vueX: vue插件,处理组件之间共享数据的读 && 写
-
引入demo(就一个Count组件,加法计算)
### Count.vue(基础的写死版) <template> <div> <h1>当前求和为 ???</h1> <select> <option value="1">1</option> <option value="2">2</option> <option value="3">3</option> </select> <button type="button">+</button> <button type="button">-</button> <button type="button">求和为奇数再加</button> <button type="button">等一等再加</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'Count', } </script> <style> button { margin-left: 5px; } </style> -
现在使用纯vue来实现
<template> <div> <h1>当前求和为{{sum}}</h1> <!--v-model用来收集用户输入的值,并转换为Number,否则会出现字符串数字拼接,计算结果异常--> <select v-model.number="n"> <!--number修饰符--> <option value="1">1</option> <option value="2">2</option> <option value="3">3</option> </select> <button type="button" @click="increment">+</button> <button type="button" @click="decrement">-</button> <button type="button" @click="incrementOdd">求和为奇数再加</button> <button type="button" @click="incrementWait">等一等再加</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'Count', data(){ return { sum:0, n:1 } }, methods:{ increment(){ // 求和 this.sum += this.n }, decrement(){ // 自减 this.sum -= this.n }, incrementOdd(){ // 奇书 if(this.sum % 2){ this.sum += this.n } }, incrementWait(){ // 计时器等一等 setTimeout(()=>{ this.sum += this.n },1000) }, } } </script> <style> button { margin-left: 5px; } </style> -
vueX原理图解
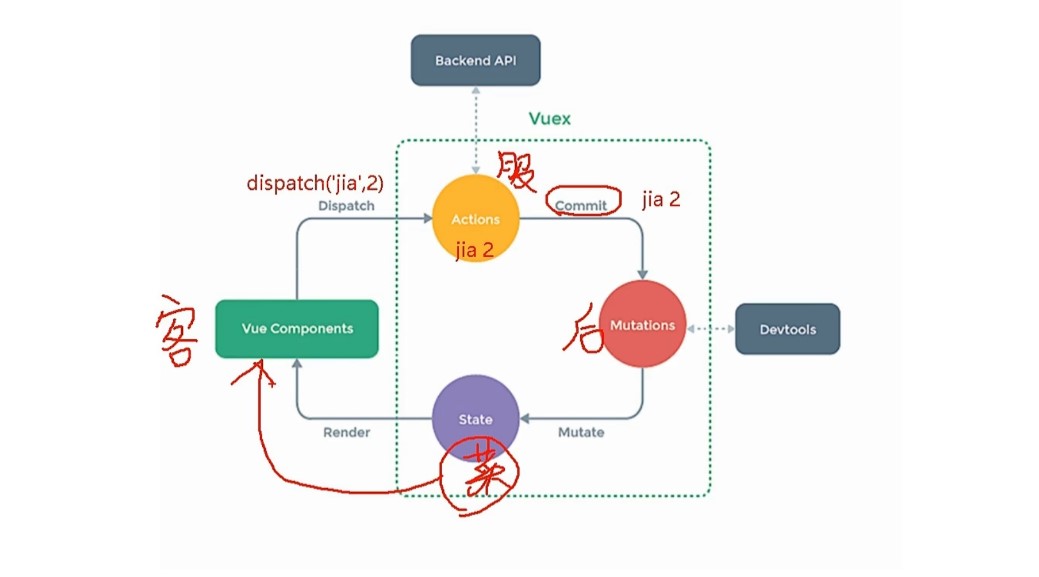
-
注意事项
- Actions 有时候可以pass,即不是必须项(需要和后端交互的时候就必须)
Vuex 环境搭建
- npm i vuex@3 # vue2搭配vuex3的版本,若安装最新版,则出现版本问题,会报错
- Vue.use(vuex)
- store 存放的位置
- vc ==> store
-
store 存放的位置处理(新建store目录,创建index.js)
# index.js import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" Vue.use(Vuex) // 把使用插件的逻辑写在这,而不是写在main.js(会报错,和vue脚手架编译顺序有关系) const actions = {} // 响应组件的动作(服务员) const mutations = {} // 操作 state的数据(厨师) const state = {} // 存储数据(菜) export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, }) # main.js import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' // import store from './store/index.js' import store from './store' // 这种引入方式也可以,store这个名字可以随便取 new Vue({ render: h => h(App), store, // 创建vm的时候,传入store配置项 beforeCreate(){ Vue.prototype.$bus = this } }).$mount('#app') - 现在,在App组件打印vc实例对象,多了一个'vc.$store'属性,包含很多强大的API 比如,dispatch/commit/state -
注意vue脚手架的编译顺序
- 先执行所有的import语句,在执行其他(以下语句,会先执行两个import语句,最后才执行console.log) import test1 from './test1' console.log(100) console.log(200) import test2 from './test2' - 所以,在main.js使用引入插件的通常写法,来引入vuex的时候,会报错(报错提示必须先使用Vue.use(vuex)) ### main.js import store from './store' // 这句会先被执行,所以报错 Vue.use(Vuex) -
搭建vuex环境小结
- 概念: 是vue插件,处理多组件之间的'共享数据',适用于任意组件之间的通讯 - 搭建步骤见上面 -
把Count案例修改成'vuex'版(这里以一个单组件为例)
