20240610刷题总结
T1
T559。
T2(带权并查集)
1380。
把行和列的取值看成变量,其中行取1代表+1,列取1代表-1,为了凑x - y = c,这样可以拿并查集来做了。
维护d[x],到根的距离,我们把边定义为+,反向走为-。这样就行了,如果在一个集合,那么判断距离是不是c。
还可以差分约束,dfs(直接遍历一遍,遇到环就判断).
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m, k;
int p[N << 1], d[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] == x) return x;
int fa = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
return p[x] = fa;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n + m; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
while (k -- )
{
int x, y, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &c);
y += n;
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
if (px != py)
{
p[py] = px;
d[py] = d[x] + c - d[y];
}
else if (d[y] - d[x] != c)
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
puts("Yes");
return 0;
}
T3(带权并查集,与上题类似)
换成乘。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20010;
int p[N];
double d[N];
int n, m;
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] == x) return x;
int fa = find(p[x]);
d[x] *= d[p[x]];
return p[x] = fa;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i, d[i] = 1;
while (m -- )
{
int x, y, a, b;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x, &y, &a, &b);
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
if (px != py)
{
p[py] = px;
d[py] = d[x] * a / b / d[y];
}
else
{
if (abs(d[x] - (d[y] * b / a)) >= 1e-5)
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
}
puts("Yes");
return 0;
}
T4(差分约束,不等式及相对关系->差分约束)
1129。 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2474
这个题首先要想到枚举,然而我们不知道他们之间的关系,无法判断。求解相对关系,我们发现a+b = c+d 加法不好处理,这个等式实际上就是a - c = d - b,这样就转化为了求差值的范围,其实就是差分约束。不等式是啥呢?根据给定的图,a-b的关系就给了,floyd求差分约束就行了。最后暴力枚举判断。

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int mind[N][N], maxd[N][N];
int n, A, B;
char g[N][N];
void floyd()
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ )
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
{
mind[i][j] = max(mind[i][j], mind[i][k] + mind[k][j]);
maxd[i][j] = min(maxd[i][j], maxd[i][k] + maxd[k][j]);
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("balance.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("balance.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &A, &B);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
