[react] react 16 新特性
16.0
一、render
支持返回这五类:React elements, 数组,Fragments,Portal,String/numbers,boolean/null。
class Example extends React.Component {
render() {
return [
<div key="1">first element</div>,
<div key="2">second element</div>,
];
}
}
二、Error boundary(错误边界)
用于捕获子组件树的JS异常。
捕获范围:
- 渲染期间
- 生命周期内
- 整个组件树构造函数内
使用范围:
- 可以放在顶层,告诉用户有东西出错。但是这感觉失去了错误边界的意义。因为有一个组件出错了,其他正常的也没办法正常显示了
- 包在子组件外面,保护其他应用不崩溃。
// 先定一个组件ErrorBoundary
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { error: null, errorInfo: null };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// Catch errors in any components below and re-render with error message
this.setState({
error: error,
errorInfo: errorInfo
})
// You can also log error messages to an error reporting service here
}
render() {
// 有错误的时候展示回退
if (this.state.errorInfo) {
// Error path
return (
<div>
<h2>Something went wrong.</h2>
<details style={{ whiteSpace: 'pre-wrap' }}>
{this.state.error && this.state.error.toString()}
<br />
{this.state.errorInfo.componentStack}
</details>
</div>
);
}
// 正常的话,直接展示组件
return this.props.children;
}
}
class BuggyCounter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { counter: 0 };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
componentWillMount() {
throw new Error('I am crash');
}
handleClick() {
this.setState(({counter}) => ({
counter: counter + 1
}));
}
render() {
if (this.state.counter === 5) {
// Simulate a JS error
throw new Error('I crashed!');
}
return <h1 onClick={this.handleClick}>{this.state.counter}</h1>;
}
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<p>
<b>
This is an example of error boundaries in React 16.
<br /><br />
Click on the numbers to increase the counters.
<br />
The counter is programmed to throw when it reaches 5. This simulates a JavaScript error in a component.
</b>
</p>
<hr />
<ErrorBoundary>
<p>These two counters are inside the same error boundary. If one crashes, the error boundary will replace both of them.</p>
<BuggyCounter />
</ErrorBoundary>
<hr />
</div>
);
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root')
);
Error Boundary无法捕获下面的错误
- 事件函数里的错误
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { error: null };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
try {
// Do something that could throw
} catch (error) {
this.setState({ error });
}
}
render() {
if (this.state.error) {
return <h1>Caught an error.</h1>
}
return <div onClick={this.handleClick}>Click Me</div>
}
}
handleClick方法里面发生的错误,Error Boundary是捕获不到的。因为它不发生在渲染阶段,所以采用try/catch来捕获。
- 异步代码
(例如setTimeout 或 requestAnimationFrame 回调函数)
class A extends React.Component {
render() {
// 此错误无法被捕获,渲染时组件正常返回 `<div></div>`
setTimeout(() => {
throw new Error('error')
}, 1000)
return (
<div></div>
)
}
}
-
服务端渲染
因为服务器渲染不支持Error Boundary -
Error Boundary自身抛出来的错误 (而不是其子组件)
三、react portal
Portal可以帮助我们在JSX中跟普通组件一样直接使用dialog, 但是又可以让dialog内容层级不在父组件内,而是显示在独立于原来app在外的同层级组件。
如何使用:
HTML:
<div id="app-root"></div>
// 这里为我们定义Dialog想要放入的位置
<div id="modal-root"></div>
JS:
// These two containers are siblings in the DOM
const appRoot = document.getElementById('app-root');
const modalRoot = document.getElementById('modal-root');
// Let's create a Modal component that is an abstraction around
// the portal API.
class Modal extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// Create a div that we'll render the modal into. Because each
// Modal component has its own element, we can render multiple
// modal components into the modal container.
this.el = document.createElement('div');
}
componentDidMount() {
// Append the element into the DOM on mount. We'll render
// into the modal container element (see the HTML tab).
// 这边会将我们生成的portal element插入到modal-root里。
modalRoot.appendChild(this.el);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// Remove the element from the DOM when we unmount
modalRoot.removeChild(this.el);
}
render() {
// Use a portal to render the children into the element
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
// Any valid React child: JSX, strings, arrays, etc.
this.props.children,
// A DOM element
this.el,
);
}
}
// The Modal component is a normal React component, so we can
// render it wherever we like without needing to know that it's
// implemented with portals.