### index.js import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" Vue.use(Vuex) const actions = {} const mutations = {} const state = { sum:0 // 准备共享的数据 } export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, }) ### Count.vue <template> <div> <!--这里修改成state存放的共享数据--> <h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}</h1> <select v-model.number="n"> <option value="1">1</option> <option value="2">2</option> <option value="3">3</option> </select> <button type="button" @click="increment">+</button> <button type="button" @click="decrement">-</button> <button type="button" @click="incrementOdd">求和为奇数再加</button> <button type="button" @click="incrementWait">等一等再加</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'Count', data(){ return { // sum:0, // 不再存放组件自身 n:1 } }, methods:{ // 以下逻辑要重新写 increment(){ }, decrement(){ }, incrementOdd(){ }, incrementWait(){ }, } } </script> <style> button { margin-left: 5px; } </style>### Count.vue <template> <div> <h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}</h1> ...... </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'Count', data(){ return { n:1 } }, methods:{ increment(){ // this.sum += this.n this.$store.dispatch('jia',this.n) // 调用dispatch分发"动作",并传参 }, decrement(){ }, incrementOdd(){ }, incrementWait(){ }, } } </script> ### index.js import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" Vue.use(Vuex) const actions = { jia(context,value){ // 响应jia动作,context是miniStore对象,value就是传过来的值 context.commit('JIA',value) // 提交动作(一般提交过去的动作,习惯大写命名) } } const mutations = { JIA(state,value){ // 接收动作并处理数据 state.sum += value } } const state = { sum:0 } export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, }) -
加法的运算搞定,其他算法一样的逻辑处理
### Count.vue <template> <div> <h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}</h1> ...... </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'Count', data(){ return { n:1 } }, methods:{ increment(){ ...... }, decrement(){ // his.sum -= this.n this.$store.dispatch('jian',this.n) }, incrementOdd(){ // if(this.sum % 2){ // this.sum += this.n // } this.$store.dispatch('odd',this.n) }, incrementWait(){ // setTimeout(()=>{ // this.sum += this.n // },1000) this.$store.dispatch('wait',this.n) }, } } </script> ### index.js import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" Vue.use(Vuex) const actions = { jia(context,value){ context.commit('JIA',value) }, // 响应动作并提交 jian(context,value){ context.commit('JIAN',value) }, odd(context,value){ context.commit('ODD',value) }, wait(context,value){ context.commit('WAIT',value) } } const mutations = { // 接收动作并处理具体的逻辑 JIA(state,value){ state.sum += value }, JIAN(state,value){ state.sum -= value }, ODD(state,value){ if(state.sum % 2) { state.sum += value } }, WAIT(state,value){ setTimeout(()=>{ state.sum += value },1000) }, } const state = { sum:0 } export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, }) -
可以发现,actions这步其实可以跳过,因为只是提交而已(根据vuex原理图,没有涉及到后端的交互)
一模一样的效果