scanf("%s", g[i] + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (i != j)
{
if (g[i][j] == '+') mind[i][j] = 1, maxd[i][j] = 2;
else if (g[i][j] == '?') mind[i][j] = -2, maxd[i][j] = 2;
else if (g[i][j] == '-') mind[i][j] = -2, maxd[i][j] = -1;
}
}
floyd();
int c1 = 0, c2 = 0, c3 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (i != j && i != A && i != B && j != A && j != B)
{
if (mind[A][i] > maxd[j][B] || mind[A][j] > maxd[i][B]) c1 ++ ;
if ((maxd[A][i] == mind[A][i] && maxd[j][B] == mind[j][B] && mind[A][i] == maxd[j][B])
|| (maxd[A][j] == mind[A][j] && maxd[i][B] == mind[i][B] && mind[A][j] == maxd[i][B]))
c2 ++ ;
if (maxd[A][i] < mind[j][B] || maxd[A][j] < mind[i][B]) c3 ++ ;
}
printf("%d %d %d\n", c1, c2, c3);
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
T5
862。
T6(离线思想,扫描线)
243。

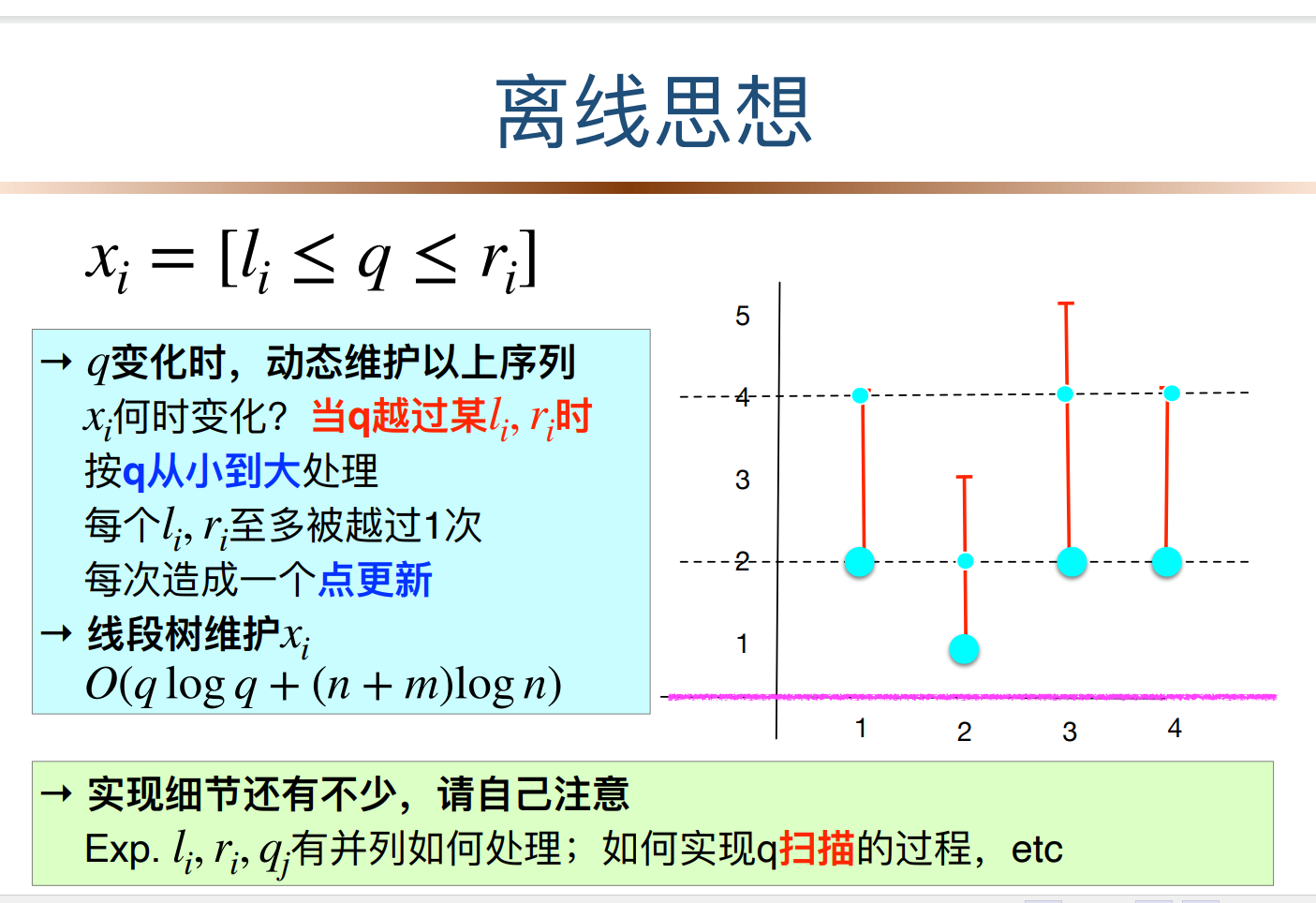
二维转一维,考虑根据q增量建,只要从小到大就能保证复杂度,按速度扫,i上建线段树,维护那个序列,就能做。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
struct Node { int l, r, lcnt, rcnt, cnt; } tr[N << 2];
int n, m;
struct Query { int x, id;
bool operator< (const Query& W) const{
return x < W.x;
}} q[N];
struct Line { int x, type, id;
bool operator< (const Line& W) const {
return x < W.x;
}} lines[N << 1];
int ans[N];
inline int len(Node a) { return a.r - a.l + 1; }
Node pushup(Node a, Node b)
{
int cnt = 0, lcnt = 0, rcnt = 0;
cnt = max(a.rcnt + b.lcnt, max(a.cnt, b.cnt));
lcnt = (a.lcnt == len(a) ? (len(a) + b.lcnt) : a.lcnt);
rcnt = (b.rcnt == len(b) ? (len(b) + a.rcnt) : b.rcnt);
return {a.l, b.r, lcnt, rcnt, cnt};
}
Node build(int u, int l, int r)
{
if (l == r) return tr[u] = {l, r, 0, 0, 0};
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return tr[u] = pushup(build(u << 1, l, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r));
}
void modify(int u, int x, int v)
{
if (tr[u].l == x && tr[u].r == x)
{
if (v == 1) tr[u].cnt = tr[u].lcnt = tr[u].rcnt = 1;
else tr[u].cnt = tr[u].lcnt = tr[u].rcnt = 0;
return;
}
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
if (x <= mid) modify(u << 1, x, v);
else modify(u << 1 | 1, x, v);
tr[u] = pushup(tr[u << 1], tr[u << 1 | 1]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
n -- ;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
