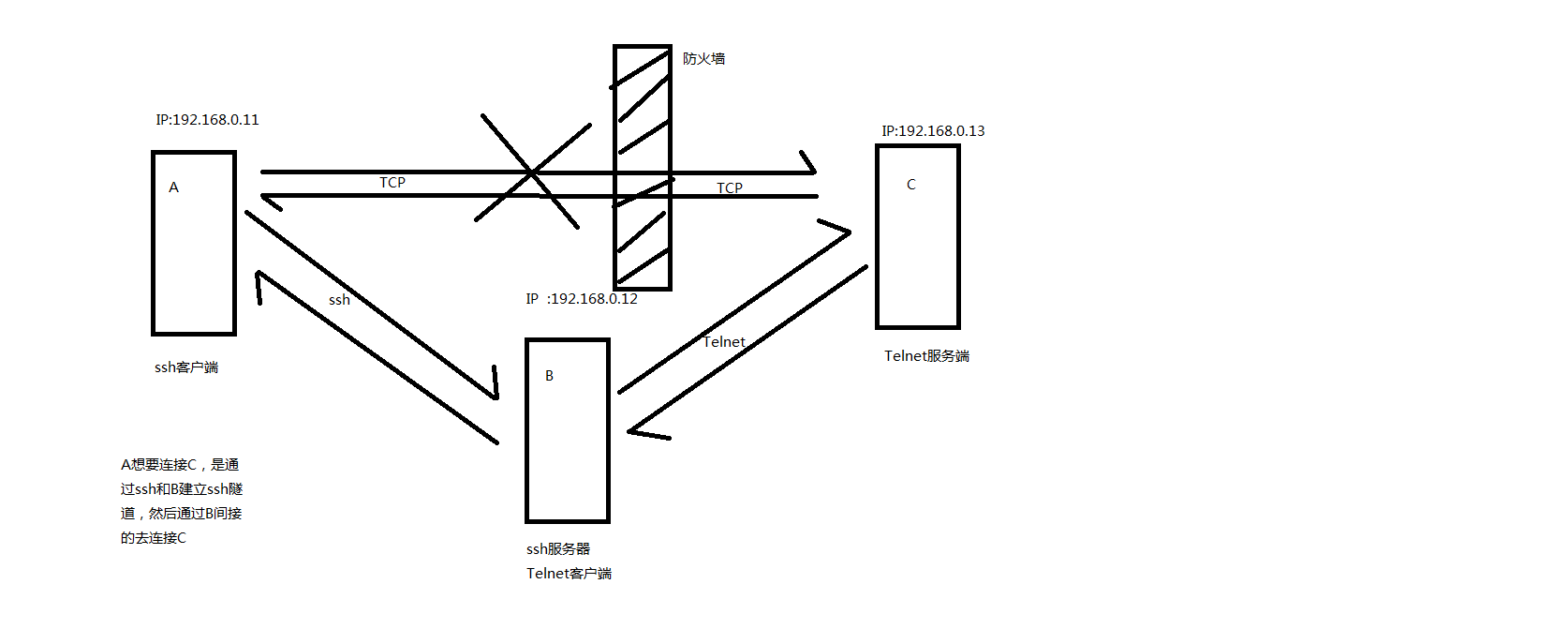
解释下上图:A想通过网络访问C,但是在A和C有防火墙,明确拒绝A的所有请求。A可以通过ssh和B连接,B可以和C连接。数据走向是这样的,data---->A本地端口2048(假设是通过2048转发)--->A连接SSH服务器的某一端口---->B作为SSH服务端22号端口---->B作为Telnet客户端连接C的某一端口---->C作为Telnet服务端端口23。
明白了以上的阐述,下面来试验吧。
首先准备以上需要的主机3台,ip地址分别是:A是192.168.0.11,B是192.168.0.12,C是192.168.0.13
在C上部署一个Telnet服务,并且在防火墙里明确拒绝A的所有请求。
[root@host_C ~]# yum install telnet-server -y Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, security Setting up Install Process Determining fastest mirrors * base: mirrors.aliyun.com * extras: mirrors.cn99.com * updates: mirrors.163.com base | 3.7 kB 00:00 epel | 5.3 kB 00:00 epel/primary_db | 6.1 MB 00:00 extras | 3.4 kB 00:00 extras/primary_db | 29 kB 00:00 updates | 3.4 kB 00:00 updates/primary_db | 6.6 MB 00:00 Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package telnet-server.x86_64 1:0.17-48.el6 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: xinetd for package: 1:telnet-server-0.17-48.el6.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package xinetd.x86_64 2:2.3.14-40.el6 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ============================================================================================== Package Arch Version Repository Size ============================================================================================== Installing: telnet-server x86_64 1:0.17-48.el6 base 37 k Installing for dependencies: xinetd x86_64 2:2.3.14-40.el6 base 122 k Transaction Summary ============================================================================================== Install 2 Package(s) Total download size: 159 k Installed size: 313 k Downloading Packages: (1/2): telnet-server-0.17-48.el6.x86_64.rpm | 37 kB 00:00 (2/2): xinetd-2.3.14-40.el6.x86_64.rpm | 122 kB 00:00 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 968 kB/s | 159 kB 00:00 Running rpm_check_debug Running Transaction Test Transaction Test Succeeded Running Transaction Installing : 2:xinetd-2.3.14-40.el6.x86_64 1/2 Installing : 1:telnet-server-0.17-48.el6.x86_64 2/2 Verifying : 1:telnet-server-0.17-48.el6.x86_64 1/2 Verifying : 2:xinetd-2.3.14-40.el6.x86_64 2/2 Installed: telnet-server.x86_64 1:0.17-48.el6 Dependency Installed: xinetd.x86_64 2:2.3.14-40.el6 Complete! [root@host_C ~]# chkconfig telnet on [root@host_C ~]# chkconfig xinetd on [root@host_C ~]# service xinetd start Starting xinetd: [ OK ] [root@host_C ~]# chkconfig --list telnet telnet on [root@host_C ~]# ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* LISTEN 0 64 :::23 :::* [root@host_C ~]#
说明:Telnet服务器已经准备就绪,也看到了相应的端口是出于监听的状态,接下来添加防火墙规则,拒绝A的所有请求。