### index.js import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" Vue.use(Vuex) const actions = { // 注释掉 // jia(context,value){ // context.commit('JIA',value) // }, // jian(context,value){ // context.commit('JIAN',value) // }, odd(context,value){ context.commit('ODD',value) }, wait(context,value){ context.commit('WAIT',value) } } const mutations = { JIA(state,value){ state.sum += value }, JIAN(state,value){ state.sum -= value }, ...... ### Count.vue ...... methods:{ increment(){ // this.sum += this.n // this.$store.dispatch('jia',this.n) // 这里直接提交了,不再进行分发 this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n) }, decrement(){ // his.sum -= this.n // this.$store.dispatch('jian',this.n) this.$store.commit('JIAN',this.n) }, -
目前为止小结
- 组件提交事件,并提交要处理的数据
-vuex 接收事件(数据),和'共享数据'进行交互
-
context小拓展: 当业务逻辑相对复杂的时候,如果全部都在一个函数可能不妥
可以利用context.dispatch()作分发,原本一个函数搞定的事情,拆分成3个搞定
### index.js
......
const actions = {
......
odd(context,value){
// context.commit('ODD',value) // 不再提交,而是进行逻辑分发
console.log('做了一些事情')
context.dispatch('demo1',value) // 分发到demo1,继续处理剩余的逻辑
},
demo1(context,value){
console.log('demo1做的事情')
context.dispatch('demo2',value) // 分发到demo2,继续处理剩余的逻辑
},
demo2(context,value){
console.log('demo2做的事情')
context.commit('ODD',value) // 事情终于做好了,提交到mutations
},
......
}
-
context 是 miniStore,所以'$store'也可以作相同的事情
- 先: $store.dispatch('action中的方法名',数据) - 然后: $store.commit('mutation中的方法名',数据)
钩子getters 介绍(可以理解为'计算属性共享版',而state就是vm的data)
-
概念: 当 state 中的数据需要经过加工后再使用,可以使用 getters 加工
-
引入场景: 把求和放大十倍,可以这么搞(组件里面使用计算属性来实现)
### Count.vue ...... <div> <h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}</h1> <!-- <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{$store.state.sum*10}}</h1> --> <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{tenSum}}</h1> <!--使用计算属性实现--> ...... computed:{ tenSum(){ return this.$store.state.sum * 10 } } -
上述示例有个缺陷,计算属性只能在本组件使用,局限性高,别的组件想使用,不能复用
现在,使用 getters解决这个问题
### index.js import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" Vue.use(Vuex) const actions = { ...... } const mutations = { ...... } const state = { sum:0 } const getters = { //定义getters tenSum(state){ // 接收state加工数据并返回 return state.sum * 10 } } export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, getters // 添加配置项 }) ### Count.vue ...... <div> <h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}</h1> <!-- <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{$store.state.sum*10}}</h1> --> <!-- <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{tenSum}}</h1> --> <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{$store.getters.tenSum}}</h1>
映射mapState && mapGetters(简写代码)
- 引入场景: 增加两个字段,并把插值搞成属性的形式,精简插值代码(vue推荐)
### index.js
......
const state = {
sum:0,
name:'JimGreen', // 新增
age:20
}
......
### Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- <h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}</h1> -->
<h1>当前求和为{{sum}}</h1>
<!-- <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{$store.state.sum*10}}</h1> -->
<!-- <h1>当前和放大十倍: {{tenSum}}</h1> -->
<h1>当前和放大十倍: {{tenSum}}</h1>
<!-- <h1>我是: {{$store.state.name}},我的年龄是: {{$store.state.age}}</h1> -->
<h1>我是: {{name}},我的年龄是: {{age}}</h1>
......
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Count',
data(){
return {
n:1
}
},
methods:{
......
