数独(sudoku),是一个填数字的游戏,规则简单,上到老爷爷老奶奶,下至小学生,都可以去解它,放松益脑。
一直以来就特别喜欢数独,第一次是从老爸手机上看到的,也做过不少题目。在初中的时候上发过了一本书,书的后面就有一个数独的题目,我是班上第一个也是唯一一个解出来的,十分骄傲。
最近学习了算法,发现里面的n皇后问题和数独特别的相似,感觉都可以使用回溯法在解空间树经行广度优先搜索。这种方法类似于穷举法,但并不是单纯的列举全部可能,不断的有剪枝函数减去不满足条件的子树。看到网上说一种叫做跳舞链的方法,下面的代码并不是采用这种方法,以后如果有时间可以去试一试。而我使用的是回溯法,使用语言是c语言。闲话就说到这里,下面分析一下代码。
核心内容:树的深度优先遍历
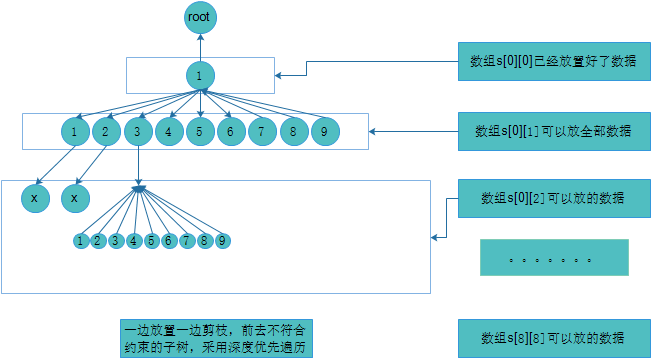
把数独想象成一个具有81层的树,然后在树上搜索剪枝。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 //定义一个二维数组sudo[9][9] 5 6 /* 7 int sudo[9][9]={ 8 { 5,7,6, -1,4,8, 1,3,-1}, 9 { -1,3,-1, -1,-1,5, -1,8,-1}, 10 { 8,2,-1, 3,-1,9, -1,-1,7}, 11 12 { 1,-1,9, -1,-1,-1, -1,-1,8}, 13 { -1,-1,3, 5,9,1, 6,-1,-1}, 14 { 7,-1,-1, -1,-1,-1, 4,-1,1}, 15 16 { 2,-1,-1, 1,-1,3, -1,4,5}, 17 { -1,1,-1, 4,-1,-1, -1,2,-1}, 18 { -1,4,7, 9,5,-1, 8,1,6,} 19 }; 20 */ 21 //测试数据1 22 int sudo[9][9]={ 23 { 1,0,0, 0,5,0, 0,0,0}, 24 { 4,0,2, 0,0,1, 0,3,0}, 25 { 8,0,0, 0,0,6, 0,1,0}, 26 27 { 0,0,0, 0,1,7, 6,0,0}, 28 { 0,0,6, 5,0,2, 4,0,0}, 29 { 0,0,7, 4,6,0, 0,0,0}, 30 31 { 0,4,0, 9,0,0, 0,0,1}, 32 { 0,9,0, 6,0,0, 7,0,5}, 33 { 0,0,0, 0,3,0, 0,0,0} 34 }; 35 36 37 int backtrack(int s[9][9],int row,int col); 38 //使用回溯法对解空间数经行深度搜索该函数就是深度搜索的函数 39 40 void showsudo(); 41 //打印当前的数独中各个格子的值 42 43 int place(int s[9][9],int t,int j); 44 //剪枝函数 45 46 int justIsRepeatIN9(int s[9][9],int x,int y,int m,int n); 47 //剪枝函数中检查3*3小块合法的的函数 48 49 50 //从二维数组的左上角开始,向右搜索 51 //row表示行号,col表示列号 52 int backtrack(int s[9][9],int row,int col){ 53 54 if(row == 9) 55 return 1; 56 //最后一个,在这之前是s[8][8];递归到最深处;成功返回 57 58 if(s[row][col] != 0){ 59 if(col == 8){ 60 row++; 61 col=0; 62 } 63 else 64 col++; 65 return backtrack(s,row,col); 66 }//如果 s[row][col]本来就有数据,需要跳过 ,分析下一个 67 68 // s[row][col]是空的,则放入1~9 69 for(int k=1;k<10;k++){ 70 s[row][col]=k; 71 if(place(s,row,col)) { 72 //判断是否合法,如果合法就分析下一个 73 if(col == 8){ 74 if(backtrack(s,row+1,0)){ 75 return 1; 76 } 77 } 78 else{ 79 if(backtrack(s,row,col+1)){ 80 return 1; 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 s[row][col] = 0; 85 //在后面的某次中发现,所有的数都有冲突,则前面的数放错了,所以需要恢复 86 } 87 //从1~9没有找到合适的数放入,之前的出错了 88 return 0; 89 } 90 91 //判断整个数独是否合法 92 int place(int s[9][9],int t,int j) 93 { 94 for(int i=0;i<9;i++) 95 { 96 if(s[t][i] == s[t][j] && i!=j){ 97 return 0 ; 98 }//判断行上没有冲突 99 if(s[i][j] == s[t][j] && i!