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {showModal: false};
this.handleShow = this.handleShow.bind(this);
this.handleHide = this.handleHide.bind(this);
}
handleShow() {
this.setState({showModal: true});
}
handleHide() {
this.setState({showModal: false});
}
render() {
// Show a Modal on click.
// (In a real app, don't forget to use ARIA attributes
// for accessibility!)
const modal = this.state.showModal ? (
//注意~~~~~~~~~~~~~这里可以自行加上这个调试
// <Modal>
<div className="modal">
<div>
With a portal, we can render content into a different
part of the DOM, as if it were any other React child.
</div>
This is being rendered inside the #modal-container div.
<button onClick={this.handleHide}>Hide modal</button>
</div>
//</Modal>
) : null;
return (
<div className="app">
This div has overflow: hidden.
<button onClick={this.handleShow}>Show modal</button>
{modal}
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, appRoot);
使用portal之后,modal不再嵌在app-root里。
四、自定义DOM属性
React 15:忽略未标准化的html 和 svg属性
React 16:去掉了这个限制
去除的原因是:
不能用自定义属性,对于非标准(proposal阶段)新属性还有其他框架(Angular)很不友好. React 15之所以可以过滤掉非标准的属性,是因为维护了一个白名单的文件(放在bundle size 里)。而随着时间的增加,标准化的属性越来越多,意味着要一直维护这个文件,同时这个文件也会越来越大,增加bundle的体积。
<h1 mycustomattribute="hello">Hello, world!</h1>
五、优化SSR
- 生成更简洁的HTML
- 宽松的客户端一致性校验
- 无需提前编译
- react 16服务端渲染速度更快
- 支持流式渲染
1、生成更简洁的HTML
下面的HTML,react 15与react 16的服务端分别会生成什么。
renderToString(
<div>
This is some <span>server-generated</span> <span>HTML.</span>
</div> );
react15:
有data-reactid, text noded ,react-text各种属性。
<div data-reactroot="" data-reactid="1"
data-react-checksum="122239856">
<!-- react-text: 2 -->This is some <!-- /react-text -->
<span data-reactid="3">server-generated</span>
<!-- react-text: 4--> <!-- /react-text -->
<span data-reactid="5">HTML.</span>
</div>
react 16:
增加易读性,同时很大程度上减少html的文件大小。
<div data-reactroot="">
This is some <span>server-generated</span>
<span>HTML.</span>
</div>
2、宽松的客户端一致性校验
react 15:会将SSR的结果与客户端生成的做一个个字节的对比校验 ,一点不匹配发出warning同时就替换整个SSR生成的树。
react 16:对比校验会更宽松一些,比如,react 16允许属性顺序不一致,而且遇到不匹配的标签,还会做子树的修改,不是整个替换。
注意点: react16不会自动fix SSR 属性跟client html属性的不同,但是仍然会报warning,所以需要自己手动去修改。
3、无需提前编译
react 15:如果直接使用SSR,会有很多需要检查process.env的地方,但是读取在node中读取process.env是很消耗时间的。所以在react 15的时候,需要提前编译,这样就可以移除 process.env的引用。
react 16:只有一次检查process.env的地方,所以就不需要提前编译了,可以开箱即用。
4、react 16服务端渲染速度更快
react 15下,server client都需要生成vDOM,但是其实在服务端, 当使用renderToString的时候,生成的vDom就会被立即抛弃掉, 所以在server端生成vDom是没有意义的。
5、支持流式渲染 (renderyToNodeStream)
使用流式渲染会提升首个字节到(TTFB)的速度。
流式渲染可以理解为内容以一种流的形式传给前端。
所以在下一部分的内容被生成之前,开头的内容就已经被发到浏览器端了。
这样浏览器就可以更早的编译渲染文件内容。
// using Express
import { renderToNodeStream } from "react-dom/server"
import MyPage from "./MyPage"
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.write("<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>My Page</title></head><body>");
res.write("<div id='content'>");
const stream = renderToNodeStream(<MyPage/>);
stream.pipe(res, { end: false });
stream.on('end', () => {
res.write("</div></body></html>");
res.end();
});
});
React 15:
// server:
// using Express client
import { renderToString } from "react-dom/server"
import MyPage from "./MyPage"
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.write("<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>My Page</title></head><body>");
res.write("<div id='content'>");
res.write(renderToString(<MyPage/>));
res.write("</div></body></html>");
res.end();
});
// client
import { render } from "react-dom"
import MyPage from "./MyPage"
render(<MyPage/>, document.getElementById("content"));
React 16:
其实就是把client端的render改成hydrate。
现在依然兼容render,但是17之后不再兼容,所以还是直接用hydrate好一点。
// client
import { hydrate } from "react-dom"
import MyPage from "./MyPage"
hydrate(<MyPage/>, document.getElementById("content"));
注意事项:不支持ErrorBoundary 跟Portal,所以需要直出的页面就不能用了。
六、减小了32%bundle的体积
React 库大小从 20.7kb(压缩后 6.9kb)降低到 5.3kb(压缩后 2.2kb)
ReactDOM 库大小从 141kb(压缩后 42.9kb)降低到 103.7kb(压缩后 32.6kb)
React + ReactDOM 库大小从 161.7kb(压缩后 49.8kb)降低到 109kb(压缩后 43.8kb)
七、Fiber
v16.1
react-call-return
v16.2
Fragement
React 15:render函数只能接受一个组件,所以一定要外层包一层
React16:可以通过Fragement直接返回多个组件。
Some text.