},
computed:{
sum(){ // 精简插值语法
return this.$store.state.sum
},
tenSum(){
return this.$store.getters.tenSum
},
name(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age(){
return this.$store.state.age
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
button {
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
-
计算属性代码中,可以使用 映射 进一步精简
### index.js ...... const state = { sum:0, name:'JimGreen', age:20 } ### Count.vue ...... <script> import {mapState} from 'vuex' // 导入映射函数 export default { name:'Count', data(){ return { n:1 } }, methods:{ ...... }, computed:{ // 全都注释掉 // tenSum(){ // return this.$store.state.sum * 10 // } // sum(){ // return this.$store.state.sum // }, // name(){ // return this.$store.state.name // }, // age(){ // return this.$store.state.age // }, // 解构赋值,注意最后要加逗号,因为下面还有一个 tenSum ...mapState({sum:'sum',name:'name',age:'age'}), // 数组写法也可以,一模一样 // ...mapState(['sum','name','age']), tenSum(){ return this.$store.getters.tenSum } }, mounted(){ // 这里不能简写成{sum,name,age},因为组件没有sum,name,age变量 const dataObj = mapState({sum:'sum',name:'name',age:'age'}) console.log(dataObj) // 包含映射关系的数据对象(比如{sum:func...}) }, } </script> -
mapGetters 是同样的套路
<script> import {mapState,mapGetters} from 'vuex' // 导入 export default { name:'Count', data(){ return { n:1 } }, methods:{ ...... }, computed:{ ...mapState({sum:'sum',name:'name',age:'age'}), ...mapGetters(['tenSum']), // 一样的套路写法(这里使用数组写法) // tenSum(){ // return this.$store.getters.tenSum // } }, mounted(){ ...... }, } </script> -
小结
- mapState()方法用于帮助我们映射state中的数据为计算属性 - mapGetters()方法用于帮助我们映射getters中的数据为计算属性 - 有两种写法 - 对象写法 - 数组写法 - 目的都是为了精简代码mapMutations 和 mapActions
-
methods里面,映射mutations里面的方法(也是精简代码)
### Count.vue(对象写法)
<template>
<div>
......
<!-- <button type="button" @click="increment">+</button> -->
<!--传给mutations的参数,是n,写在这里,-->
<button type="button" @click="increment(n)">+</button>
<!-- <button type="button" @click="decrement">-</button> -->
<button type="button" @click="decrement(n)">-</button>
......
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations} from 'vuex' // 导入mapMutations
export default {
name:'Count',
data(){
return {
n:1
}
},
methods:{
// increment(){
// // this.sum += this.n
// // this.$store.dispatch('jia',this.n)
// this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n)
// },
// decrement(){
// // his.sum -= this.n
// // this.$store.dispatch('jian',this.n)
// this.$store.commit('JIAN',this.n)
// },
// increment对应mutations的'JIA',其他类同
...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
......
},
### index.js
......
const mutations = {
JIA(state,value){ // 要映射的方法源
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state,value){
state.sum -= value
},
......
}
- 数组写法(还要修改html元素里面的方法名称,个人觉得,对象写法比较好...)
### Count.vue
<template>
<div>
......
<!-- <button type="button" @click="increment">+</button> -->
<!-- <button type="button" @click="increment(n)">+</button> -->
<!--修改函数名称为JIA-->
<button type="button" @click="JIA(n)">+</button>
<!-- <button type="button" @click="decrement">-</button> -->
<button type="button" @click="JIAN(n)">-</button>
<!-- <button type="button" @click="decrement(n)">-</button> -->
......
</div>
</template>
......
methods:{
......
// ...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
// 映射的名称,以 mutations里面的为准...
...mapMutations(['JIA','JIAN']),
- 这里如果不想修改html元素的方法名称,可以这么搞(但是不推荐这么写,即使用另外一个函数去代理,该函数体里面调用映射方法并传参)
### Count.vue
<template>
<div>
......
<!--采用之前的写法-->
<button type="button" @click="increment">+</button>
<!-- <button type="button" @click="increment(n)">+</button> -->
<!-- <button type="button" @click="JIA(n)">+</button> -->
<button type="button" @click="decrement">-</button>
<!-- <button type="button" @click="JIAN(n)">-</button> -->
<!-- <button type="button" @click="decrement(n)">-</button> -->
......
