普通用户的提权
当我们使用普通用户执行/sbin目录下的命令时,会发现没有权限。这中情况会照成无法正常管理服务器。这时候我们需要不使用root用户直接登录系统,同时又要保证普通用户可以完成日常工作,我们可以使用su、sudo来完成需求。
- 1,
su user身份切换,使用普通用户登录。这个简单但是需要知道root密码,不安全 - 2,
sudo提权,当需要使用root权限时进行提权。无需切换至root用户。方便,安全。但是需要预先定义规则,较为复杂。
1,su 命令身份切换
- 在使用
su切换身份前,我们需要shell登录分类、环境变量配置文件加载顺序
1.1 Shell登录分类
- 登录
shell需要输入用过户名和密码才能进入Shell - 非登录
shell不要输入用户和密码就能进入Shell,比如运行bashhi开启一个新的会话窗口
1.1.2
profile类文件:设定环境变量,登录前运行的脚本和命令bashrc类文件:设定本地变量,定义命令别名- 用户配置文件:
~/.bash_profile~/.bashrc
- 全局环境变量
/etc/profile/etc/profile.d/*.sh/etc/bashrc
- 登录式
Shell配置文件加载顺序:/etc/profile--->/etc/profile.d/*.sh--->~/.bash_profile--->~/.bashrc--->/etc/bashrc - 非登录式
shell配置文件加载顺序:/.bashrc--->/etc/bashrc--->/etc/profile.d/*.sh
1.1.3, su与环境变量的关系
su -username属于登录式Shellsu username属于非登录式Shell- 他们最大的区别就在与加载的环境变量不一样
#以某个用户的身份执行某个服务,使用命令`su -c username`
[root@Linux.net: ~]#su - zhao -c 'pwd '
/home/zhao
2,sudo命令提权
- 快速配置
sudo方式
1,将用户加入
wheel组,默认wheel组有sudo权限;
[root@Linux.net: ~]#usermod zhao -G wheel
2,切换到普通用户
[root@Linux.net: ~]#su - zhao
3,普通用户正常情况下无法删除
/opt目录
[zhao@Linux ~]$ rm -rf /opt/
rm: cannot remove ‘/opt/file-1000’: Permission denied
4.使用sudo提权,然后输入普通用户密码,就可以删除
/opt目录了。
[zhao@Linux ~]$ rm -rf /opt/
5,后期还可以通过审计日志查看普通用户提权都执行了什么操作。在
root下查询
[root@Linux.net: ~]#tail -f /var/log/secure
3,sudo权限分配
-
通过快速提权的方式,我们会发现
sudo什么操作都可以执行,所以我们需要限制ta,也就是说只给普通用户开启某几个命令的sudo使用权限,其他命令不允许。 -
我们来模拟个场景
1.,创建用户,并为用户设定对应的密码;
#先创建用户
[root@Linux.net: ~]#useradd ops1