=t){ 100 return 0 ; 101 }//判断列上没有冲突 102 } 103 104 //判断块中是否有重复的 105 int x=t%3; 106 int y=j%3; 107 /* 108 00 01 02 109 10 11 12 110 20 21 22 111 */ 112 if(x == 0 && y == 0){ 113 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t,j,t,j)){ 114 return 1; 115 } 116 else{ 117 return 0; 118 } 119 } 120 121 if(x == 0 && y == 1){ 122 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t,j-1,t,j)){ 123 return 1; 124 } 125 else{ 126 return 0; 127 } 128 } 129 130 if(x == 0 && y == 2){ 131 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t,j-2,t,j)){ 132 return 1; 133 } 134 else{ 135 return 0; 136 } 137 } 138 139 if(x == 1 && y == 0){ 140 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t-1,j,t,j)){ 141 return 1; 142 } 143 else{ 144 return 0; 145 } 146 } 147 148 if(x == 1 && y == 1){ 149 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t-1,j-1,t,j)){ 150 return 1; 151 } 152 else{ 153 return 0; 154 } 155 } 156 157 if(x == 1 && y == 2){ 158 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t-1,j-2,t,j)){ 159 return 1; 160 } 161 else{ 162 return 0; 163 } 164 } 165 166 if(x == 2 && y == 0){ 167 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t-2,j,t,j)){ 168 return 1; 169 } 170 else{ 171 return 0; 172 } 173 } 174 175 if(x == 2 && y == 1){ 176 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t-2,j-1,t,j)){ 177 return 1; 178 } 179 else{ 180 return 0; 181 } 182 } 183 184 if(x == 2 && y == 2){ 185 if(justIsRepeatIN9(s,t-2,j-2,t,j)){ 186 return 1; 187 } 188 else{ 189 return 0; 190 } 191 } 192 } 193 194 int justIsRepeatIN9(int s[9][9],int x,int y,int m,int n){ 195 //判断一个九宫格中是否有重复的数 196 //其中s是数组,x是起始的位置,y是起始是位置 197 //因为之前的数据都是有序的,并不需要判断其他的是否合法,只要判断指定的数 198 //只要知道特殊的 199 //m,n是需要判断的内容 200 for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ 201 for(int j=0;j<3;j++){ 202 if(s[x+i][y+j] == s[m][n] && x+i != m && y+j != n){ 203 return 0; 204 } 205 } 206 } 207 return 1; 208 } 209 210 //打印数独中各个格子的值 211 void showsudo() 212 { 213 for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ 214 for(int j=0;j<9;j++) 215 { 216 printf("%2d ",sudo[i][j]) ; 217 if(j%3 == 2) 218 { 219 printf(" "); 220 } 221 } 222 printf("\n"); 223 if(i%3 == 2){ 224 printf("\n"); 225 } 226 } 227 printf("\n"); 228 } 229 230 int main() 231 { 232 showsudo(); 233 backtrack(sudo,0,0) ; 234 showsudo(); 235 return 0; 236 }