[root@host_C ~]# iptables -L -n Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination [root@host_C ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.11 -j REJECT [root@host_C ~]# iptables -L -n Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination REJECT all -- 192.168.0.11 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination [root@host_C ~]#
在主机A上建立与B连通的ssh隧道,并指定转发特定端口2048(这个端口可以任意指定一个,不一定是这个)
[root@host_A ~]# telnet 192.168.0.13 Trying 192.168.0.13... telnet: connect to address 192.168.0.13: Connection refused [root@host_A ~]# ssh -L 2048:root@192.168.0.13:23 -Nf 192.168.0.12 The authenticity of host '192.168.0.12 (192.168.0.12)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 3d:c6:e6:3a:2d:76:34:ba:59:7a:1c:33:f2:0a:6b:95. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '192.168.0.12' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. root@192.168.0.12's password: [root@host_A ~]# ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:2048 *:* LISTEN 0 128 ::1:2048 :::* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* [root@host_A ~]# ss -nt State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.11:13551 192.168.0.12:22 ESTAB 0 52 192.168.0.11:22 192.168.0.232:8351
说明:主机A第一次连接主机B,所以会提示我们否相信对方公钥的提示。可以看到在主机A上我们指定的端口2048,已经处于监听状态了,并且主机A和主机B已经建立连接,说明ssh隧道已经建立好了,接下来我们在来用主机A来连接本地2048端口。
[root@host_A ~]# telnet 127.0.0.1 2048
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to 127.0.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
CentOS release 6.7 (Final)
Kernel 2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 on an x86_64
in: root
Password:
Login incorrect
login: test
Password:
Last login: Mon Oct 28 03:01:05 from 192.168.0.12
[test@host_C ~]$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:b5:b3:f7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.13/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global eth0
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb5:b3f7/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[test@host_C ~]$
说明:可以看到我们主机A可以正常连接主机C,这里说一下Telnet默认不允许用root去连接,所以我们试着用root连接,它会拒绝我们,用普通用户没有问题。通过上面的本地端口转发,我们发现一个问题,我们指定的端口监听在127.0.0.1上,这样一来,如果我们用其他主机来连接就是一个问题,怎么样才能让它监听在任何地址都可以连接的地址上呢?有办法,我们只需要在刚才的命令上加上-g选项,-g选项表示开启网关功能。在指定-g选项前,我们一定要确保ssh服务器上把GatewayPorts 参数配置成yes。
[root@host_b ~]# grep -i gatewayports /etc/ssh/sshd_config #GatewayPorts no GatewayPorts yes [root@host_b ~]#
说明:在本实验host_b作为ssh服务器的角色,所以我们要在B主机上更改其对应的参数。
[root@host_A ~]# ssh -L 2048:192.168.0.13:23 -fNg 192.168.0.12 root@192.168.0.12's password: [root@host_A ~]# ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 :::2048 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:2048 *:* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* [root@host_A ~]#
说明:我们加了-g 选项后,我们所指定的端口监听在×上面了,×表示任何地址,这样我们就可以用互联网地址去连接这个端口,从而达到连接C主机的目的。
[root@host_A ~]# telnet 192.168.0.11 2048
Trying 192.168.0.11...