</div>
</template>
......
methods:{
increment(){ // 代理函数
this.add(this.n) // 函数体调用映射方法并传参
},
decrement(){
this.subtract(this.n)
},
// 写法不变
...mapMutations({add:'JIA',subtract:'JIAN'}),
- mapActions是一样的套路(对象写法)
### Count.vue
<template>
<div>
......
<!--对象写法,增加传参-->
<button type="button" @click="incrementOdd(n)">求和为奇数再加</button>
<button type="button" @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'Count',
data(){
return {
n:1
}
},
methods:{
// ...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
// incrementOdd(){
// // if(this.sum % 2){
// // this.sum += this.n
// // }
// this.$store.dispatch('odd',this.n)
// },
// incrementWait(){
// // setTimeout(()=>{
// // this.sum += this.n
// // },1000)
// this.$store.dispatch('wait',this.n)
// },
// 映射actions里面的方法
...mapActions({incrementOdd:'odd',incrementWait:'wait'}),
},
......
}
</script>
- 数组写法
<template>
<div>
......
<!-- <button type="button" @click="incrementOdd(n)">求和为奇数再加</button> -->
<!--名称得变-->
<button type="button" @click="odd(n)">求和为奇数再加</button>
<!-- <button type="button" @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加</button> -->
<button type="button" @click="wait(n)">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'Count',
data(){
return {
n:1
}
},
methods:{
...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
// 数组写法
...mapActions(['odd','wait']),
},
......
}
</script>
- 小结
- mapActions方法: 帮助我们生成与actions对话的方法,即包含: $store.disptch(xxx)的函数
- mapMutations方法: 帮助我们生成与mutations对话的方法,即包含: $store.commit(xxx)的函数
- 均支持对象 && 数组 写法
- 注意事项: 两个方法若需要传参,则需要在模板中绑定事件时传递好参数,否则参数默认是'事件对象'
vuex模块化
-
引入场景: 两个组件互相引用vuex的共享数据
新增person组件,列表展示个人信息数据
### Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" />
<button type="button">添加</button>
<ul>
<!--渲染数据-->
<li v-for="person in personList" :key="person.id">{{person.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'Person',
computed:{
// ...mapState(['personList']), // 这里先不这样写
personList(){ // 使用普通的计算属性实现
return this.$store.state.personList
}
}
}
</script>
### index.js
......
const state = {
sum:0,
name:'JimGreen',
age:20,
personList:[ // 新增Person组件数据源
{id:1,name:'JimGreen'},
{id:2,name:'KateGreen'},
{id:3,name:'LiLei'},
{id:4,name:'HanMeiMei'}
]
}
- Person组件实现按钮添加人员信息的功能
### index.js(mutations加工Person组件传过来的数据)
......
const mutations = {
......
ADD_PERSON(state,value){
state.personList.unshift(value) // 往数组最开头插入
}
}
const state = {
sum:0,
name:'JimGreen',
age:20,
personList:[
{id:1,name:'JimGreen'},
{id:2,name:'KateGreen'},
{id:3,name:'LiLei'},
{id:4,name:'HanMeiMei'}
]
}
### Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<!--v-model收集用户输入-->
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" v-model="nameMsg" />
<!--新增add点击事件-->
<button type="button" @click="add">添加</button>
......
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
// import nanoid from 'nanoid' // 这样写会报错,要包裹{}
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name:'Person',
data(){
return {
nameMsg:'' // 默认值
}
},
computed:{
......
},
methods:{
add(){
// 根据用户输入的值,构造数据并传给mutations加工
const personObj = {id:nanoid(),name:this.nameMsg}
this.$store.commit('ADD_PERSON',personObj)
this.nameMsg = ''
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- Count组件引用PersonList数据,可以这么干
### Count.vue
<template>
<div>
......
