11--Java--JDBC知识梳理
JDBC
一、概述:JDBC(java database connection),使用java语言连接数据库,是java提供一套操作数据库的接口(标准),实现对数据库的统一访问,是一个java引用应用程序与数据库交互的桥梁。
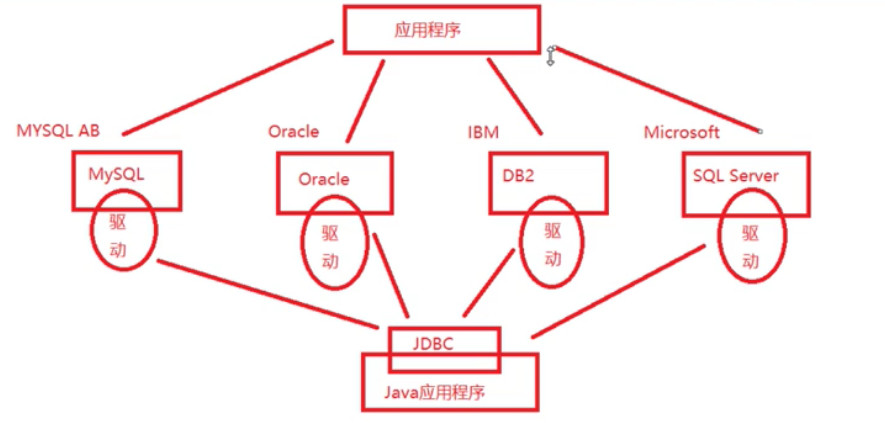
二、组成:
DriverManager类:驱动管理类,用户注册驱动,获取连接对象
Connection接口:数据库的连接对象
Statement接口:执行SQL语句,操作数据
PreparedStatement接口:执行SQL语句,操作数据
ResultSet接口:接收SQL查询结果(一张虚拟的表)

三、通过JDBC实现Query操作
第一步:在数据库中创建数据库、新建表等一系列操作。
第二步:在myeclipse中新建Web Project,创建与数据库中数据表相对应的实体类
第三步:引入数据库厂商提供的数据库对应的驱动包(.jar格式...)到项目文件夹中的WebContent/WEB INF/lib/
第四步:写代码
使用JDBC访问数据库的步骤:
1.加载数据库驱动(推荐方式二)
import java.sql.DriverManager;
方式一:DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());//不推荐
方式二:Class.forName("驱动类全称:包名+类名"); //通过反射加载驱动,此处JDBC4.0后自动加载,可不用写,但建议写。
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
2.获取数据库的连接对象(三种方式)
import java.sql.Connection;
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("url","user","password");
url:1)统一资源定位符,标识网络上的一个具体资源(一个网页,一张照片,一个视频等)
2)url格式是 协议+ip地址+端口+资源名称
jdbc:mysql :// localhost : 3306 / 数据库名称
jdbc:mysql :// 127.0.0.1 : 3306 / 数据库名称
jdbc:mysql :/// 数据库名称 (此种写法默认本机)
user:数据库用户名
password:数据库用户密码
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("Path");//path等于url+user+password
path:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名称?user = ...&password = ...
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("url",properties);
properties:属性对象
Properties p = new Properties();
p.setProperty("user","...");
p.setProperty("password","...");
3.编写SQL语句
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
1)获取SQL语句对象
Statement st = conn.CreateStatement();
2)执行SQL语句,返回结果
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from student");//执行查询SQL语句,将查询结果返回到结果集中
String sql = "delete ....";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);//执行更新(增删改)SQL语句,返回的是int型的成功执行语句条数
4.处理结果集
方式一:不建议使用
while(rs.next()){//next()获取的一张表的一行,也称一条记录
Object id = rs.getObject(1);//获取的是一张表的第一列,也称一个字段
Object name = rs.getObject(2);//第二列
Object age = rs.getObject(3);//第三列
}
方式二:方法中的参数名称需要和数据表中的字段名称一致,并且建议创建数据库中数据表的字段时不要使用中文!!!