scanf("%d%d", &lines[i].x, &lines[n + i].x);
lines[n + i].x ++ ;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) lines[i].type = 1, lines[i].id = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) lines[n + i].type = -1, lines[n + i].id = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &q[i].x), q[i].id = i;
n <<= 1;
sort(lines + 1, lines + n + 1);
sort(q + 1, q + m + 1);
build(1, 1, (n >> 1) + 2);
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (j + 1 <= n && lines[j + 1].x <= q[i].x)
{
++ j;
modify(1, lines[j].id, lines[j].type); //注意这里是id,维护的是wi = [li <= q <= ri]
}
ans[q[i].id] = tr[1].cnt;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) printf("%d ", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
T7(数大取模,最短路加状态)
1130。
首先肯定能考虑到按t开状态,然而开不下。这就好办了。这里发现一个重要性质:首先,起点一定能到,假设当前时间t,那么沿起点任意一条边w走,t+2w,w+4w是都可以的·,这就是说大于>2w的就没有意义了。无论最短路怎么走,都能到起点的邻边,选别的边就不一定了(包括终点邻边。因为要保证所有路径都能到。只要保证这条边所有路径都能到了,那么最短路只要和规定时间取模一致就行,给所有路径+2kw。
本质有待探究。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110;
LL dist[N][20010];
int n, m, T, mod;
LL t;
int h[N], e[N << 1], w[N << 1], ne[N << 1], idx;
struct Node { int id; LL d; };
bool st[N][20010];
queue<Node> q;
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[ ++ idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx;
}
void spfa()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1][0] = 0;
q.push({1, 0});
st[1][0] = true;
while (q.size())
{
Node t = q.front(); q.pop();
st[t.id][t.d] = false;
for (int i = h[t.id]; i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j][(t.d + w[i]) % mod] > dist[t.id][t.d] + w[i])
{
dist[j][(t.d + w[i]) % mod] = dist[t.id][t.d] + w[i];
if (!st[j][(t.d + w[i]) % mod])
{
st[j][(t.d + w[i]) % mod] = true;
q.push({j, (t.d + w[i]) % mod});
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("travel.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("travel.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T -- )
{
scanf("%d%d%lld", &n, &m, &t);
mod = 20009;
idx = 0;
memset(h, 0, sizeof h);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
a ++ , b ++ ;
add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c);
if (a == 1 || b == 1) mod = min(mod, c << 1);
}
spfa();
if (dist[n][t % mod] > 1e9) puts("Impossible");
else puts("Possible");
