Day10 API
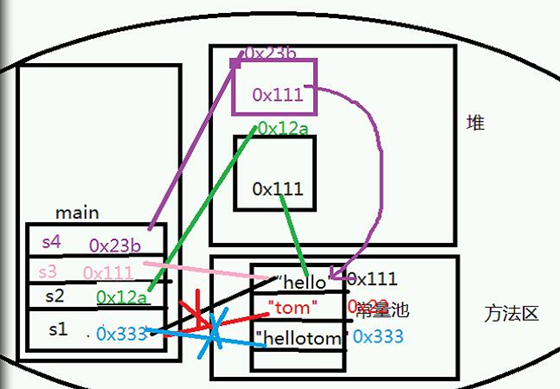
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello";//到常量池里找对象 String s2 = new String("hello"); s1 = "Tom"; s1 = "hello"+"Tom"; String s3 = "hello"; String s4 = new String("hello"); // ==判断是否为同一对象,判断内存地址 System.out.println(s1==s2);//false System.out.println(s2==s4);//false System.out.println(s1==s3);//false s1 = "hello"; System.out.println(s1==s3);//true }
字符串连接,返回连接后的串
1 String s1 = "hello"; 2 //concat 字符串连接,返回连接后的串 3 s1 = s1.concat("tom"); 4 System.out.println(s1);//hellotom
字符串长度
System.out.println(s1.length());
比较字符序列是否相同,区分大小写
String s2 = "hellotom"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
比较字符序列是否相同,不区分大小写
String s3 = "HEllotom"; System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));
大写兼容,全部转为大写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
小写兼容,全部转为小写
System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());
首次出现的位置索引,没有返回-1
s1 = "hellohellotom"; System.out.println(s1.indexOf("hello")); System.out.println(s1.indexOf("abc"));
最后一次出现的位置索引
System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf("hello"));
取出某一个位置的字符
System.out.println(s1.charAt(0));//h
取字符串
//取子串(起始位置)取到最后 System.out.println(s1.substring(10));//tom //[起始位置,终止位置) 不包括终止位置 System.out.println(s1.substring(10, 13));//tom
去除字符串的首尾空格
s1 = " h e l l o t o m "; System.out.println(s1);// h e l l o t o m System.out.println(s1.trim());//h e l l o t o m
字符串替换(旧串,新串)用新串替换旧串
s1 = "hellotom"; System.out.println(s1.replace(s1, "你好"));//你好 //去掉是s1串中的所有空格 s1 = " h e l l o t om "; System.out.println(s1.replace(" ", ""));//hellotom
判断是否以某个字符串结尾,是true,否false
s1 = "hello.java"; System.out.println(s1.endsWith("java"));//true
startsWith
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("he"));//true
字符串比较大小
s1 = "abc"; //unicode s1在参数之前,返回负数,s1在参数之后,返回正数,相对返回0 System.out.println(s1.compareTo("cc"));//-2 System.out.println(s1.compareTo("aa"));//1 System.out.println(s1.compareTo("abc"));//0
是否包含指定参数的字符串,包含true,不包含false
System.out.println(s1.contains("bc"));//true
把字符串转换成字符数组
char[] c = s1.toCharArray();//'a','b','c' for(char cc:c) { System.out.print("字符:"+cc);//字符:a字符:b字符:c }
用某个字符串把原始字符串分割为一个字符串数组
s1 = "aa bb cc dd ee"; String[] strs = s1.split(" ");//"aa","bb","cc","dd","ee" for(String ss : strs) { System.out.print("元素:"+ss);//元素:aa元素:bb元素:cc元素:dd元素:ee }

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 // String 常用的方法 3 String s1 = "hello"; 4 /* System.out.println(s1);//hello 5 s1 = s1 + "tom";// "hellotom" 6 */ 7 //连接字符串,返回连接后的串 8 s1 = s1.concat("tom");//"hellotom" 9 System.out.println(s1);//"hellotom" 10 //字符串长(字符序列的个数) 11 System.out.println(s1.length());//8 12 //equals比较字符序列是否相同 相同 true 区分大小写 13 String s2 = "hellotoM"; 14 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//fasle 15 //忽略大小写 16 System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); 17 //大小写兼容 