<h2>A heading</h2>
More text.
<h2>Another heading</h2>
Even more text.
React 15:
- 数组里的子节点必须要用逗号分离
- 数组里的子节点必须要带key防止warning
- string类型要用双引号
render() {
return [
"Some text.",
<h2 key="heading-1">A heading</h2>,
"More text.",
<h2 key="heading-2">Another heading</h2>,
"Even more text."
];
}
React16:
render() {
return (
// Extraneous div element :(
<Fragement>
Some text.
<h2>A heading</h2>
More text.
<h2>Another heading</h2>
Even more text.
</Fragement>
);
}
render() {
return (
<>
<ChildA />
<ChildB />
<ChildC />
</>
);
}
<> </> 不支持写入属性,包括keys。如果需要key,可以直接使用<Fragment> (但是Fragment目前也只接受key这一个属性,将来会支持更多)
function Glossary(props) {
return (
<dl>
{props.items.map(item => (
// Without the `key`, React will fire a key warning
<Fragment key={item.id}>
<dt>{item.term}</dt>
<dd>{item.description}</dd>
</Fragment>
))}
</dl>
);
}
16.3
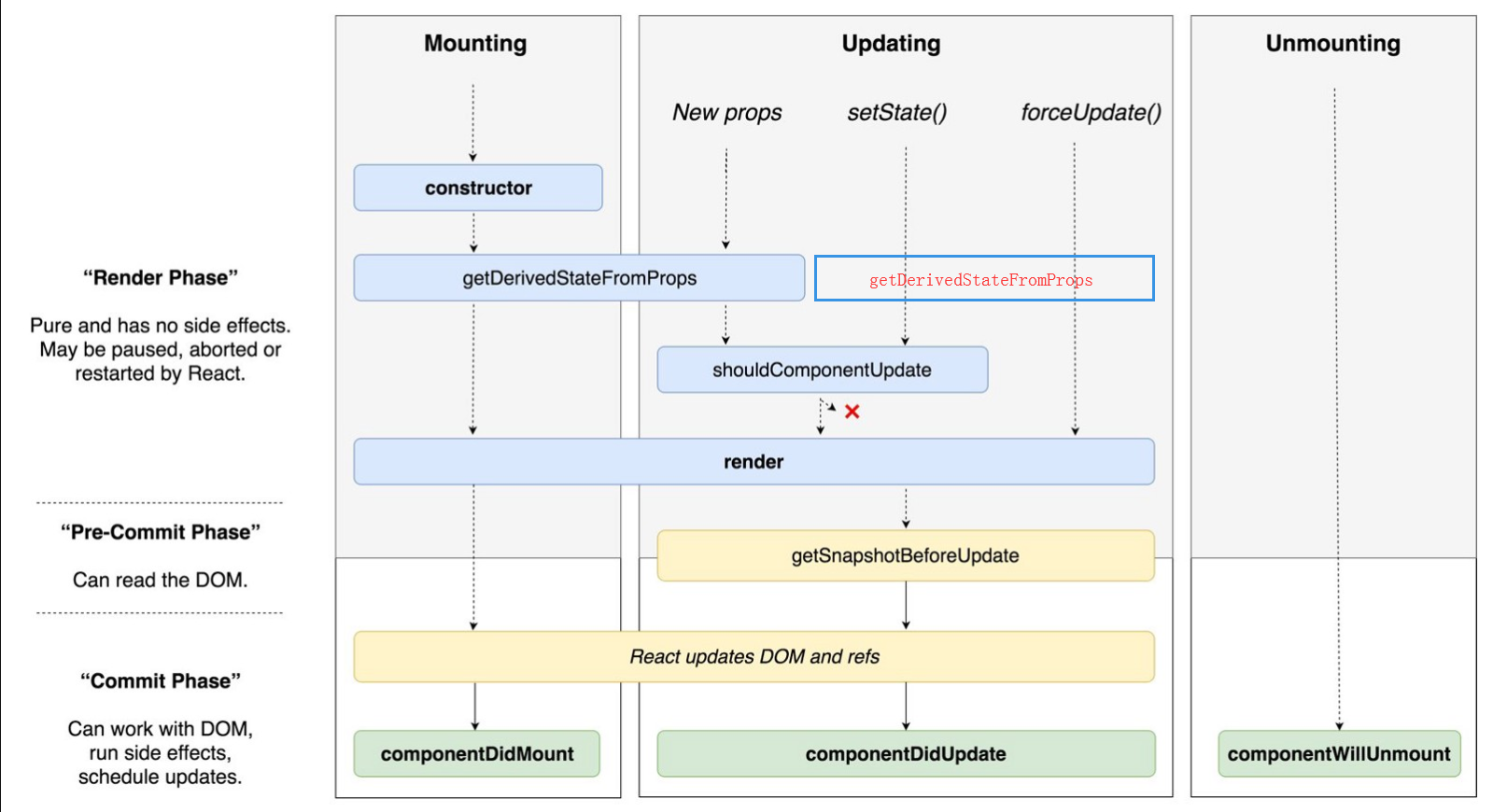
一、新的生命周期函数
由于异步渲染的改动,componentWillMount, componentWillReceiveProps,componentWillUpdate 三个函数将被废弃。
由于这是一个很大的改变会影响很多现有的组件,所以需要慢慢的去改。
目前react 16 只是会报warning,在react 17就只能在前面加UNSAFE_ 的前缀来使用。
可以使用rename-unsafe-lifecycles辅助.
getDerivedStateFromProps
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state)在调用render方法之前调用,无论是在初始安装还是后续更新。它应返回一个对象来更新状态,或者返回null以不更新任何内容。
根据props更新state
这个生命周期可用于替代componentWillReceiveProps
// Before
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
isScrollingDown: false,
};
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
if (this.props.currentRow !== nextProps.currentRow) {
this.setState({
isScrollingDown:
nextProps.currentRow > this.props.currentRow,
});
}
}
}
// After
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {
// Initialize state in constructor,
// Or with a property initializer.
state = {
isScrollingDown: false,
lastRow: null,
};
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
if (props.currentRow !== state.lastRow) {
return {
isScrollingDown: props.currentRow > state.lastRow,
lastRow: props.currentRow,
};
}
// Return null to indicate no change to state.
return null;
}
}
props更改时获取外部数据
// Before
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
externalData: null,
};
componentDidMount() {
this._loadAsyncData(this.props.id);
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
if (nextProps.id !== this.props.id) {
this.setState({externalData: null});
this._loadAsyncData(nextProps.id);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this._asyncRequest) {
this._asyncRequest.cancel();
}
}
render() {
if (this.state.externalData === null) {
// Render loading state ...
} else {
// Render real UI ...
}
}
_loadAsyncData(id) {
this._asyncRequest = loadMyAsyncData(id).then(
externalData => {
this._asyncRequest = null;
this.setState({externalData});
}
);
}
}
getDerivedStateFromProps经常要配合componentDidUpdate使用
// After
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
externalData: null,
};
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
// Store prevId in state so we can compare when props change.
// Clear out previously-loaded data (so we don't render stale stuff).
if (props.id !== state.prevId) {
return {
externalData: null,
prevId: props.id,
};
}
// No state update necessary
return null;
}
componentDidMount() {
this._loadAsyncData(this.props.id);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (this.state.externalData === null) {
this._loadAsyncData(this.props.id);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this._asyncRequest) {
this._asyncRequest.cancel();
}
}
render() {
if (this.state.externalData === null) {
// Render loading state ...