}
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
T8(数学题)
dp好想的要死。
数学:假设左传x,则右传m-x,则如果可行,他们%n同余,即:(m - 2 * x) % n == 0。那么直接枚举x就好了。枚举完了怎么求呢?
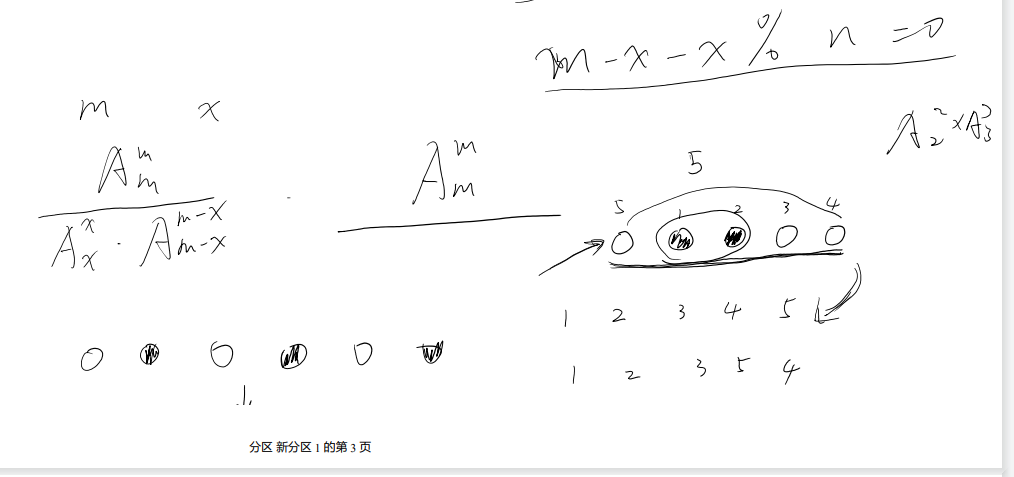
也就是m个数的排列中对x,m-x去序(选法嘛,不计顺序)。可行,也就是m次传递,左右可以任意互换顺序奥。
__int128偷个懒。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 40;
__int128_t fac[N];
int n, m;
inline void print(__int128_t x){
if (x < 0){
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if (x > 9) print(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
fac[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i;
__int128_t ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
if (!((m - i * 2 ) % n))
{
ans += fac[m] / fac[i] / fac[m - i];
}
print(ans);
return 0;
}
T9(莫队,增量式维护答案)
938。
可加性不好想,考虑增量式,也就是莫队。问的显然是:
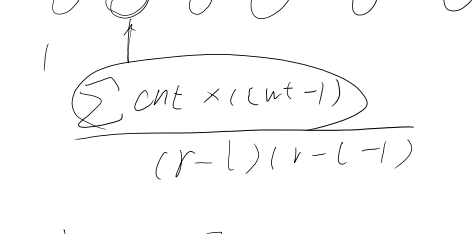
这样直接暴力维护计数器,我原本的想法是线段树增量式or暴力查询(这个过不了),其实没必要哈哈,直接暴力维护答案就行了。光去想查询的时候求答案了,忘了答案可以直接维护。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 50010;
int n, m, L;
int cnt[N], w[N];
struct Query { int l, r, bcnt, id;
bool operator< (const Query& W) const
{
if (bcnt != W.bcnt) return bcnt < W.bcnt;
return r > W.r;
}}q[N];
PLL ans[N];
void work(int x, int type, LL& res)
{
res -= (LL)cnt[x] * (cnt[x] - 1) / 2; //无论加还是减,之前的都没了
cnt[x] += type;
if (cnt[x] >= 2) res += (LL)cnt[x] * (cnt[x] - 1) / 2;
}
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
L = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &w[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
{
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
q[i] = {l, r, (l - 1) / L + 1, i};
}
sort(q + 1, q + m + 1);
LL res = 0;
for (int i = 1, l = 1, r = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (l > q[i].l) -- l, work(w[l], 1, res);
while (r < q[i].r) ++ r, work(w[r], 1, res);
while (l < q[i].l) work(w[l], -1, res), l ++ ;
while (r > q[i].r) work(w[r], -1, res), r -- ;
if (!res) ans[q[i].id] = {0, 1};
else
{
LL a = q[i].r - q[i].l + 1;
LL k = gcd(res, a * (a - 1) / 2);
ans[q[i].id] = {res / k, a * (a - 1) / 2 / k};
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
if (!ans[i].first) puts("0/1");
else printf("%lld/%lld\n", ans[i].first, ans[i].second);
return 0;
}
T10(贪心,线段覆盖的转化)
372。
前置题371or
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/909/ 。
