自动化运维工具Ansible工具
一、初识Ansible
Ansible是一个简单的自动化引擎,可完成配置管理,应用部署,服务编排以及其他各种IT需求。Ansible也是一款使用Python语言开发实现的开源软件,其依赖Jinja2,Paramiko和PyYAML这几个库
Ansbile的优点:
- 安装部署简单: Ansible只需要在主控端部署Ansible环境,被控端无须任何操作。
- 基于SSH进行配置管理,不依赖于客户端,直接使用SSH进行配置管理
- Ansible不需要守护进程。
- 日志集中存储。
- Ansible简单易用。
- Ansible功能强大,Ansible通过模块来实现各种功能
- Ansblie设计优秀,便于分享。
- Ansible对云计算和大数据平台都有很好的支持。
Ansible作为自动化系统运维的一大利器,在构建整个体系过程中有着举足轻重的地位。其简单易用,易于安装,功能强大,便于分享,内含大量模版等都是它的魅力所在,再加上易封装,接口调用方便,Ansible正在被越来越多的大公司采用。
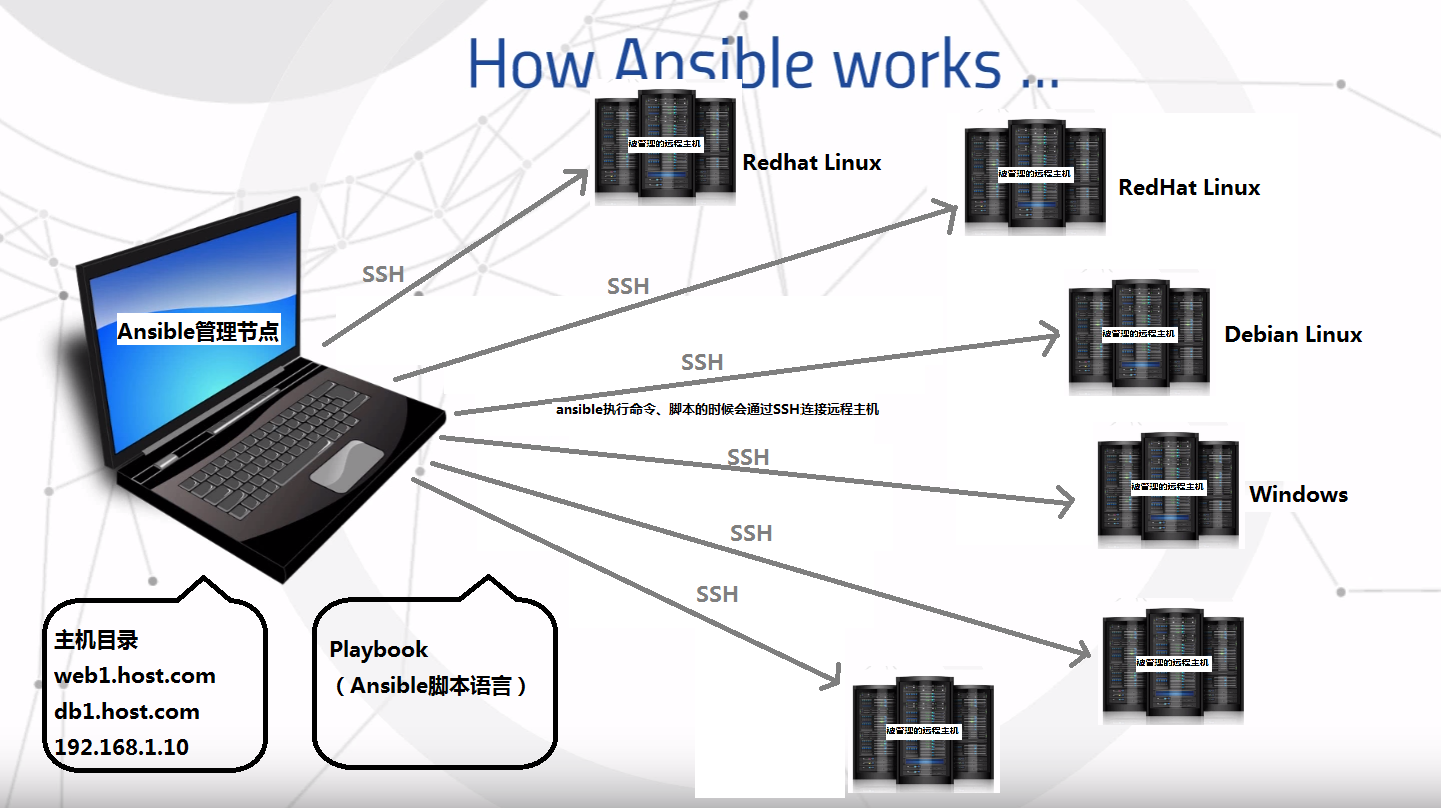
二、Ansible的架构
Ansilbe管理员节点和远程主机节点通过ssh协议进行通信。
Ansible配置的时候只需要与被控端做免密即可。
三、Ansible基础使用
安装
# Redhat/CentOS Linux上,Ansible目前放在的epel源中
# Fedora默认源中包含ansible,直接安装包既可
[root@master ~]# yum install epel-release
[root@master ~]# yum install ansible -y
配置Linux不同机器间免密 略...
主机清单
什么是Host Invenory(主机目录,主机清单)?
Host Inventory是配置文件,用来告诉Ansible需要管理那些主机。并且把这些主机根据需分类。
默认的配置文件是:/etc/ansible/hosts
最简单的host文件:
192.168.32.130
管理主机
Ansible 提供了一个命令行工具
ansible命令的格式是:
ansible <host-pattern> [options]
-
检查ansible安装环境
[root@192.168.32.130 /etc/ansible]$ ansible all -m ping -u root 192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } -
执行命令
[root@192.168.32.130 /etc/ansible]$ ansible all -a "ls /etc/ansible" 192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> ansible.cfg hosts hosts.py roles -
拷贝文件
[root@192.168.32.130 /tmp]$ ansible all -m copy -a "src=/etc/ansible/hosts dest=/tmp/" 192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS => { "changed": true, "checksum": "2e304266c75c95987fb111c5482443bb41408cd7", "dest": "/tmp/hosts", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "md5sum": "827317b4e0cd727bf245f2044319d31d", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0", "size": 15, "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1572083478.93-155762973748871/source", "state": "file", "uid": 0 } -
安装包
[root@192.168.32.130 /tmp]$ ansible all -m shell -a "yum -y install nc" 192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security Setting up Install Process Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.cn99.com * extras: ftp.sjtu.edu.cn * remi-safe: ftp.riken.jp * updates: mirrors.163.com Package nc-1.84-24.el6.x86_64 already installed and latest version Nothing to do -
