栈的应用——迷宫问题的求解
利用栈实现迷宫问题的求解(找到迷宫的通路,如下面给定的迷宫,0代表通路,1代表不通,利用栈的特点,求出他的通路)
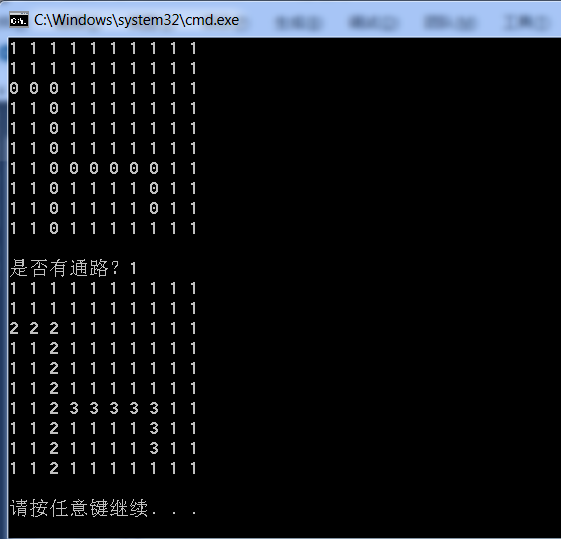
给定的迷宫:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
自己实现的栈
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<assert.h>
template<class T>
class Stack
{
public:
Stack()
:_capacity(0)
,_data(NULL)
, _top(0)
{}
~Stack()
{
delete[] _data;
_data = NULL;
_top= _capacity = 0;
}
void Push(const T&x)
{
_CheckCapacity();
_data[_top++] = x;
}
void Pop()
{
if (!IsEmpty())
--_top;
}
bool IsEmpty()
{
return _top == 0;
}
bool IsFull()
{
return _top == _capacity;
}
T& Top()
{
return _data[_top-1];
}
void Display()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _top; ++i)
{
cout << _data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
public:
void _CheckCapacity()
{
if (_top >= _capacity)
{
size_t NewCapacity = 2 * _top + 3;
T* tmp = new T[NewCapacity];
// memcpy(tmp, _data, sizeof(T)*size); //内置类型
for (int i = 0; i <_top; ++i)
{
tmp[i] = _data[i];
}
delete[] _data;
_data = tmp;
_capacity = NewCapacity;
}
}
private:
T* _data;
size_t _top;
size_t _capacity;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
迷宫的几种操作:
#include"Stack.h"
const int N = 10;
struct Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
Pos(int row=0,int col=0)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
{}
};
void InitMaze(int *Maze) //初始化迷宫
{
FILE* fp = fopen("Maze.txt", "r");
assert(fp);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; )
{
int value = fgetc(fp);
if (value ==32 || value == 10)
continue;
Maze[i*N + j] = value - '0';
++j;
}
}
}
bool CheckAccess(int *Maze,Pos p,int rows,int cols)
{
return (p._col >= 0 && p._col < cols&&p._row >= 0 && p._row < rows&&Maze[p._row*rows+ p._col] == 0);
}
bool GetPath(int *Maze, int cols, int rows, Stack<Pos>&s, Pos entry)
{
Pos cur = entry;
s.Push(entry);
Maze[entry._row*rows+ entry._col] = 2; //走过的路径被设为2
while (!s.IsEmpty())
{
Pos next = s.Top();
cur = next;
Maze[cur._row*rows + cur._col] = 2;
if (next._row == rows-1 || next._col == cols-1) //3面可以出
return true;
//右
next._col = next._col + 1;
if (CheckAccess(Maze, next, N, N))
{
s.Push(next);
continue;
}
next._col = next._col - 1;
//下
next._row = next._row + 1;
if (CheckAccess(Maze,next,N,N))
{
s.Push(next);
continue;
}
next._row = next._row - 1;
//上
next._row = next._row - 1;
if (CheckAccess(Maze, next, N, N))
{
s.Push(next);
continue;
}
next._row = next._row + 1;
//左
next._col = next._col - 1;
if (CheckAccess(Maze, next, N, N))
{
s.Push(next);
continue;
}
next._col = next._col + 1;
//右
next._col = next._col + 1;
if (CheckAccess(Maze, next, N, N))
{
s.Push(next);
continue;
}
next._col = next._col - 1;
s.Pop();
Maze[next._row * rows+ next._col] = 3; //如果走过的路径不通,则标记为3
}
return false;
}
void PrintMaze(int *Maze)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
{
cout << Maze[i*N + j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////
测试:
#include"Maze.h"
void main()
{
int maze[N][N];
InitMaze((int *)maze);
PrintMaze((int *)maze);
Stack<Pos> paths;
cout << "是否有通路?" <<GetPath((int *)maze, N, N, paths, Pos(2, 0)) << endl;
//cout << "是否有通路?" << GetPath( N, N,(int *)maze, paths, Pos(2, 0)) << endl;
PrintMaze((int *)maze);
}
测试结果: