学习笔记3_LINQ
C#对LINQ的支持
数据访问一直是大多数应用程序的一个非常重要的工作.用于.NET领域的数据访问框架有Enterprise Library,ActiveRecord,HHibernate,SubSonic等.
微软公司推出的数据访问技术为语言集成查询(Language-Integrated Query简称LINQ)和实体框架(Entity Framework简称EF).
在LINQ查询中,始终使用对象而非针对某种具体数据源操作命令,可以使用相同的编码模式来查询和转换XML文档,SQL数据库,ADO.NET数据集,.NET集合中的数据以及对
其有LINQ提供程序可用的任何其它格式数据.
1.对象初始化器
在编程过程中经常用到的一个功能就是在创建对象时为对象的某些属性赋值.
public class Student { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } static void main(string[] args) { //对象初始器 Student s1 = new Student() { Name = "xiaohh", Age = 21 }; } }
2.隐式类型
使用LINQ进行查询时,很多时候编程人员不容易判断某个查询的返回类型,或者类型名太长不方便写出来.通过使用var关键字,就可以很方便的表示LINQ的查询结果.
var query = from p in products select p;
用var关键字声明的变量可以被初始化为任何类型的值.
//var 定义的变量必须被初始化 var var1 = 21; var var2 = "MM"; var var3 = DateTime.Now; var var4 = new object[10]; var var5 = new List<string>();
在定义var关键字的时候变量必须被初始化.每一个var关键字只能定义一个变量.
var i = 10, j = 20;
否则会提示:"隐式类型的局部变量不能有多个声明符"
使用var关键字只能声明局部变量(for,foreach,)
class Class2 { //错误 var name = "name"; //错误 private void method1(var v) { Console.WriteLine(v); } //for foreach using private static void method2() { for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine(i); } int[] nums = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; foreach (var item in nums) { Console.WriteLine(item); } //@"e:temp.txt"还行 多路径就不行了@"e:temp\temp.txt" using (var file = new System.IO.StreamWriter(@"e:temp\temp.txt")) { file.WriteLine("sky"); } } }
注意:使用var关键字声明的隐式类型变量是强类型变量,在声明时必须赋值,而且其类型一旦确定不能更改.
3.匿名类型
指的是没有名字的类型.在同一个程序中,如果两段匿名类型对象的代码具有相同的参数(包括参数类型,名称和顺序),那么这两个匿名类型就属于同一个匿名类型.
static void Main(string[] args) { var class1 = new { id = "123", name = "ff", age = 40 }; var class2 = new { id = "1231", name = "aa", age = 23 }; string s1 = class1.GetType().Name; string s2 = class2.GetType().Name; if (s1.Equals(s2, StringComparison.Ordinal)) { Console.WriteLine("class1和class2类型相同"); } Console.ReadLine(); }
4.扩展方法
允许向现有类中添加方法而不用修改现有类的代码.微软建议谨慎使用.现在为.NET Framework中的string类型添加一个IsInt方法,判断某个字符串是否是个整数,
以及是否为正整数.
public static bool IsInt(this string text, bool positive = false) { int n; if (int.TryParse(text, out n)) { if (positive) { return n > 0; } return true; } return false; }
第一个参数前面有个this关键字,表示这是一个扩展方法.
this关键字后面有个string类型,表示是对string类的扩展.现在这个方法已经被Visual Studio识别了.
string text = "-50505"; bool b = text.IsInt(); Console.WriteLine(text + (b ? "是" : "不是") + "整数"); b = text.IsInt(true); Console.WriteLine(text + (b ? "是" : "不是") + "正整数"); b = "100".IsInt(); Console.ReadLine();
注意out关键字用法
string str = "-10010"; int result; //out关键字 result得到输出值 bool b = int.TryParse(str, out result); Console.WriteLine(str + Environment.NewLine + result); Console.ReadLine();
5.Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式是对匿名方法的一种改进.所有的Lambda表达式都是有Lamdba运算符=>,该运算符读为"goes to".
Lamdba表达式用的最多的地方是集合操作,如元素查找.
创建一个学生成绩列表,并利用Lamdba表达式查询条件,对学生成绩列进行查找,删除等操作.