<h1 style="color: red;">Person组件的总人数为{{personList.length}}</h1>
......
computed:{
// 多映射一个personList字段
...mapState({sum:'sum',name:'name',age:'age',personList:'personList'}),
......
},
- 模块化vuex的思想
- store(原来的结构)
- actions
- mutations
- state
- getters
- 如果组件很多的时候,上述四个子模块的逻辑就很乱了,后期维护相当困难
解决办法:为每一个组件都划分上述四个子模块,逻辑就清晰很多
- store(现在的结构)
- a组件
- actions
- mutations
- state
- getters
- b组件
- actions
- mutations
- state
- getters
### index.js
import Vue from "vue"
import Vuex from "vuex"
Vue.use(Vuex)
const countOptions = { // 存放Count组件逻辑相关
namespaced:true, // 取个名字(必须)
actions:{
jia(context,value){
context.commit('JIA',value)
},
jian(context,value){
context.commit('JIAN',value)
},
odd(context,value){
context.commit('ODD',value)
// context.dispatch('demo1',value)
},
// demo1(context,value){
// console.log('demo1做的事情')
// context.dispatch('demo2',value)
// },
// demo2(context,value){
// console.log('demo2做的事情')
// context.commit('ODD',value)
// },
wait(context,value){
context.commit('WAIT',value)
}
},
mutations:{
JIA(state,value){
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state,value){
state.sum -= value
},
ODD(state,value){
if(state.sum % 2) {
state.sum += value
}
},
WAIT(state,value){
setTimeout(()=>{
state.sum += value
},1000)
},
},
state:{
sum:0,
name:'JimGreen',
age:20,
},
getters:{
tenSum(state){
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
const personOptions = { // 存放Person组件逻辑相关
namespaced:true,
mutations:{
ADD_PERSON(state,value){
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
state:{
personList:[
{id:1,name:'JimGreen'},
{id:2,name:'KateGreen'},
{id:3,name:'LiLei'},
{id:4,name:'HanMeiMei'}
]
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
// actions,
// mutations,
// state,
// getters
modules:{ // 模块化
countAbout:countOptions,// 模块名称
personAbout:personOptions
}
})
### Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{sum}}</h1>
<h1>当前和放大十倍: {{tenSum}}</h1>
<h1>我是: {{name}},我的年龄是: {{age}}</h1>
<h1 style="color: red;">Person组件的总人数为{{personList.length}}</h1>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<!--需要传参-->
<button type="button" @click="increment(n)">+</button>
<button type="button" @click="decrement(n)">-</button>
<button type="button" @click="odd(n)">求和为奇数再加</button>
<button type="button" @click="wait(n)">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'Count',
data(){
return {
n:1
}
},
methods:{
// 传入模块名+配置对象
...mapMutations('countAbout',{increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN',odd:'ODD',wait:'WAIT'}),
......
},
computed:{
// 传入模块名+配置对象
...mapState('countAbout',['name','age','sum']),
...mapState('personAbout',['personList']),
...mapGetters('countAbout',['tenSum'])
......
},
......
}
</script>
- Person组件使用模块化演示(不使用map映射,手动写不那么方便,稍繁琐)
- 拆分index.js,变成 index.js,count.js,person.js
### count.js
export default {
namespaced:true,
actions:{
jia(context,value){
context.commit('JIA',value)
},
jian(context,value){
context.commit('JIAN',value)
},
odd(context,value){
context.commit('ODD',value)
// context.dispatch('demo1',value)
},
wait(context,value){
context.commit('WAIT',value)
}
},
mutations:{
JIA(state,value){
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state,value){
state.sum -= value
},
ODD(state,value){
if(state.sum % 2) {
state.sum += value
}
},
WAIT(state,value){
setTimeout(()=>{
state.sum += value
},1000)
},
},
state:{
sum:0,
name:'JimGreen',
age:20,
},
getters:{
tenSum(state){
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
### person.js
export default {
namespaced:true,
actions:{
// 新增王姓人员专属api
addPersonWang(context,value){
if(value.name.indexOf('王') == 0){
context.commit('ADD_PERSON',value)
}else{
alert('王姓专属噢!')
