迭代器模式
The Iterator design pattern provides a way to acess the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation.
迭代器模式提供了顺序访问聚合对象中元素的方式,而不需要暴露底层表示。
UML Class Diagram
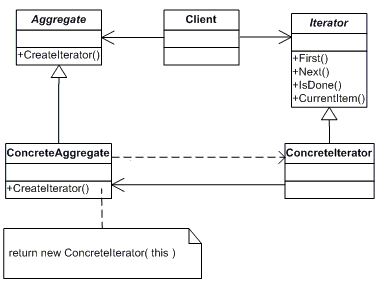
Iterator; This is going to be an interface defining the operations for accessing and traversing elements in a sequence.
ConcreteIterator: This is going to be a concrete class implementing the Iterator interface and providing implementation for Iterator interface method. This class also keep track of the current position of the elment in the traversal.
Aggregate: This is going to be an interface that defines an operation to create an interator object.
ConcreteAgregate: This is going to be a conrecte class that implements the Aggreate interface to return an instance of the proper Conrete Itorator class i.e. an instance of the Iterator class.
Client:This is class that going to use the Iterator and Aggregate interface and access the elments.
Structure Code in C#

public interface IAggregate { IIterator CreateIterator(); } public class ConcreteAggregate : IAggregate { private List<object> items = new List<object>(); public IIterator CreateIterator() { return new ConcreteIterator(this); } public Int32 Count { get { return items.Count; } } public object this[Int32 index] { get { return items[index]; } set { items.Insert(index, value); } } }

public interface IIterator { object First(); object Next(); bool IsLast(); object CurrentItem(); } public class ConcreteIterator: IIterator { ConcreteAggregate aggregate; Int32 current = 0; public ConcreteIterator(ConcreteAggregate aggregate) { this.aggregate = aggregate; } public object First() { return aggregate[0]; } public object Next() { object next = null; if (current < aggregate.Count - 1) next = aggregate[++current]; return next; } public object CurrentItem() { return aggregate[current]; } public bool IsLast() { return current >= aggregate.Count; } }
Why do we need to use the Iterator Design Pattern in C#?
The Iterator Design Pattern in C# allows us to Access the elements of a collection wihout exposing its internal data structure. That means it allows you to navigate through a different collection of data using a common interface wihout knowing about their underlying implementation.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号