其实就是能不能覆盖就是判断上面那个点。上面点行了,自然全行了。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
struct Node {double l, r;
bool operator< (const Node& W) const
{
return l < W.l;
}} w[N];
int n, L, W, cnt;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &L, &W);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int x, r;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &r);
if (r >= W / 2)
{
double delta = sqrt(r * r - W * W / 4);
w[ ++ cnt] = {x - delta, x + delta};
}
}
sort(w + 1, w + cnt + 1);
int res = 0;
double k = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i <= cnt; i = j)
{
double r = -2e9;
while (j <= cnt && w[j].l <= k)
{
r = max(r, w[j].r);
j ++ ;
}
if (r < k){ puts("-1"); return 0; } //无解特判
res ++ ;
k = r;
if (k >= L) break;
}
if (k >= L) cout << res << endl;
else puts("-1");
return 0;
}
T11(最优决策分析,MST)
384。
分析清零k条边,原来不选的现在也不选(不影响答案,那最好就选最大的k条边。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1010;
int n, k, cnt;
struct Node { LL a, b, c, d; }w[N];
bool st[N];
LL res;
LL dist[N];
int tmp[N];
LL get_dist(Node x, Node y)
{
LL da = x.a - y.a, db = x.b - y.b, dc = x.c - y.c, dd = x.d - y.d;
return abs(da * da + db * db + dc * dc - dd * dd);
}
void prim()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j;
st[t] = true;
res += dist[t];
tmp[ ++ cnt] = dist[t];
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) dist[j] = min(dist[j], get_dist(w[t], w[j]));
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int a, b, c, d;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
w[i] = {a, b, c, d};
}
prim(); //注意这里连通块减1不行,因为剩下的边不一定最大
sort(tmp + 1, tmp + 1 + cnt);
for (int i = cnt - k + 1; i <= cnt; i ++ ) res -= tmp[i];
printf("%lld\n", res);
return 0;
}
12,13
423,2525。搜索题
T14(生成树,控制变量法,最优决策分析)
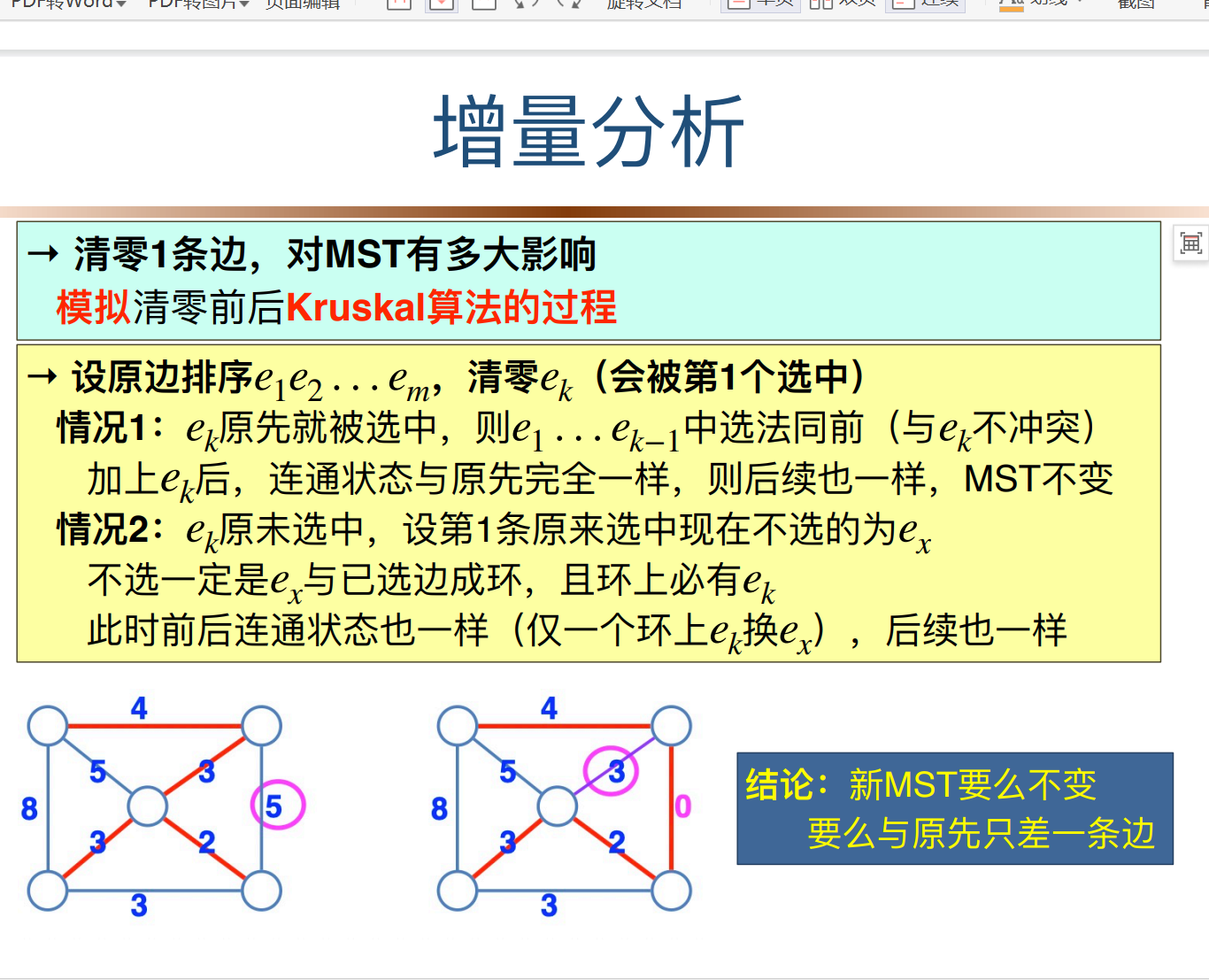

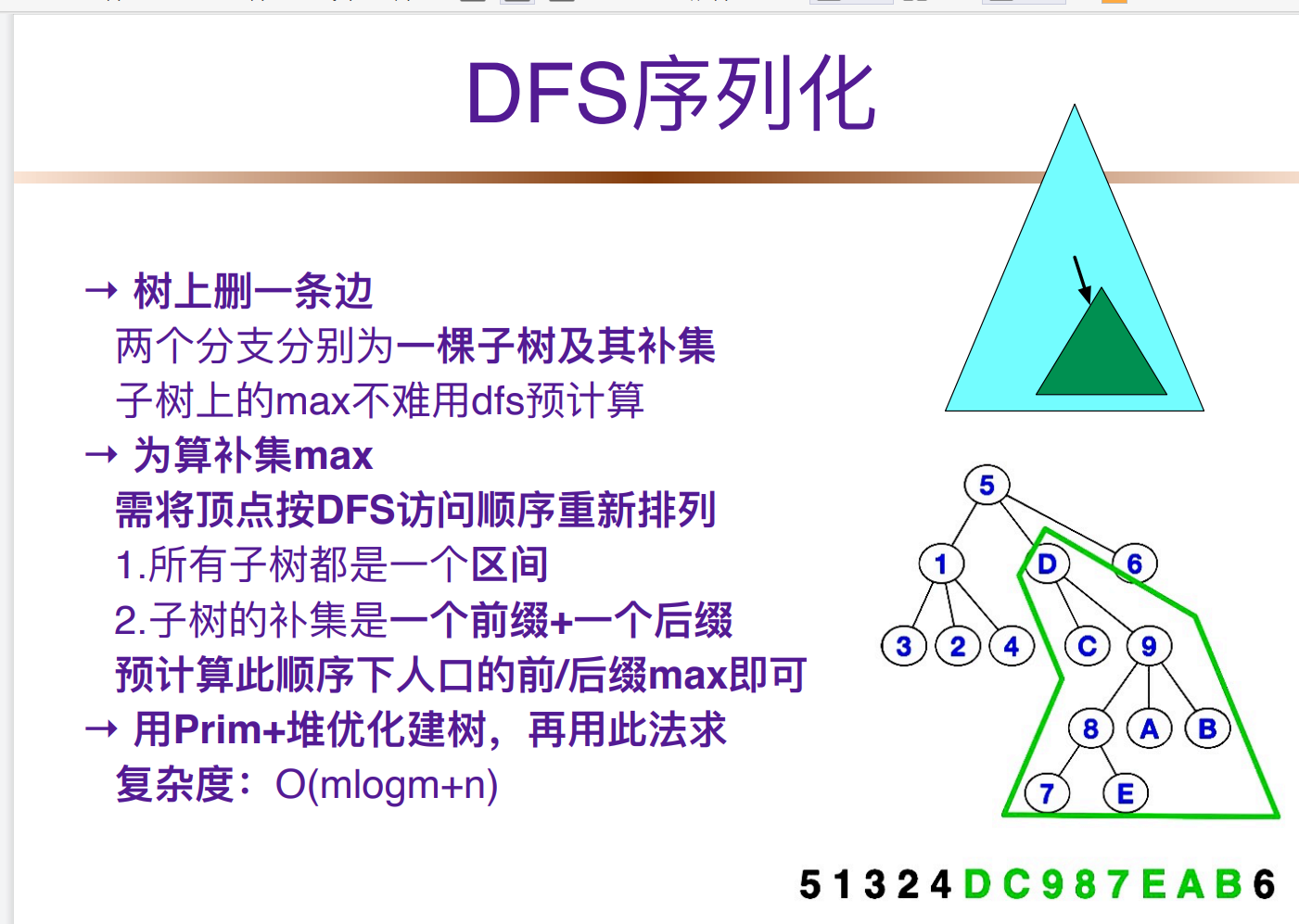
有一条0边的最优比例生成树。已经知道清0一条边的影响,也就是说清零后,这个村村通的道路连通方案,也就只有删边在加边那几种,可以直接枚举处理。(枚举0边影响的那条边),删边枚举相当于固定b,让a最小,显然选两侧最大的。(枚举0边),加边相当于a固定,求b最小,显然删去最大边。*
->暴力:枚举高速路,暴力求一遍最小生成树。->真的要暴力求嘛?改变大不大?->一条边最多改变MST一条边。实际上由于清0,一定改变。
->增量式:在原来最小生成树基础上,枚举高速路,改变的只有最大边(相当于固定a)
->预处理,可以做了
->既然这样,固定b(枚举改变的那条边),这样求最大的高速路点权和,这样就是求两边的点权最值。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, M = N << 1;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx; double w[M]; //生成树