Connected to 192.168.0.11.
Escape character is '^]'.
CentOS release 6.7 (Final)
Kernel 2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 on an x86_64
in: test
Password:
Last login: Mon Oct 28 03:06:55 from 192.168.0.12
[test@host_C ~]$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:b5:b3:f7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.13/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global eth0
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb5:b3f7/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[test@host_C ~]$
2、远程端口转发:把登录主机端口通过本地主机端口转发到远程主机。远程端口转发通过选项-R指定,其格式为
ssh -R <local port>:<remote host>:<remote port> <SSH hostname>
说明:和上面对本地端口转发不同的是,远程端口转发在本实验中,host_b就充当着ssh客户端的角色,host_a就充当着ssh服务端的角色,我们要在host_b 上执行ssh -R 2048:192.168.0.13:23 -fN 192.168.0.11
[root@host_b ~]# ssh -R 2048:192.168.0.13:23 -fN 192.168.0.11 root@192.168.0.11's password: [root@host_b ~]# ss -nt State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 52 192.168.0.12:22 192.168.0.232:7960 ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.12:33508 192.168.0.11:22 [root@host_b ~]# ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* LISTEN 0 80 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 0 32 :::21 :::* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::* [root@host_b ~]# [root@host_A ~]# ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:2048 *:* LISTEN 0 128 ::1:2048 :::* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* [root@host_A ~]# ss -nt State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.11:22 192.168.0.12:33508 ESTAB 0 52 192.168.0.11:22 192.168.0.232:8351 [root@host_A ~]#
说明:我们在B上执行了相应的命令,在A上是可以看到对应的端口已经处于监听状态。在B上可以看到是一个任意端口连接着A上的22号端口。充分说明了A是ssh服务端,B是客户端。
接下来我们在A端来连接刚才指定的端口
[root@host_A ~]# telnet 127.0.0.1 2048
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to 127.0.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
CentOS release 6.7 (Final)
Kernel 2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 on an x86_64
in: test
Password:
Last login: Mon Oct 28 03:24:30 from 192.168.0.12
[test@host_C ~]$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:b5:b3:f7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.13/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global eth0
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb5:b3f7/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[test@host_C ~]$
说明:可以看到我们是可以正常连接的。当然我这次是监听在127.0.0.1上,如果要监听在任意地址上,我们也可以在上面的命令加上-g选项,在A主机上确保其GatewayPorts这个参数是被开启运行的。这里就不在演示。
3、动态端口转发:动态转发不需要指定特定的目标主机和端口号,可以实现不加密的网络连接,全部走SSH连接,从而提高安全性。动态转发通过参数 -D 指定,其格式:
ssh -D <local port> <SSH Server>
我们在C上搭建一个http服务。其网络环境不变,A还是无法访问C,B可以访问C ,A通过B的代理来访问C
[root@host_C ~]# yum install -y httpd
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, security
Setting up Install Process
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.cn99.com
* updates: mirrors.163.com
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package httpd.x86_64 0:2.2.15-69.el6.centos will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: httpd-tools = 2.2.15-69.el6.centos for package: httpd-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: apr-util-ldap for package: httpd-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package apr-util-ldap.x86_64 0:1.3.9-3.el6_0.1 will be installed