} else {
// Render real UI ...
}
}
_loadAsyncData(id) {
this._asyncRequest = loadMyAsyncData(id).then(
externalData => {
this._asyncRequest = null;
this.setState({externalData});
}
);
}
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)在最近呈现的输出被提交到例如DOM之前调用。它使组件可以在可能更改之前从DOM捕获一些信息(例如滚动位置)。此生命周期返回的任何值都将作为参数传递给componentDidUpdate()。
class ScrollingList extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.listRef = React.createRef();
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
// Are we adding new items to the list?
// Capture the scroll position so we can adjust scroll later.
if (prevProps.list.length < this.props.list.length) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
// If we have a snapshot value, we've just added new items.
// Adjust scroll so these new items don't push the old ones out of view.
// (snapshot here is the value returned from getSnapshotBeforeUpdate)
if (snapshot !== null) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
list.scrollTop = list.scrollHeight - snapshot;
}
}
render() {
return (
<div ref={this.listRef}>{/* ...contents... */}</div>
);
}
}
二、新的context API
context 就是可以使用全局的变量,不需要一层层传递props下去,比如主题颜色
// Context lets us pass a value deep into the component tree
// without explicitly threading it through every component.
// Create a context for the current theme (with "light" as the default).
const ThemeContext = React.createContext('light');
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
// Use a Provider to pass the current theme to the tree below.
// Any component can read it, no matter how deep it is.
// In this example, we're passing "dark" as the current value.
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value="dark">
<Toolbar />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}
}
// A component in the middle doesn't have to
// pass the theme down explicitly anymore.
function Toolbar(props) {
return (
<div>
<ThemedButton />
</div>
);
}
class ThemedButton extends React.Component {
// Assign a contextType to read the current theme context.
// React will find the closest theme Provider above and use its value.
// In this example, the current theme is "dark".
static contextType = ThemeContext;
render() {
return <Button theme={this.context} />;
}
}
一般来说,如果你只是想避免需要传很多次props的话,可以直接使用component composition(就是通过props自己传给指定的)会更好。
function Page(props) {
const user = props.user;
// 简单来说就是直接父组件将props传下去
const userLink = (
<Link href={user.permalink}>
<Avatar user={user} size={props.avatarSize} />
</Link>
);
return <PageLayout userLink={userLink} />;
}
// Now, we have:
<Page user={user} />
// ... which renders ...
<PageLayout userLink={...} />
// ... which renders ...
<NavigationBar userLink={...} />
// ... which renders ...
{props.userLink}
context一般用于一些相同的data需要被大多的component用到,并且还是在不同的层级里。如主题,存储数据等。
三、createRef API
react15 提供了两种refs的方法: string 跟 callback:
//string:
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
// 通过this.refs.textInput 来获取
render() {
return <input type="text" ref='textInput' />;
}
}
//callback:
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
// 通过this.textInput 来获取
render() {
return <input type="text" ref={element => this.textInput = element} />;
}
}
string的用法可能会有问题,一般用callback
createRef
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.inputRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return <input type="text" ref={this.inputRef} />;
}
componentDidMount() {
this.inputRef.current.focus();
}
}
注意事项:
1、functional component 是不能传ref属性的,因为他们没有instance
function MyFunctionComponent() {
return <input />;
}
class Parent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.textInput = React.createRef();
}
render() {
// 这个不能工作
return (
<MyFunctionComponent ref={this.textInput} />
);
}
}
但是只要引用的对象是DOM元素或者是class component, 那就可以在functional component里可以使用ref属性
function CustomTextInput(props) {
// textInput must be declared here so the ref can refer to it
let textInput = React.createRef();
function handleClick() {
textInput.current.focus();
}
return (
<div>
<input
type="text"
ref={textInput}
/>
<input
type="button"
value="Focus the text input"
onClick={handleClick}
/>
</div>
);
}
functional component里可以使用refs 但是不能把ref属性给它本身。
四、forwardRef API
父组件需要将自己的引用传给子组件
const TextInput = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => (
<input type="text" placeholder="Hello forwardRef" ref={ref} />
))
const inputRef = React.createRef();