List<int> scores = new List<int>(); Random rand = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { scores.Add(rand.Next(20, 100)); } Console.WriteLine("原始数据"); PrintScore(scores); //查找90分及其以上人数 int match = scores.Count(s => s >= 90); Console.WriteLine(match + "人数成绩高于90分"); //删除不及格学生 scores.RemoveAll(s => s < 60); PrintScore(scores); //从高到低排序 scores.Sort((x, y) => x - y); Console.WriteLine("排序后的数据"); PrintScore(scores); Console.ReadLine();
输出学生成绩,注意每行15个以及左对齐操作
private static void PrintScore(List<int> scores) { for (int i = 0; i < scores.Count; i++) { if (i > 0 && i % 15 == 0) { Console.WriteLine(); } //{0,负整数} 左对齐 Console.Write(String.Format("{0,-4}", scores[i])); } Console.ReadLine(); }
6.表达式树
...
LINQ基本操作
1.创建数据源
LINQ为IEnumerable<T>泛型接口添加了很多扩展方法,.NET所有泛型集合类都实现了IEnumerable接口,通过这些扩展方法可以实现对泛型集合的查询功能.
LINQ查询语法有两种.一种是方法语法,另一种是查询语法.实际上C#在遇到查询语法的时候,会翻译成相应的方法语法再执行.
使用一组随机生成的商品销售数据作为数据源演示LINQ的使用.与此相关的有3个类:商品类别Category,商品信息Product和销售记录ProductSale.
为了随机生成数据,3个类分别包含一个随机填充数据的方法.
public class Category { public string Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public static List<Category> GetCategories(int count) { Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond); List<Category> categories = new List<Category>(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Category category = new Category(); category.Id = "C" + random.Next(1000); category.Name = "Category" + i.ToString(); categories.Add(category); } return categories; } }
public class Product { public string Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Storage { get; set; } public double Price { get; set; } public Category Category { get; set; } public static List<Product> GetProducts(int count) { Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond); List<Product> products = new List<Product>(); //随机生成类别,设类别数量为商品数量的1/10,但至少有3种,最多20种 int categoryCount = Math.Min(20, Math.Max(count / 10, 3)); Category[] categorise = Category.GetCategories(categoryCount).ToArray(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Product p = new Product(); p.Id = "p" + random.Next(10000).ToString("0000"); p.Name = "product" + i.ToString(); p.Storage = random.Next(10, 10000); //4舍5入 p.Price = Convert.ToDouble((1 + random.NextDouble() * 300).ToString("0.00")); p.Category = categorise[random.Next(categoryCount)]; products.Add(p); } return products; } }
public class ProductSale { public Product Product { get; set; } public DateTime Date { get; set; } public int Quantity { get; set; } public static List<ProductSale> GetProductSales(int count) { //商品种类为销售记录的1/5 int productCount = count / 5 + 1; Product[] products = Product.GetProducts(productCount).ToArray(); Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond); List<ProductSale> sales = new List<ProductSale>(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { ProductSale sale = new ProductSale(); sale.Product = products[random.Next(productCount)]; sale.Quantity = random.Next(100); sale.Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(random.Next(-30, 30)); sales.Add(sale); } return sales; } }
2.投影
Select查询
public static void SelectDemo() { List<Product> products = Product.GetProducts(5); //查询商品本身 var query = products.Select(p => p); foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2},Storage={3},Category={4}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price, item.Storage, item.Category.Name); } //查询商品的一部分信息,这些信息构成一个匿名类型 var query2 = products.Select(p => new { Id = p.Id, Name = p.Name, category = p.Category.Name }); foreach (var item in query2) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Category={2}", item.Id, item.Name, item.category); } }
对应的查询语法
var query = from p in products select p;
3.选择
Where过滤数据
public static void WhereDemo() { List<Product> products = Product.GetProducts(10); var query = from p in products where p.Price > 180 select p; foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2},Category={3}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price, item.Category.Name); } var query2 = from p in products where p.Price > 180 select new { Id = p.Id, Name = p.Name, category = p.Category.Name }; foreach (var item in query2) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Category={2}", item.Id, item.Name, item.category); } }
对应的方法语法
var query = products.Where(p => p.Price > 180);
4.排序
OrderBy,OrderByDescending,ThenBy,ThenByDescending
public static void SortDemo() { List<Product> products = Product.GetProducts(10); //升序 var query = from p in products where p.Price > 180 orderby p.Price select p; foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2},Category={3}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price, item.Category.Name); } Console.WriteLine("方法语法"); var query3 = products.Where(p => p.Price > 180).OrderBy(p => p.Price); foreach (var item in query3) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2},Category={3}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price, item.Category.Name); } Console.WriteLine("*****"); var query2 = from p in products where p.Price < 180 orderby p.Category.Id, p.Price descending select p; foreach (var item in query2) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Category={2},Price={3},CategoryId={4}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Category.Name, item.Price, item.Category.Id); } Console.WriteLine("方法语法"); var query4 = products.Where(p => p.Price < 180).OrderBy(p => p.Category.Id).ThenByDescending(p => p.Price); foreach (var item in query4) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Category={2},Price={3},CategoryId={4}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Category.Name, item.Price, item.Category.Id); } }
5.数据分页
Skip方法和Take方法
如果数据库有很多Product数据,先取100条,然后按照每页10条来分页也不错哦.然后这100条用完,再取100条,再分页.这个思路很正常.