---> Package httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.2.15-69.el6.centos will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
httpd x86_64 2.2.15-69.el6.centos base 836 k
Installing for dependencies:
apr-util-ldap x86_64 1.3.9-3.el6_0.1 base 15 k
httpd-tools x86_64 2.2.15-69.el6.centos base 81 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 3 Package(s)
Total download size: 932 k
Installed size: 3.2 M
Downloading Packages:
(1/3): apr-util-ldap-1.3.9-3.el6_0.1.x86_64.rpm | 15 kB 00:00
(2/3): httpd-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64.rpm | 836 kB 00:00
(3/3): httpd-tools-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64.rpm | 81 kB 00:00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 1.9 MB/s | 932 kB 00:00
Running rpm_check_debug
Running Transaction Test
Transaction Test Succeeded
Running Transaction
Installing : apr-util-ldap-1.3.9-3.el6_0.1.x86_64 1/3
Installing : httpd-tools-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64 2/3
Installing : httpd-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64 3/3
Verifying : httpd-tools-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64 1/3
Verifying : httpd-2.2.15-69.el6.centos.x86_64 2/3
Verifying : apr-util-ldap-1.3.9-3.el6_0.1.x86_64 3/3
Installed:
httpd.x86_64 0:2.2.15-69.el6.centos
Dependency Installed:
apr-util-ldap.x86_64 0:1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.2.15-69.el6.centos
Complete!
[root@host_C ~]# echo "THIS IS HOST_C" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@host_C ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart
Stopping httpd: [ OK ]
Starting httpd: httpd: apr_sockaddr_info_get() failed for host_C
httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.0.1 for ServerName
[ OK ]
[root@host_C ~]# curl 192.168.0.13
THIS IS HOST_C
[root@host_C ~]# ss -ntl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 511 :::80 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 64 :::23 :::*
[root@host_C ~]#
说明:我们在主页上写了THIS IS HOST_C,并开启了http服务。可以看到80端口已经处于监听状态,主页面也是可以正常访问。
[root@host_A ~]# ssh -D 2048 192.168.0.12 -fN root@192.168.0.12's password: [root@host_A ~]# ss -nt State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.11:13558 192.168.0.12:22 ESTAB 0 52 192.168.0.11:22 192.168.0.232:8351 [root@host_A ~]# ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:2048 *:* LISTEN 0 128 ::1:2048 :::* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
接下来我们启动代理来访问下C
[root@host_A ~]# curl 192.168.0.13 curl: (7) couldn't connect to host [root@host_A ~]# curl --socks5 127.0.0.1:2048 192.168.0.13 THIS IS HOST_C [root@host_A ~]#
说明:curl启动代理需要加上 --socks5 来指定代理服务器和端口,可以看到在没有指定代理服务器的时候,A是不能够访问C的,指定了代理服务器和端口就可以正常访问了。
总结:本地端口转发和远程端口转发都需要指定目标主机的端口,通常我们转发特定端口下的网络数据可以用这两种。动态端口可以实现socks代理从而实现加密以及突破防火墙对web浏览器的限制。

 ssh端口转发也叫ssh隧道,我们知道ssh客户端与服务端之间的通讯会自动加密和解密,除此以外,ssh为其他tcp连接提供了一个安全的通道进行数据传输,并提供了一系列相应的加密和解密服务,这一过程被称之为“隧道”。例如,Telnet,SMTP,LDAP这些tcp应用均能够从中得益,避免了用户名,密码以及隐私信息的铭文传输。与此同时,如果工作环境的防火墙限制了一些网络端口的使用,只要允许ssh连接,也能够通过将TCP端口转发,来使用ssh进行通讯。
ssh端口转发也叫ssh隧道,我们知道ssh客户端与服务端之间的通讯会自动加密和解密,除此以外,ssh为其他tcp连接提供了一个安全的通道进行数据传输,并提供了一系列相应的加密和解密服务,这一过程被称之为“隧道”。例如,Telnet,SMTP,LDAP这些tcp应用均能够从中得益,避免了用户名,密码以及隐私信息的铭文传输。与此同时,如果工作环境的防火墙限制了一些网络端口的使用,只要允许ssh连接,也能够通过将TCP端口转发,来使用ssh进行通讯。