while(rs.next()){//next()获取的一张表的一行,也称一条记录
int id = rs.getInt("学号");//获取的是一张表的第一列,也称一个字段
String name = rs.getString("姓名");//第二列
int age = rs.getInt("年龄");//第三列
//如果数据库中的Date类型,建议使用String接收
}
5.释放连接资源。
import java.sql.SQLException;
finally{ //finally意思是在结尾无论前面发生了啥,程序总会执行这段代码
if(conn != null){
try{ conn.close();
}catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}}
if(st != null){
try{ st.close();
}catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} }
if(rs != null){
try{ rs.close();
}catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} }//所有对象通通关闭
}
四、注意:
1.JDBC使用Statement会存在数据库注入问题,因此需用PrepareStatement对象来解决
String username = "1' or 1 = '1'";//设用户名
String password = "1' or 1 = '1'";//设密码
PreparedStatement pre = conn.prepareStatement("select * from student where username = ? and password = ?");//将SQL语句进行预处理,采用问号占位符的形式
pre.setString(1,username);//给第一个问号的位置赋值
pre.setString(2,password);//给第二个问号的位置赋值
ResultSet rs = pre.executeQuery();//执行赋值后的SQL语句
五、封装并调用JDBC工具类
封装工具类的代码:
1 public class JDBCfunction{ 2 //静态块 优先执行,并且只执行一次 3 static{ 4 try{ 5 //加载驱动 6 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 7 }catch(ClassNotFoundExcption e){ 8 e.printStackTrack(); 9 } 10 } 11 //连接对象 12 public static Connection getConnection(){ 13 Connection conn = null; 14 try{ 15 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/databasename","username","password"); 16 }catch(SQLExcption e){ 17 e.printStackTrack(); 18 } 19 return conn; 20 } 21 //释放连接资源 22 public static void close(Connection conn,Statement st,ResultSet rs){ 23 if(conn != null){ 24 try{ 25 conn.close(); 26 }catch(SQLExcption e){ 27 e.printStackTrack(); 28 } 29 } 30 if(st != null){ 31 try{ 32 st.close(); 33 }catch(SQLExcption e){ 34 e.printStackTrack(); 35 } 36 } 37 if(rs != null){ 38 try{ 39 rs.close(); 40 }catch(SQLExcption e){ 41 e.printStackTrack(); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 }
调用工具类的代码:(使用时需导入Import JDBCfunction所在的文件包)
1 public class UseJDBCfunction(){ 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException{ 3 //加载驱动,建立连接 4 Connection conn = JDBCfunction.getConnection(); 5 //创建预处理对象 6 PreparedStatement pre = conn.prepareStatement("select * from student"); 7 //查询 8 ResultSet rs = pre.executeQuery(); 9 //遍历输出 10 while(rs.next()){ 11 int uid = rs.getInt("uid"); 12 String username = rs.getString("username"); 13 String password = rs.getString("password"); 14 User user = new User(uid,username,password); 15 System.out.println(user); 16 } 17 //释放资源 18 JDBCfunction.close(conn,pre,rs); 19 } 20 }
六、JDBC批量操作
1.jdbc设置事务自动提交,处理异常
在连接对象conn与数据库通过用户名和密码建立连接了之后,如果后续操作有catch异常,则不让其conn对象最终对数据库进行修改。
conn.setAutoCommit(false);//设置事务是否自动提交,默认为ture,自动提交。
conn.commit();//立即提交事务,对数据库进行修改。
conn.rollback();//如果异常,事务回滚
1 public class UseJDBCfunction(){ 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException{ 3 Connection conn = null; 4 PrepareStatement pre = null; 5 try{ 6 //加载驱动,建立连接 7 conn = JDBCfunction.getConnection(); 8 conn.setAutoCommit(false);//禁止自动提交事务 9 //创建预处理对象 10 pre = conn.prepareStatement("insert into user(username,password) value(?,?)"); 11 pre.setString(1,"xiaoming"); 12 pre.setString(2,"123"); 13 //更新 14 int update = pre.executeUpdate(); 15 if(update > 0){ 16 System.out.println("添加成功"); 17 conn.commit();//提交事务 18 } 19 }catch(SQLException e){ 20 e.printTrackTrace(); 21 try{ 22 conn.rollback();//出现异常,事务回滚 23 }catch(SQLException e){ 24 e.printTrackTrace();26 } 27 } 28 //释放资源 29 JDBCfunction.close(conn,pre,rs); 30 } 31 }
2.jdbc批量添加
在给预处理对象赋值时,采用pre.addBatch();的方式,对数据库语句中的问号进行批量添加操作
1 public class UseJDBCfunction(){ 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException{ 3 Connection conn = null; 4 PrepareStatement pre = null; 5 try{ 6 //加载驱动,建立连接 7 conn = JDBCfunction.getConnection(); 8 conn.setAutoCommit(false);//禁止自动提交事务 9 //创建预处理对象 10 pre = conn.prepareStatement("insert into user(username,password) value(?,?)"); 11 pre.addBatch(); 12 pre.setString(1,"m1"); 13 pre.setString(2,"123"); 14 15 pre.addBatch(); 16 pre.setString(1,"m2"); 17 pre.setString(2,"1234"); 18 19 pre.addBatch(); 20 pre.setString(1,"m3"); 21 pre.setString(2,"12345"); 22 //...... 23 24 //更新(这是没用批量操作的写法) 25 //int update = pre.executeUpdate(); 26 //更新(用批量操作的写法,返回的是一个数组,因为数据库添加了多条数据) 27 int[] executeBatch = pre.executebatch(); 28 if(executeBatch.length > 0){ 29 System.out.println("添加成功"); 30 conn.commit();//提交事务 31 } 32 }catch(SQLException e){ 33 e.printTrackTrace(); 34 try{ 35 conn.rollback();//出现异常,事务回滚 36 }catch(SQLException e){ 37 e.printTrackTrace();26 } 38 } 39 //释放资源 40 JDBCfunction.close(conn,pre,rs); 41 } 42 }





