Spring中使用事务搭建转账环境 转账操作,
演示不使用事务出现异常情况
Dao层两个方法lessMoney()和moreMoney()
package com.swift; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; public class AccountDao { private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } //少钱的方法 public void lessMoney(String from,double number) { String sql="update account set money=money-? where username=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, number,from); } //多钱的方法 public void moreMoney(String to,double number) { String sql="update account set money=money+? where username=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, number,to); } }
Service层调用两个方法
package com.swift; public class AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } public void moneyTransfer(String from,String to,double number) { accountDao.lessMoney(from,number); int i=10/0; accountDao.moreMoney(to,number); } }
但是两个操作减与加之间,如果出现异常,则会导致转账钱已经转了,但对方却没有到账的bug,可能服务器突然故障等引起
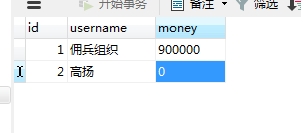
解决添加事务,出现异常进行回滚操作
下面使用配置文件的方法进行事务管理
没有改变的测试类
package com.swift; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; @WebServlet("/test") public class ServletTest extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public ServletTest() { super(); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); response.getWriter().append("Served at: ").append(request.getContextPath()); //使用JdbcTemplat的queryForObject方法 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("c3p0.xml"); AccountService accountService= (AccountService) context.getBean("accountService"); accountService.moneyTransfer("佣兵组织", "高扬", 100000); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
使用配置文件进行事务处理步骤如下:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <!-- c3p0连接池得到dataSource --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sw_database"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </bean> <!-- 第一步 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 注入dataSource --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 第二步 配置事务增强 --> <tx:advice id="txadvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <!-- 做事务操作 --> <tx:attributes> <!-- 事务操作的方法匹配规则 --> <tx:method name="money*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 第三步 配置切面 --> <aop:config> <!-- 切入点 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.swift.AccountService.*(..))" id="pointcut1"/> <!-- 切面 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/> </aop:config> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.swift.AccountDao"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property> </bean> <bean id="accountService" class="com.swift.AccountService"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property> </bean> </beans>
分三个步骤 管理 增强和切面
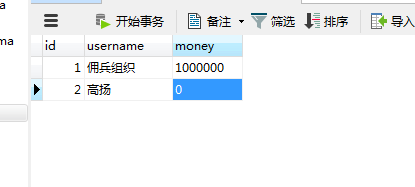
虽然还是会有异常,但是数据库中不会出错,不会钱转出了,却没有到账
工具类Account
package com.swift; public class Account { private int id; private String username; private String money; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(String money) { this.money = money; } public Account(int id, String username, String money) { this.id = id; this.username = username; this.money = money; } public Account() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public String toString() { return "Account [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", money=" + money + "]"; } }
Spring事务中的传播行为如下:
Require:支持当前事务,如果没有事务,就建一个新的,这是最常见的;
Supports:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行;
Mandatory:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常;
RequiresNew:新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起;
NotSupported:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把事务挂起;
Never:以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
Nested:新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。与RequireNew的区别是与父事务相关,且有一个savepoint。
其中,Require、Supports、NotSupported、Never两个看文字也就能了解,就不多说了。而Mandatory是要求所有的操作必须在一个事务里,较Require来说,对事务要求的更加严格。
RequireNew:当一个Require方法A调用RequireNew方法B时,B方法会新new一个事务,并且这个事务和A事务没有关系,也就是说B方法出现异常,不会导致A的回滚,同理当B已提交,A再出现异常,B也不会回滚。
Nested:这个和RequireNew的区别是B方法的事务和A方法的事务是相关的。只有在A事务提交的时候,B事务都会提交。也就是说当A发生异常时,A、B事务都回滚,而当B出现异常时,B回滚,而A回滚到savepoint;
Spring事务的隔离级别,事务隔离级别如下:
Serializable:最严格的级别,事务串行执行,资源消耗最大;
Repeatable Read:保证了一个事务不会修改已经由另一个事务读取但未提交(回滚)的数据。
Read Committed:大多数主流数据库的默认事务等级,保证了一个事务不会读到另一个并行事务已经修改但未提交的数据。适用于大多数系统。
Read Uncommitted:保证了读取过程中不会读取到非法数据。
想要理解这四个级别,还需要知道三种不讨人喜欢的事情:
dirty reads:脏读,就是说事务A未提交的数据被事务B读走,如果事务A失败回滚,将导致B所读取的数据是错误的。
non-repeatable reads:不可重复读,就是说事务A中两处读取数据,第一次读时是100,然后事务B把值改成了200,事务A再读一次,结果就发现值变了,造成A事务数据混乱。
phantom read:幻读,和不可重复读相似,也是同一个事务中多次读不一致的问题。但是不可重复读的不一致是因为它所要取的数据集被改变了,而幻读所要读的数据不一致却不是他所要读的数据改变,而是它的条件数据集改变。比如:Select id where name="ppgogo*",第一次读去了6个符合条件的id,第二次读时,由于事务B把第一个贴的名字由"dd"改成了“ppgogo9”,结果取出来7个数据。