[root@Linux.net: ~]#useradd ops2
[root@Linux.net: ~]#useradd dev1
[root@Linux.net: ~]#useradd dev2
#为每个用户设定密码
[root@Linux.net: ~]#echo "1" | passwd --stdin ops1
Changing password for user ops1.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@Linux.net: ~]#echo "1" | passwd --stdin ops2
Changing password for user ops2.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@Linux.net: ~]#echo "1" | passwd --stdin dev1
Changing password for user dev1.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@Linux.net: ~]#echo "1" | passwd --stdin dev2
Changing password for user dev2.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
2.,在
/etc/sudoers文件中配置规则
[root@Linux.net: ~]#vim /etc/sudo
#1.使用sudo定义逻辑分组
User_Alias OPS = ops1,ops2
User_Alias DEV = dev1,dev2
#2,在相同命令逻辑上划分为一个命令集:
Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping
Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service, /sbin/chkconfig, /usr/bin/systemctl start
Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /bin/mount, /bin/umount
Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall
#3,进行权限划分,为OPS和DEV分配对象的命令集名称
OPS ALL=(ALL) NETWORKING,SERVICES,STORAGE,PROCESSES
DEV ALL=(ALL) STORAGE,PROCESSES
3,然后登录对应的用户检查相应的
sudo权限;
#检查ops用户sudo权限
[ops1@Linux root]$ sudo -l
[dev1@Linux root]$ sudo -l
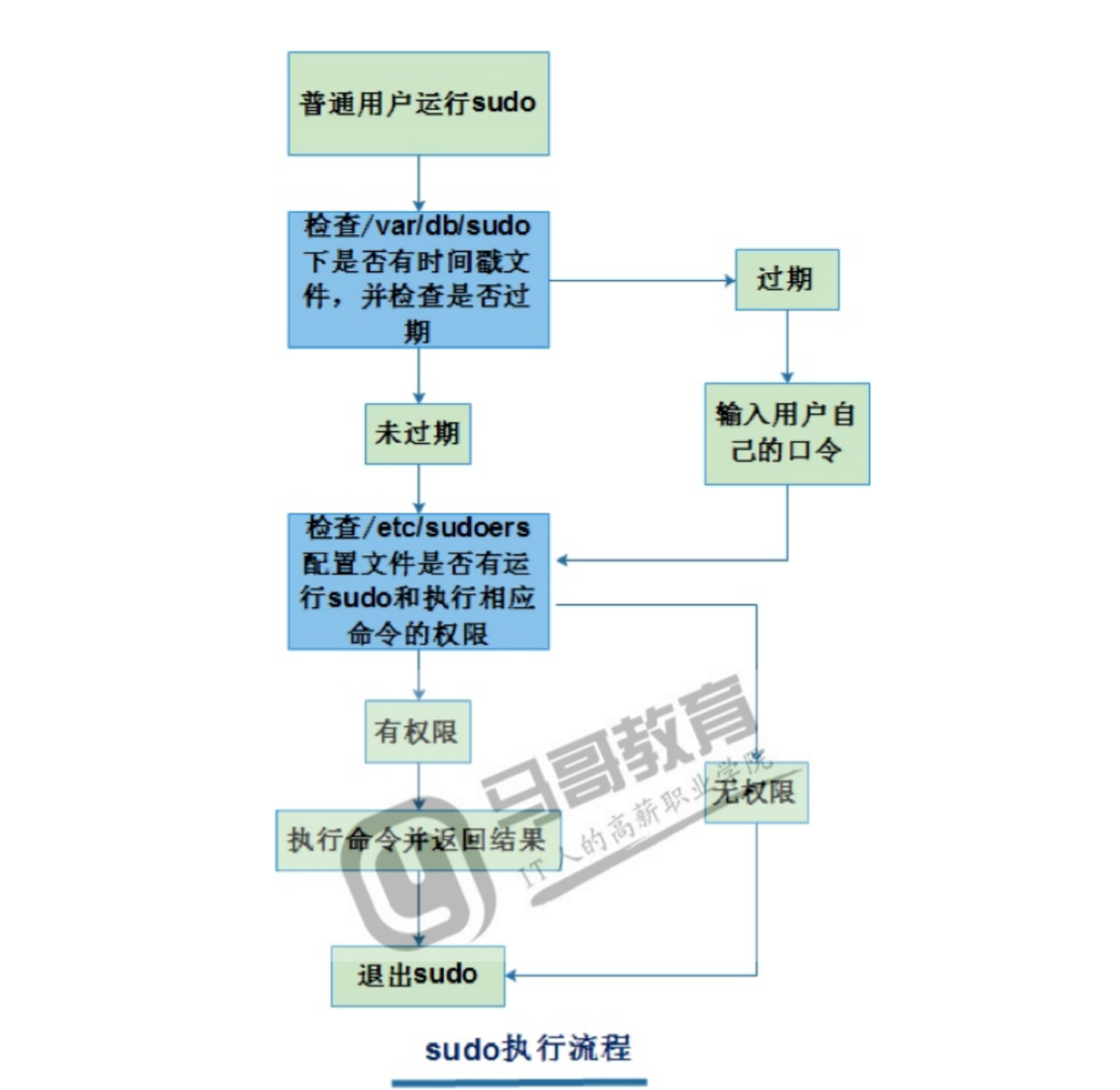
4,sudo执行流程
sudo命令执行流程
- 普通用户执行
sudo命令时,会去检查/var/db/sudo是否存在时间戳缓存;如果存在则不需要输入密码。否则需要输入用户与密码。输入密码会检测该用户是否拥有该权限,有则执行,否则报错