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.myRef = React.createRef()
}
handleSubmit = event => {
event.preventDefault()
alert('input value is:' + inputRef.current.value)
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<TextInput ref={inputRef} />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
)
}
}
const FancyButton = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => (
<button ref={ref} className="FancyButton">
{props.children}
</button>
));
// You can now get a ref directly to the DOM button:
const ref = React.createRef();
<FancyButton ref={ref}>Click me!</FancyButton>;
这样就可以直接用this.ref 拿到对button的引用。
如果写的是一个高阶组件,推荐使用forwardAPI 将ref传给下面的component。
五、strictMode component
严格模式用来帮助开发者发现潜在问题的工具。就像Fragment 一样,它不会render任何的DOM 元素。注意:只有在development模式下才能用。
它可以帮助我们:
- 识别出使用不安全生命周期的组件
- 对使用string ref进行告警
- 对使用findDOMNode进行告警
- 探测某些产生副作用的方法
- 对使用弃用context API进行警告
- 还会有更多的功能在后续版本加进来。
function ExampleApplication() {
return (
<div>
<Header />
<React.StrictMode>
<div>
<ComponentOne />
<ComponentTwo />
</div>
</React.StrictMode>
<Footer />
</div>
);
}
v16.4
新增指针事件
新增了对对指针设备(例如鼠标,触控笔,或者手指触摸)触发的dom事件
onPointerDown
onPointerMove
onPointerUp
onPointerCancel
onGotPointerCapture
onLostPointerCapture
onPointerEnter
onPointerLeave
onPointerOver
onPointerOut
fix生命周期函数 - getDerivedStateFromProps
v16.5
React Profiler
React Developer Tools
v16.6
memo
React 15:如果想阻止组件的重复渲染,在class component里可以使用PureComponent, shouldComponentUpdate来优化。但是function component,没有这个功能, 只能每次都重新渲染。
React 16:为了全面拥抱function component,React团队写了memo来帮助function component实现这个阻止重复渲染的功能。
import React, { memo } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import "./styles.css";
function Demo(props) {
console.log("render");
return <div>{props.name}</div>;
}
// const Demo = memo(function Demo(props) {
// console.log("render");
// return <div>{props.name}</div>;
// })
class App extends React.Component {
state = { count: 0 };
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({ count: 1 });
};
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Hello Memo</h1>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
This is Memo Demo{this.state.count}
</button>
<Demo name={"daisy"} />
</div>
);
}
}
const rootElement = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App />, rootElement);
lazy、suspense
lazy需要跟Suspence配合使用。
lazy实际上是帮助我们实现代码分割的功能。
由于有些内容,并不一定要在首屏展示,所以这些资源没有必要一开始就要去获取,那么这些资源就可以动态获取。
这样的话,相当于把不需要首屏展示的代码分割出来,减少首屏代码的体积,提升性能。
Suspence 很像Error Boundary,不同的是Error Boundary是用来捕获错误,显示相应的callback组件。而Suspence是用来捕获还没有加载好的组件,并暂停渲染,显示相应的callback。
import React, { lazy, Suspense } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { Tab, Tabs, TabList, TabPanel } from "react-tabs";
import "react-tabs/style/react-tabs.css";
import "./styles.css";
import A from "./A";
// import B from "./B";
// 需要用到的时候才加载进来,当然还有预加载更好
const B = lazy(() => import("./B"));
import C from "./C";
function App() {
console.log(A);
console.log(B);
console.log(C);
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>React 16</h1>
<Tabs>
<TabList>
<Tab>A</Tab>
<Tab>B</Tab>
<Tab>C</Tab>
</TabList>
<TabPanel>
<A />
</TabPanel>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<TabPanel>
<B />
</TabPanel>
</Suspense>
<TabPanel>
<C />
</TabPanel>
</Tabs>
</div>
);
}
const rootElement = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App />, rootElement);
需要注意:
SSR不支持lazy这个特性。
Lazy 必须搭配Suspence使用,否则会报错
简化static contextType
之前需要用一个在外层包裹一个<Consumer>
// Theme context, default to light theme
const ThemeContext = React.createContext('light');
// Signed-in user context
const UserContext = React.createContext({
name: 'Guest',
});
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
const {signedInUser, theme} = this.props;
// App component that provides initial context values
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>
<UserContext.Provider value={signedInUser}>
<Layout />
</UserContext.Provider>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}
}
function Layout() {
return (
<div>
<Sidebar />
<Content />
</div>
);
}
// A component may consume multiple contexts
// 同时如果是function component 用Consumer
function Content() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{theme => (
<UserContext.Consumer>
{user => (
<ProfilePage user={user} theme={theme} />
)}
</UserContext.Consumer>
)}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
);
}
现在可以直接通过this.context获取。