}
}
},
mutations:{
ADD_PERSON(state,value){
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
state:{
personList:[
{id:1,name:'JimGreen'},
{id:2,name:'KateGreen'},
{id:3,name:'LiLei'},
{id:4,name:'HanMeiMei'}
]
},
getters:{ // 新增 输出最开头人员的名字
firstPersonName(state){
return state.personList[0].name
}
}
}
### index.js
import Vue from "vue"
import Vuex from "vuex"
import countOptions from './count.js' // 引入
import personOptions from './person.js'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
countAbout:countOptions, // 配置
personAbout:personOptions
}
})
- Person组件的逻辑如下
### Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" v-model="nameMsg" />
<button type="button" @click="add">添加</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="person in personList" :key="person.id">{{person.name}}</li>
</ul>
<!--新增以下三个逻辑-->
<h1>当前求和为: {{sum}}</h1>
<h1>第一个人的姓名为: {{firstPersonName}}</h1>
<button type="button" @click="addWang">添加王姓人员</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name:'Person',
data(){
return {
nameMsg:''
}
},
computed:{
personList(){
return this.$store.state.personAbout.personList // 通过 personAbout.personList 正常展示数据
},
sum(){
return this.$store.state.countAbout.sum // 通过countAbout.sum 正常展示数据
},
firstPersonName(){
// return this.$store.getters.personAbout.firstPersonName // 语法不是这样写的
return this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName'] // 可以这样获取属性['属性值']
}
},
methods:{
add(){
const personObj = {id:nanoid(),name:this.nameMsg}
this.$store.commit('personAbout/ADD_PERSON',personObj)
this.nameMsg = ''
},
addWang(){ // 分发actions
const personObj = {id:nanoid(),name:this.nameMsg}
// 注意这种语法: dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang',personObj)
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang',personObj)
this.nameMsg = ''
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- actions和后端交互演示
- 后端API地址: https://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social
- 返回一句话
### person.js
import axios from 'axios'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid' // 不能写成: import nanoid from 'nanoid',会报错
export default {
namespaced:true,
actions:{
addPersonWang(context,value){
......
},
addPersonServer(context){
// 向后端发请求并打包数据,发送给mutations
axios.get('https://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social').then(
(response)=>{
context.commit('ADD_PERSON',{id:nanoid(),name:response.data})
},
(error)=>{alert(error.message)}
)
}
},
mutations:{
ADD_PERSON(state,value){
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
state:{
personList:[
......
]
},
getters:{
......
}
}
### Person.vue
<template>
<div>
......
// 新增
<button type="button" @click="addPersonServer">后端交互</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name:'Person',
data(){
......
},
computed:{
......
},
methods:{
......
addPersonServer(){ // 分发请求
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonServer')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
7.模块化+命名空间(小结)
-
目的:让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确。
-
修改
store.jsconst countAbout = { namespaced:true,//开启命名空间 state:{x:1}, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }, getters: { bigSum(state){ return state.sum * 10 } } } const personAbout = { namespaced:true,//开启命名空间 state:{ ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { countAbout, personAbout } }) -
开启命名空间后,组件中读取state数据:
//方式一:自己直接读取 this.$store.state.personAbout.list //方式二:借助mapState读取: ...mapState('countAbout',['sum','school','subject']), -
开启命名空间后,组件中读取getters数据:
//方式一:自己直接读取 this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName'] //方式二:借助mapGetters读取: ...mapGetters('countAbout',['bigSum']) -
开启命名空间后,组件中调用dispatch
//方式一:自己直接dispatch this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang',person) //方式二:借助mapActions: ...mapActions('countAbout',{incrementOdd:'jiaOdd',incrementWait:'jiaWait'}) -
开启命名空间后,组件中调用commit
//方式一:自己直接commit this.$store.commit('personAbout/ADD_PERSON',person) //方式二:借助mapMutations: ...mapMutations('countAbout',{increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}), -
手写语法方面,只有state语法和想象的一样,其他均不一样