public static void SkipTake() { //先取100条 List<Product> products = Product.GetProducts(100); var query = from p in products where p.Price > 100 orderby p.Price descending select p; int pageSize = 10; //注意Math.Ceiling()的用法 int pageCount = (int)Math.Ceiling(query.Count() * 1.0 / pageSize); for (int i = 0; i < pageCount; i++) { Console.WriteLine("=====第{0}页数据=====", i + 1); var query2 = query.Skip(i * pageSize).Take(pageSize); foreach (var item in query2) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price); } } }
6.数据分组
GroupBy方法
将所有商品按照类别ID进行分组,并输出各组的键值(类别ID)和各组中的商品列表
public static void GroupDemo() { List<Product> products = Product.GetProducts(10); foreach (var item in products) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2},CategoryId={3}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price, item.Category.Id); } var query = from p in products group p by p.Category.Id into categoryGroup select new { categoryId = categoryGroup.Key, products = categoryGroup }; int i = 1; //循环输出每组的类别ID和组中的商品 foreach (var group in query) { Console.WriteLine("===================第{0}组(类别Id:{1})===================", i++, group.categoryId); foreach (var item in group.products) { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2}", item.Id, item.Name, item.Price); } } }
7.返回单个元素
根据主键查询,返回的结果最多只有一项.
//Single只有一个 //SingleOrDefault可以有一个或者0个,NULL //First必须有,取第一个 //FirstOrDefault如果有,取第一个,没有则为NULL public static void SingleFirst() { List<Product> products = Product.GetProducts(10); var query = products.Where(p => p.Price > 200); Product product = null; try { product = query.Single(); Console.WriteLine("Single方法查询结果为:"); Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2}", product.Id, product.Name, product.Price); } catch (InvalidOperationException ex) { Console.WriteLine("Single发生异常.查询结果不是正好包含单条数据."); Console.WriteLine("异常信息:" + ex.Message); } try { product = query.SingleOrDefault(); Console.WriteLine("SingleOrDefault方法查询结果为:"); if (product == null) { Console.WriteLine("NULL"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2}", product.Id, product.Name, product.Price); } } catch (InvalidOperationException ex) { Console.WriteLine("SingleOrDefault发生异常.查询结果包含多于一条数据."); Console.WriteLine("异常信息:" + ex.Message); } try { product = query.First(); Console.WriteLine("First方法查询结果为:"); Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2}", product.Id, product.Name, product.Price); } catch (InvalidOperationException ex) { Console.WriteLine("First发生异常.查询结果不包含数据."); Console.WriteLine("异常信息:" + ex.Message); } try { product = query.FirstOrDefault(); Console.WriteLine("FirstOrDefault方法查询结果为:"); if (product == null) { Console.WriteLine("NULL"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Id={0},Name={1},Price={2}", product.Id, product.Name, product.Price); } } catch (ArgumentNullException ex) { Console.WriteLine("First发生异常.查询结果不包含数据."); Console.WriteLine("异常信息:" + ex.Message); } }
8.延迟执行与立即执行
在LINQ表达式的from...where...select语句中,并没有执行实际的查询工作,而仅仅是生成了一个查询命令,实际的查询要等到使用查询结果时(如在foreach中使用查询结果)才被执行.
