FileInputStream与FileOutputStream学习笔记
这是我的第一篇博客,纪念一下吧!
最近学习了IO流,想着学长说的话,就突然想要写写博客了,别管这是什么逻辑了,进入正题。
一.FileInputStream
1.概念
FileInputStream是Java语言中抽象类InputStream用来具体实现类的创建对象。FileInputStream可以从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节,获取的文件可用性取决于主机环境。--百度百科
FileInputStream是节点流,是字节流
2.API文档
1)构造方法:
FileInputStream(File file) 通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream ,该文件由文件系统中的 File对象 file命名
FileInputStream(String name) 通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream ,该文件由文件系统中的路径名 name命名。
2)常用方法:
int read() 从该输入流读取一个字节数据
int read() 从该输入流读取最多b.length个字节的数据。
void close() 关闭此文件输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。
1)从输入流中一个字节一个字节读取
public class IOTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建File类对象 File src = new File("abc.txt"); //多态 InputStream is = null; try { is = new FileInputStream(src); //操作 int temp; /* * 返回的是读取到的一个字节数据对应的int值 * 返回值为-1时说明文件读取完毕 * */ while((temp=is.read()) != -1) { //这里强制转换为char类型 System.out.print((char)temp); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { //关闭流 is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
2)将流中数据读取到字节数组中
public class IOTest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); //选择流 InputStream is = null; try { is = new FileInputStream(src); byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len = -1; /*从当前位置从输入流中读取b.length个字节的数据存放到flush中, 实际读取到的数据要看输入流中的字节数, 最多读取的数量就是flush.length,返回值为实际读取的字节数 */ while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { //将输入流中的数据读取到flush容器中,从flush容器偏移量为0的地方开始,读取最多这么多个字节 //用得到的flush数组构造字符串,从flush数组偏移量为0处开始 String str = new String(buffer, 0, len); //len是当前flush的实际长度 System.out.println(str); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
注:这里解释一下偏移量的概念。就是假如我字节数组下标为0~10,现在偏移量为1,那么字节数据就是从字节数组下标为1的地方开始存放,同时要注意既然偏移了1个单位,那么字节数组可存放的数据个数就为10(1~10)个了
二、FileOutputStream
1.概念
文件输出流是用于将数据写入 File 或 FileDescriptor 的输出流 -百度百科
2.API文档
1)构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file) 创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) 创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。(可追加写出)
FileOutputStream(String name) 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) 创建文件输出流以指定名称写入文件
2)常用方法
void write(int b) 将指定字节写入到此文件输出流。
void write(byte[] b) 将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流。
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从指定的字节数组开始,从偏移量 off开始写入此文件输出流。
3.代码
public class IOTest4 { public static void main(String[] args) { File src = new File("nb.txt"); //文件不存在会自动创建 OutputStream os = null; try { //os = new FileOutputStream(src); os = new FileOutputStream(src,true); //append标识,追加写入 //操作 String message = "change\r\n"; //写入的信息 byte[] data = message.getBytes(); //转换成字节数组(编码) //将字节数组中的数据写入到输出流中 os.write(data, 0, data.length); os.flush(); //写入后及时刷新流 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(os != null) { try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
最后再附上一张图和一篇很好的博客
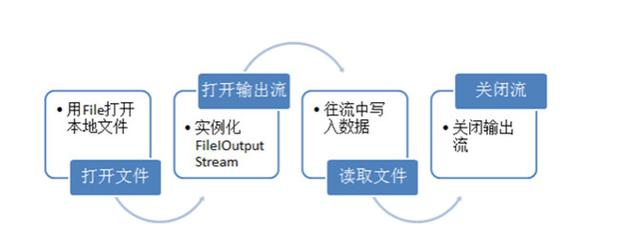
https://blog.csdn.net/jeryjeryjery/article/details/72236643



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号