18 //大写 19 System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase()); 20 //小写 21 System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase()); 22 // zhangsan@163.com 23 // 0123------------------------------------ 24 s1 = "hellohellotom"; 25 //位置索引 26 //首次出现的位置索引 ,没有返回 -1 27 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("hello"));// 0 28 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("@"));//-1 29 //最后一次出现的位置索引 30 System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf("hello"));//5 31 //取出 某一个 位置 的字符 32 System.out.println(s1.charAt(0));//'h' 33 //取 子串 (起始位置) 取到最后 34 System.out.println(s1.substring(10));//"tom" 35 //[起始位置,终止位置) 不包括终止位置 36 System.out.println(s1.substring(10, 13)); 37 //---------------------------------------- 38 s1 = " h e l l o tom "; 39 //去除字符串 的 首尾 空格 40 System.out.println(s1.trim()); 41 // 42 s1 = "hellotom"; 43 //字符串 替换 (旧串,新串) 用新串 替换 旧串 44 System.out.println(s1.replace("hello","你好"));//"hello"->“你好” 45 s1 = " h e l l o t om "; 46 //问题:去掉 s1串 中的 所有空格 47 System.out.println(s1.replace(" ", "")); 48 // 49 s1 = "hello.java"; 50 //判断 是否 以 某个 字符串 结尾 是 true 51 System.out.println(s1.endsWith("java"));//true 52 //判断 是否 以 某个 字符串 开头 是 true 53 System.out.println(s1.startsWith("he"));//true 54 //字符串 比较大小 55 s1 = "abc"; 56 //unicode s1 在 参数之前 ,返回 负数 ,s1 在参数后 ,返回正数,相等 返回0 57 System.out.println(s1.compareTo("cc"));//-2 58 System.out.println(s1.compareTo("aa"));//1 59 System.out.println(s1.compareTo("abc"));//0 60 //----------------------------------------- 61 //是否 包含 指定参数 的字符串 ,包含 true 62 System.out.println(s1.contains("ab")); 63 //把 字符串 转换成字符数组 64 char [] c = s1.toCharArray();// 'a','b','c' 65 for(char cc :c) { 66 System.out.println("字符:"+cc); 67 } 68 // 69 s1 = "aa bb cc dd ee"; 70 //用某个 字符串 把原始字符串 分割为 一个 字符串数组 71 String [] strs = s1.split(" ");//"aa","bb","cc","dd","ee" 72 for(String ss:strs) { 73 System.out.println("元素:"+ss); 74 } 75 76 77 78 }
如果频繁更改字符串的值,不要用String类,效率低,用变长字符串类StringBuffer和StringBuilder类
返回容量
StringBuffer sf1 = new StringBuffer(); //具备16个字符的缓冲区 System.out.println(sf1.capacity());//16 StringBuffer sf2 = new StringBuffer("hello"); System.out.println(sf2.capacity());//21=16+5 //直接规定缓冲区大小 StringBuffer sf3 = new StringBuffer(100); System.out.println(sf3.capacity());//100
追加字符串
StringBuffer sf = new StringBuffer(50); sf.append("hello"); System.out.println(sf);//hello char[] c = {'a','b','c'}; sf.append(c,1,2);//bc System.out.println(sf);//hellobc
缩小容量为我存储的字符的个数大小
System.out.println(sf.capacity());//50 sf.trimToSize(); System.out.println(sf.capacity());//7
向索引位置插入一个字符串
System.out.println(sf);//hellobc sf.insert(5, "你好"); System.out.println(sf);//hello你好bc
修改指定位置的一个字符
sf.setCharAt(5, '您'); System.out.println(sf);//hello您好bc
删除指定位置索引的一个字符
sf.deleteCharAt(5); System.out.println(sf);//hello好bc
删除指定范围的字符串[起始位置,终止位置),不包括终止位置
sf.delete(5, 8); System.out.println(sf);//hello