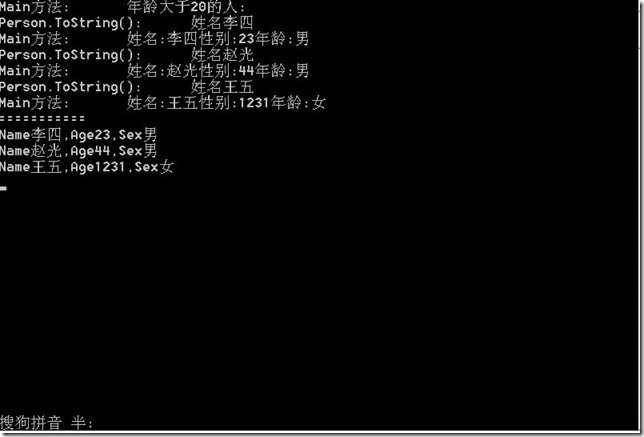
创建一个Person类
class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public string Sex { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public override string ToString() { Console.WriteLine("Person.ToString():\t姓名" + Name); //线程休眠1s System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000); return string.Format("姓名:{0}性别:{1}年龄:{2}", Name, Age, Sex); } }
public static void LazyLoad() { List<Person> persons = new List<Person>(); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "张三", Age = 20, Sex = "女" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "李四", Age = 23, Sex = "男" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "小妹", Age = 4, Sex = "女" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "赵光", Age = 44, Sex = "男" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "王五", Age = 1231, Sex = "女" }); var query = from p in persons where p.Age > 20 select p.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("Main方法:\t年龄大于20的人:"); foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("Main方法:\t" + item); } var query2 = from p in persons where p.Age > 20 select p; Console.WriteLine("==========="); foreach (var item in query2) { Console.WriteLine("Name{0},Age{1},Sex{2}", item.Name, item.Age, item.Sex); } }
可以看到Person.ToString方法和Main方法是交替执行的.也就是说,在Main方法的foreach中,每当使用query结果集中的一个元素时,这个元素才被计算生成,而不是在声明query结果集
的时候一次性生成所以元素.
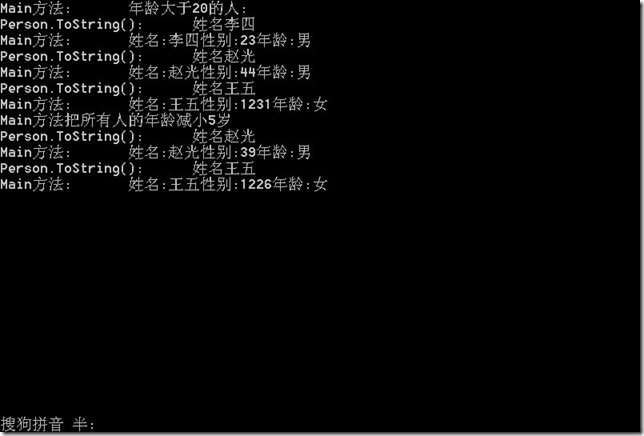
由于LINQ查询延迟执行,所以在读取时,其中的元素总是最新的.
public static void LazyLoad2() { List<Person> persons = new List<Person>(); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "张三", Age = 20, Sex = "女" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "李四", Age = 23, Sex = "男" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "小妹", Age = 4, Sex = "女" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "赵光", Age = 44, Sex = "男" }); persons.Add(new Person { Name = "王五", Age = 1231, Sex = "女" }); var query = from p in persons where p.Age > 20 select p.ToString(); Console.WriteLine("Main方法:\t年龄大于20的人:"); foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("Main方法:\t" + item); } Console.WriteLine("Main方法把所有人的年龄减小5岁"); persons.ForEach(p => p.Age -= 5); foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("Main方法:\t" + item); } }
LINQ查询默认情况下是延迟执行,若想让LINQ查询立即执行,可以调用ToList方法和ToArray.
var query = (from p in persons where p.Age > 20 select p.ToString()).ToList();