int n;
double dist[N]; bool st[N]; int fa[N]; //prim,fa是为了知道方案
struct Node { int x, y, p; } a[N];
double res;
struct Edge { int a, b, id, enid; double w; } edges[N]; int cnt; //方便枚举删了,不需要重新遍历
double get_dist(Node a, Node b)
{
int dx = a.x - b.x, dy = a.y - b.y;
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
void add(int a, int b, double c)
{
edges[ ++ cnt] = {a, b, idx, idx + 1, c};
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
e[idx] = a, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[b], h[b] = idx ++ ;
}
int dfs(int u, int fro, int fa)
{
int res = a[u].p;
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (i == fro) continue;
if (j == fa) continue;
res = max(res, dfs(j, fro, u));
}
return res;
}
void prim()
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ ) dist[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j;
st[t] = true;
res += dist[t];
if (t != 1) add(fa[t], t, dist[t]);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (get_dist(a[t], a[j]) < dist[j])
{
dist[j] = get_dist(a[t], a[j]);
fa[j] = t;
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int x, y, p;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &p);
a[i] = {x, y, p};
}
prim();
//枚举删边
double ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++ )
{
int a = edges[i].a, b = edges[i].b, id = edges[i].id, enid = edges[i].enid;
double w = edges[i].w;
ans = max(ans, (dfs(a, id, -1) + dfs(b, enid, -1)) / (res - w));
}
printf("%.2lf\n", ans);
return 0;
}
T15,16(标准的wqs二分好题!!!)
1624。有空再补吧,先只交这题。390。也是。
我的理解就是本质利用了k和x单调性,以及切点与截距max的唯一性。二分斜率,现在问题转化为求(x,f(x)),然后把直线写出来,导到截距上,这样就转化为了与k无关的问题(每选一个-k),只要在这个问题把x和maxb求出来就能反推回f(x)。但就是感觉不是特别理解。
其实放到正常题目,我的理解就是二分每个物品附带的权值,从而使物品数更偏向k,剩下的就是解决在附带权值下的问题了,这个问题一般都容易。
这个附带的权值其实就是kx,剩下的解决的问题就是原来的截距。
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3623
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2619
https://www.luogu.com/article/knpufhxe
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50010;
int p[N];
int find(int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]); }
int n, m, k, mid;
struct Node { int a, b, w, c;
bool operator< (const Node& W) const
{
int x = (c ? mid : 0);
int y = (W.c ? mid : 0);
return w - x < W.w - y;
}
} edges[N << 1];
struct Res { int res, cnt; };
