Vue — VueX
一、VueX概述
1.概述:
vuex是一个vue的状态管理工具,状态就是数据;可以帮助我们管理vue通用的数据(多组件共享的数据)
2.场景:
(1)某个状态在很多个组件中使用 例如 个人信息
(2)多个组件共同维护一份数据 例如 购物车
3.优势:
(1)共同维护一份数据,数据集中化管理
(2)响应式变化
(3)操作简单(vuex提供了函数方法)
二、构建VueX【多组件数据共享】
1.创建项目 vue create app
2.创建一个空仓库
(1)安装vuex vue2.0安装vuex@3 vue3.0安装vuex@4
npm i vuex@3
(2)新建vuex模块文件
(3)创建仓库
//引入核心包 import Vuex from 'vuex' import Vue from 'vue' //插件注册 Vue.use(Vuex) //创建仓库
export default store
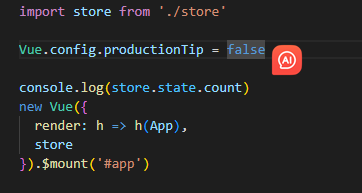
(4)main.js导入挂载
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import store from './store' Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ render: h => h(App), store }).$mount('#app')
三、使用store仓库
1.state状态
(1)提供数据:
State提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到Store中的State存储。在state对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据。
(2)使用数据:
-通过store直接访问(模板中、组件逻辑中、js中)
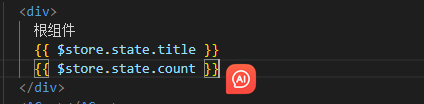
-通过辅助函数简化
![]()
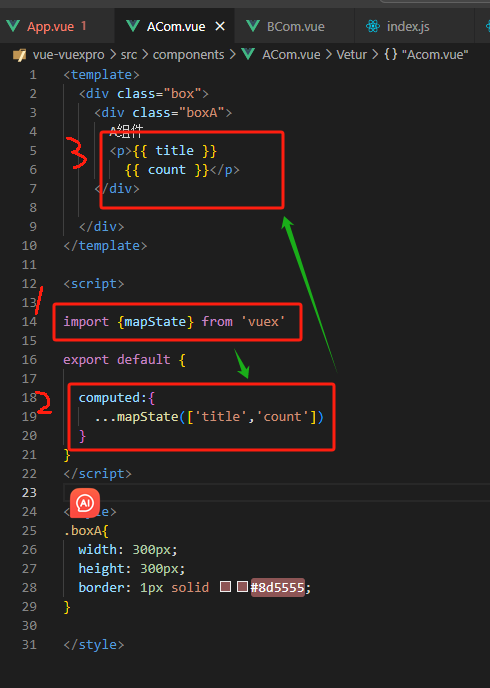
<template> <div class="box"> <div class="boxA"> A组件 <p>{{ title }} {{ count }}</p> </div> </div> </template> <script> import {mapState} from 'vuex' export default { computed:{ ...mapState(['title','count']) } } </script>
(3)修改数据 (mutations)
vuex同样遵循单项数据流,组件中不能直接修改仓库的值
2.mutations
(1)定义mutations对象,对象中存放修改state的方法
const store = new Vuex.Store({ strict : true, state : { title : '共享标题', count : 100 }, mutations : { //第一个参数是state addCount(state){ state.count+=1 } } })
(2)组件中提交调用mutation
<button @click="add">count+1</button> add(){ this.$store.commit("addCount") }
(3)传参 只能额外传递一个参数
mutations : { //第一个参数是state addCount(state,n){ state.count+=n } }
<button @click="add(1)">count+1</button> <button @click="add(5)">count+5</button> <button @click="add(10)">count+10</button> <button @click="add(20)">count+20</button> this.$store.commit("addCount",n)
(3)mapMutations(映射store的方法)
import {mapState,mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['title','count'])
},
methods :{
...mapMutations(['addCount','reduceCount'])
}
}
<button @click="addCount(20)">count+20</button> <button @click="reduceCount(20)">count-20</button>
3.actions (处理异步操作)
mutationa是同步的
(1)提供action方法
const store = new Vuex.Store({ strict : true, state : { title : '共享标题', count : 100, number : 66 }, mutations : { //第一个参数是state addCount(state,n){ state.count+=n }, reduceCount(state,n){ state.count-=n }, changeNum(state,num){ state.number = num }, }, actions : { //处理异步,不能直接操作state //context:上下文 没有分模块,可以当做store仓库 //context.commit('mutations名字',参数) changeCountAsync(context,num){ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('changeNum',num) },2000) } } })
(2)页面中dispath调用
<button @click="changeAsync">异步</button> methods :{ changeAsync(){ this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAsync','8') } }
(3)mapActions(映射actions的方法,映射到组件的methods)
<button @click="changeCountAsync(9999999)">异步</button> <script> import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { computed: { ...mapState(['title', 'count']) }, methods: { ...mapMutations(['addCount', 'reduceCount']), ...mapActions(['changeCountAsync']) } } </script>
4.getters(类似计算属性)
除了state,我们还需要从state中派生出一些状态,这些状态是依赖state的,此时会用到getters
(1)定义getters
getters : { //形参第一个参数就是state //必须有返回值 返回值就是getters的值 filterList(state){ return state.list.filter(item=>item>5) } }
(2)访问getters
<ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in $store.getters.filterList" :key="index">{{ item }}</li> </ul>
(3)mapGetters
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions ,mapGetters} from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapState(['title', 'count','list']),
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
},
<li v-for="(item,index) in filterList" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>