添加用户
[root@192.168.32.130 /tmp]$ ansible all -m shell -a "useradd jack" 192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> -
并行执行
# 开启10个线程执行 [root@192.168.32.130 /tmp]$ ansible all -a "ip addr" -f 10 192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:b8:5c:ad brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.32.130/24 brd 192.168.32.255 scope global eth0 inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb8:5cad/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 3: pan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN link/ether 16:86:d7:59:08:da brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff # 查看远程主机的全部系统信息 [root@192.168.32.130 /tmp]$ ansible all -m setup
四、Ansible用脚本管理主机
只有脚本才可以重用,避免总敲重复的代码
Ansible脚本的名字叫 Playbook,使用YAML的格式,文件以yml结尾
YAML 和 JSON 类似,是一种表示数据的格式
执行脚本的方法:[root@192.168.32.130 /tmp]$ ansible-playbook xxx.yml
yml文件的功能可以写一些部署、启停服务逻辑,例如:安装Apache,步骤如下:
1、 安装Apache包
2、 拷贝配置文件httpd,并保证拷贝文件后,apache服务会被重启
3、 拷贝默认的网页index.html
4、 启动Apache服务
yml文件包含以下几个关键字:
- hosts:主机ip,或者主机组名,或者关键字all
- remote_user:以哪个用户执行
- vars:变量
- tasks:任务,定义顺序执行的动作
- action:
- handers:event
示例:
- hosts: web
vars:
http_port: 80
max_clients: 200
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ensure apache is at the latest version
yum: pkg=httpd state=latest
- name: Write the configuration file
template: src=templates/httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart apache
- name: Write the default index.html file
template: src=templates/index.html.j2 dest=/var/www/html/index.html
- name: ensure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart apache
service: name=httpd state=restarted
不懂yml没有关系,上面的yml格式可以转化为json格式:
[
{
"hosts": "web",
"vars": {
"http_port": 80,
"max_clients": 200
},
"remote_user": "root",
"tasks": [
{
"name": "ensure apache is at the latest version",
"yum": "pkg=httpd state=latest"
},
{
"name": "Write the configuration file",