Res kruskal()
{
Res res = {0, 0};
sort(edges + 1, edges + 1 + m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
{
int pa = find(edges[i].a), pb = find(edges[i].b);
if (pa != pb)
{
p[pa] = pb;
res.cnt += edges[i].c;
res.res += edges[i].w;
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
freopen("network.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("network.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
{
int a, b, c, d;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
a ++ , b ++ ;
d = 1 - d;
edges[i] = {a, b, c, d};
}
int l = -100, r = 100;
while (l < r)
{
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
Res res = kruskal();
if (res.cnt >= k) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
mid = r;
Res res = kruskal();
cout << res.res - (res.cnt - k) * mid << endl; //斜率为r可能有很多个,这里强制二分最右边那个
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
没调出来。
T17(归程,kruskal重构树)
归程。
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4768

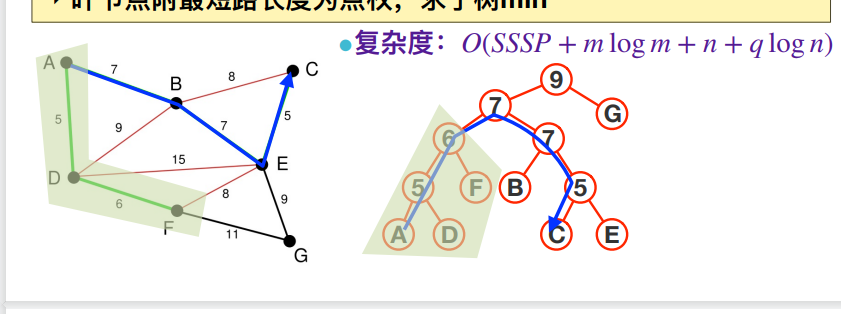
查询v只经过边权>=p经过的点。我们可以使用kruskal重构树。考虑把合并过程全部记录下来。由于kruskal加入边权单调,呈现一种大/小根堆的样子。这个性质就好多了,我们倍增找到父节点,父节点为根的子树都<=自己,往上走不了了。这样问题就得到了解决。本质思想还是想查询任意时刻kruskal重构树p所在的集合,我们通过可持久化的形式,就记录了下来。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010, M = N << 1;
typedef long long LL;
int T, n, m, q, k, s, cur_cnt;
int h[N], e[M << 1], w[M << 1], ne[M << 1], idx; //原图,dij建两倍啦
struct Node { int l, r, f[25]; LL mindist, weight;}tr[M]; int p[M];//重构树上函数,我们这样建重构树,方便
struct Edge { int a, b, w, h;
bool operator< (const Edge& W) const { return h > W.h; }
}edges[M]; //kruskal用
LL dist[N]; bool st[N]; //dijkstra
struct Dij { int id, dist;
bool operator< (const Dij& W) const { return dist < W.dist; }
};
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[ ++ idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx;
}
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
// priority_queue<Dij> heap;
// void dijkstra()
// {
// memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
// memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
// dist[1] = 0;
// heap.push({1, 0});
// while (heap.size())
// {
// Dij t = heap.top(); heap.pop();
// if (st[t.id]) continue;
// st[t.id] = true;
// for (int i = h[t.id]; i; i = ne[i])
// {
// int j = e[i];