class MyClass extends React.Component {
static contextType = MyContext;
componentDidMount() {
let value = this.context;
/* perform a side-effect at mount using the value of MyContext */
}
componentDidUpdate() {
let value = this.context;
/* ... */
}
componentWillUnmount() {
let value = this.context;
/* ... */
}
render() {
let value = this.context;
/* render something based on the value of MyContext */
}
}
MyClass.contextType = MyContext;
新增static getDerivedStateFromError
v16.3这个版本里,React 除了Error Boundaries来捕获错误,里面主要是使用了componentDidCatch来捕获 错误。但是它是在错误已经发生之后并且render函数被调用之后,才会被调用。 也就是说如果一个组件出现的错误,在调用 componentDidCatch之前只能返回null给用户。
而 getDerivedStateFromError 可以在render函数之嵌捕获到错误,所以它更适合写用来显示fallback UI的逻辑。
注意事项: componentDidCatch,getDerivedStateFromError都无法捕获服务端的错误,但是React团队正在努力支持SSR。
改进前的ErrorBoundary:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false };
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
this.setState({ hasError: false })
logErrorToMyService(error, info);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
改进后的ErrorBoundary(推荐写法):
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false };
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI.
// 更新state所以下次render可以立刻显示fallback UI
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
// You can also log the error to an error reporting service
logErrorToMyService(error, info);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
升级
因为prop变更而更新state的,写到 getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) 里
因为prop变更而需要执行方法的,写到componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState)里
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate在render之前调用,state已更新
杂
老的context
// 父组件,中间组件
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class MiddleComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return <ChildComponent />
}
}
class ParentComponent extends React.Component {
// 声明Context对象属性
static childContextTypes = {
propA: PropTypes.string,
methodA: PropTypes.func
}
// 返回Context对象,方法名是约定好的
getChildContext() {
return {
propA: 'propA',
methodA: () => 'methodA'
}
}
render() {
return <MiddleComponent />
}
}
//普通子组件
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class ChildComponent extends React.Component {
// 声明需要使用的Context属性
static contextTypes = {
propA: PropTypes.string
}
render() {
const {
propA,
methodA
} = this.context
console.log(`context.propA = ${propA}`) // context.propA = propA
console.log(`context.methodA = ${methodA}`) // context.methodA = undefined
return (<div></div>)
}
}
//stateless 子组件
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
const ChildComponent = (props, context) => {
const {
propA
} = context
console.log(`context.propA = ${propA}`) // context.propA = propA
return (<div></div>)
}
ChildComponent.contextProps = {
propA: PropTypes.string
}
新的context
感觉是变复杂了,没有变简单
//单独的context文件
import React from 'react';
export const ThemeContext = React.createContext({
theme: 'white',
switchTheme: () => { }
});
//父组件,需要引入context文件
class ParentComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
contextObj: {
theme: 'red',
switchTheme: (theme) => {
this.setState({ theme });
}
}
};
}
render() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={this.state.contextObj}>
<MiddleComponent />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
)
}
}
//子组件,需要引入context文件
class ChildComponent extends React.Component {
//如果不用Consumer,也可以用contextType来通过this.context获取值
//但它目前似乎只支持单一context
static contextType = ThemeContext;
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context);
const { theme, switchTheme } = this.context;
}
componentDidMount() {
const { theme, switchTheme } = this.context;
}
componentDidUpdate() {
const { theme, switchTheme } = this.context;
}
componentWillUnmount() {
const { theme, switchTheme } = this.context;
}
render() {
const { theme, switchTheme } = this.context;
return (
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{context => (
<div style={{ color: context.theme }} onClick={() => { context.switchTheme('green') }}>
主题
</div >
)}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
)
}
}
生命周期
不知道为啥有的还是获取不到context
constructor(props, context)
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, nextContext)
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext)
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext)
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, prevContext)