"template": "src=templates/httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf",
"notify": [
"restart apache"
]
},
{
"name": "Write the default index.html file",
"template": "src=templates/index.html.j2 dest=/var/www/html/index.html"
},
{
"name": "ensure apache is running",
"service": "name=httpd state=started"
}
],
"handlers": [
{
"name": "restart apache",
"service": "name=httpd state=restarted"
}
]
}
]
playbook 是指一个可以被ansible执行的yml文件
五、Ansible模块Module
module就是Ansible的“命令”,即执行任务的方式,常见的module有yum、copy、shell
- -m:后面跟上module的名字
- -a:后面接调用module的参数
例如使用mudule copy拷贝文件
六、Ansible常用的module介绍
- ping:检测连通性
- debug:打印输入信息,和linux 上echo命令很像
- copy:拷贝文件
- template:
- file:设置远程机器行文件相关的操作比如权限
- user:为远程主机新增或删除账户
- yum:管理远程主机的Linux上的安装包
- service:管理远程节点上的服务
- firewalld:为某服务和端口添加firewalld规则
- shell:通过/bin/sh在远程节点上执行命令
- command:在远程节点上执行命令。和Shell Module类似,不过不支持$HOME and operations like “<”, “>”, “|”, “;” and “&”。
七、Ansible进阶
Ansible配置文件
主机目录的文件,远程机的临时文件存储位置,管理机的临时文件存储文件
[root@192.168.32.130 /etc/ansible]$ vim ansible.cfg
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts
library = /usr/share/my_modules/
remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp
local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp
连接端口号"accelerate_port",超时时间等。
accelerate_port = 5099
accelerate_timeout = 30
accelerate_connect_timeout = 5.0
accelerate_daemon_timeout = 30
accelerate_multi_key = yes
Ansible主机目录
主机目录管理,告诉ansible需要管理那些server,和server的分类和分组信息
# 默认文件
/etc/ansible/hosts
# 修改主机目录的配置文件
...
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts
...
# 命令行中传递主机目录配置文件
$ ansible-playbook -i hosts site.yml
或者参数—inventory-file
$ ansible-playbook --inventory-file hosts site.yml
远程主机的分组([]内是组名):
[webservers]
foo.example.com
[databases]
db-[a:f].example.com
指定Server的连接参数,包括连接方法、用户等
Ansible的脚本
执行playbook的语法
ansible-playbook deploy.yml
查看输出的细节
ansblie-playbook playbook.yml --verbose
查看该脚本影响哪些hosts
ansible-playbook playbook.yml --list-hosts
并行执行脚本
ansible-playbook playbook.yml -f 10
最基本的playbook脚本分为三个部分:
在什么机器上以什么身份执行
- hosts
- users
- tasks:任务都有什么
- handlers。。。