获取指定索引处的字符
System.out.println(sf.charAt(1));//e
首次出现的位置索引,没有返回-1
System.out.println(sf.indexOf("l"));//2
最后一次出现的位置索引
System.out.println(sf.lastIndexOf("l"));//3
反转
System.out.println(sf);//hello sf.reverse(); System.out.println(sf);//olleh
String类与StringBuffer类之间的转换
String str = sf.toString(); StringBuffer sfr = new StringBuffer(str);

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 // StringBuffer StringBuilder 3 //String 不可变类 4 //如果频繁 更改字符串的值,不要用String效率低,用 变 长字符串类 StringBuffer StringBuilder 5 //StringBuffer 6 StringBuffer sf1 = new StringBuffer(); 7 //具备 16个字符的缓冲区 8 System.out.println(sf1.capacity());//16 9 StringBuffer sf2 = new StringBuffer("hello"); 10 //容量 11 System.out.println(sf2.capacity());//21 12 sf2.append("aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa"); 13 System.out.println(sf2.capacity());// 14 15 StringBuffer sf3 = new StringBuffer(100); 16 System.out.println(sf3.capacity()); 17 18 //----------------StringBuffer-------------------------------- 19 StringBuffer sf = new StringBuffer(50); 20 //容量 21 System.out.println(sf.capacity()); 22 //追加字符串的 23 sf.append("hello"); 24 char[] c = {'a','b','c'}; 25 sf.append(c, 1, 2);//bc 26 System.out.println(sf);//"hellobc" 27 28 System.out.println(sf.capacity()); 29 //缩小容量为 我 存储的字符的个数大小 30 sf.trimToSize(); 31 System.out.println(sf.capacity()); 32 System.out.println(sf);//"hellobc"// 33 //向 索引 位置 插入一个字符串 34 sf.insert(5, "你好");//"hello你好bc" 35 System.out.println(sf); 36 //修改 指定位置的一个 字符 37 sf.setCharAt(5, '您');//"hello您好bc" 38 System.out.println(sf); 39 //删除 指定 位置索引的 一个 字符 40 sf.deleteCharAt(5);//"hello好bc" 41 System.out.println(sf); 42 //删除 指定 范围 的字符串 【起始位置,终止位置)不包括 终止位置 43 sf.delete(5, 8); 44 System.out.println(sf);//"hello" 45 46 System.out.println(sf.charAt(1));//e 47 System.out.println(sf.indexOf("l"));//2 48 System.out.println(sf.lastIndexOf("l"));//3 49 50 //------------其它---------------------- 51 sf.reverse(); 52 System.out.println(sf); 53 String str = sf.toString();//StringBuffer -> String 54 //String - > StingBuffer 55 StringBuffer sfr = new StringBuffer(str); 56 //----------------------------------------------------- 57 /* 58 * String:定长字符串类,不可变类,表示一个简单的字符串 用 String 59 * 但是,如果 字符串的值大量更改频繁更改 ,选择StringBuffer,StringBuilder 60 * StringBuffer :线程安全的,数据准确,但速度慢 61 * StringBuilder:线程非安全的,多线程环境下数据不准确,但是速度快。 62 */ 63 //-------------------------------------------------- 64 }
StringBuffer:线程安全的,数据准确,但速度慢
StringBuilder:线程非安全的,多线程环境下数据不准确,但是速度快
正则表达式
用某种模式去匹配指定字符串的一种表达方式。
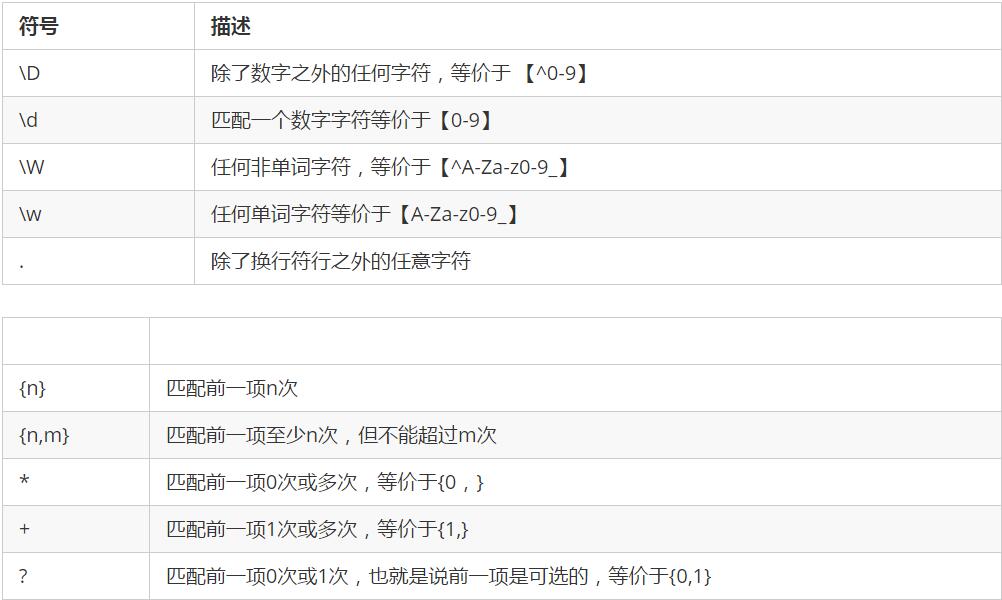
语法
表达式的模式:Matcher matcher = p.matcher();
验证:matcher.matches()
public static void main(String[] args) { //正则验证:邮政编码必须6位 //1.指定正则表达式[0-9]{6}或\\d{6} Pattern p =Pattern.compile("[0-9]{6}"); //2.指定要验证的数据 Matcher m = p.matcher("123456"); //3.验证 System.out.println(m.matches());//格式验证true }
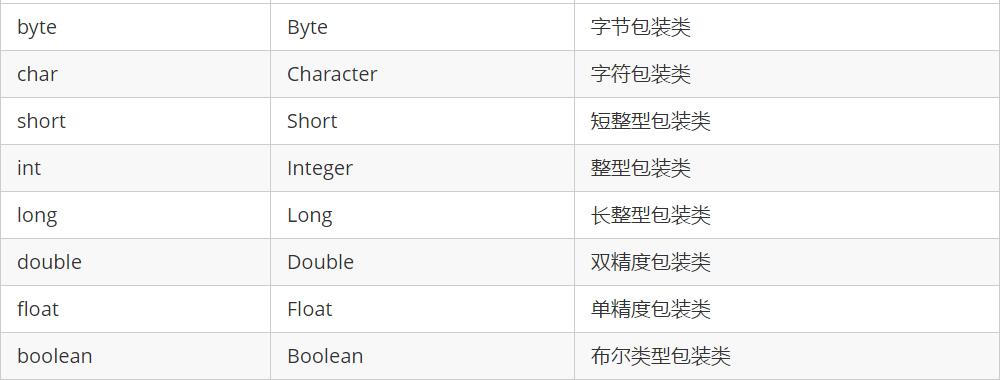
作用
2.提供了更加丰富的功能。