// if (dist[j] > dist[t.id] + w[i])
// {
// dist[j] = dist[t.id] + w[i];
// heap.push({j, dist[j]});
// }
// }
// }
// }
void dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
dist[1] = 0;
heap.push({0, 1});
while (heap.size())
{
PII t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second, distance = t.first;
if (st[ver]) continue;
st[ver] = true;
for (int i = h[ver]; i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > distance + w[i])
{
dist[j] = distance + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
}
int find(int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]); }
void kruskal()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= (n << 1); i ++ ) p[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
tr[i].l = tr[i].r = tr[i].f[0] = 0;
tr[i].mindist = dist[i];
tr[i].weight = 0x3f3f3f3f;
}
sort(edges + 1, edges + m + 1);
cur_cnt = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
{
int pa = find(edges[i].a), pb = find(edges[i].b), w = edges[i].w, hi = edges[i].h;
if (pa != pb)
{
cur_cnt ++ ;
p[pa] = p[pb] = cur_cnt;
tr[cur_cnt].l = pa, tr[cur_cnt].r = pb;
tr[pa].f[0] = cur_cnt, tr[pb].f[0] = cur_cnt; tr[cur_cnt].f[0] = 0;
tr[cur_cnt].mindist = min(tr[pa].mindist, tr[pb].mindist);
tr[cur_cnt].weight = hi;
}
if (cur_cnt == 2 * n - 1) break;
}
}
void dfs(int u)
{
if (!u) return;
for (int k = 1; k <= 20; k ++ ) tr[u].f[k] = tr[tr[u].f[k - 1]].f[k - 1];
dfs(tr[u].l), dfs(tr[u].r);
}
LL query(int u, int p)
{
for (int k = 20; ~k; k -- )
if (tr[u].f[k] && tr[tr[u].f[k]].weight > p) u = tr[u].f[k];
return tr[u].mindist;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T -- )
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
idx = 0;
memset(h, 0, sizeof h);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
{
int a, b, w, h;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &w, &h);
edges[i] = {a, b, w, h};
add(a, b, w), add(b, a, w);
}
dijkstra(); //预处理最短路
kruskal();//建树就应该把目标函数维护好
dfs(cur_cnt); //处理倍增数组,查询用
scanf("%d%d%d", &q, &k, &s);
int lastans = 0;
while (q -- )
{
int v, p;
scanf("%d%d", &v, &p);
v = (v + k * lastans - 1) % n + 1;
p = (p + k * lastans) % (s + 1);
lastans = query(v, p);
printf("%lld\n", lastans); //v走>=p的最短路
}
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号