Non-maximum suppression(非极大值抑制算法)
在RCNN系列目标检测中,有一个重要的算法,用于消除一些冗余的bounding box,这就是non-maximum suppression算法。
这里有一篇博客写的挺好的:
http://www.cnblogs.com/liekkas0626/p/5219244.html
借用博客里的两张图,如有问题,请联系我删除。
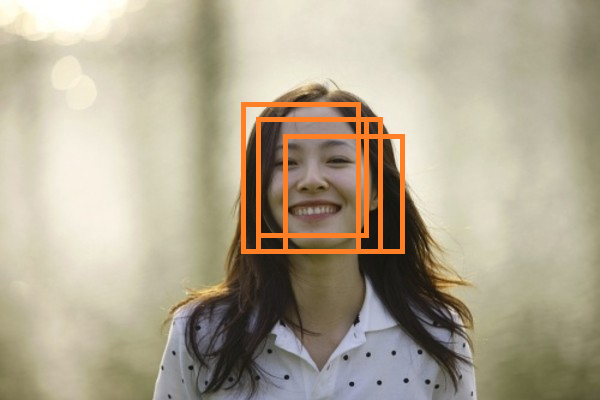
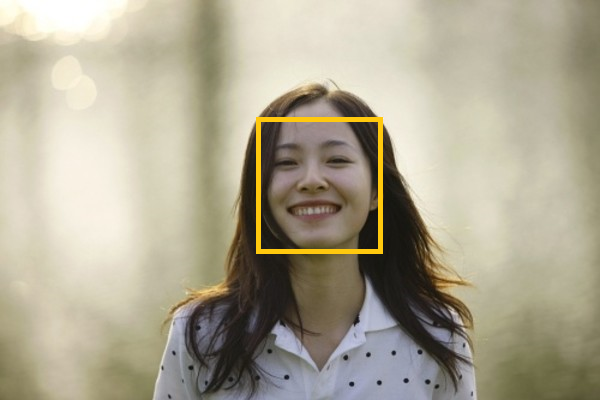
在目标检测中,这些bounding box都表示检测到了人脸,并且会给每一个bounding box一个score,最终我们需要只保留score最大的bounding box(记为bounding box1),將与bounding box1 overlap (重叠) 较大的一些bounding box消除,即只保留在这个局部区域score最高的一个bounding box。可能在一张图中有多个人脸,那么我们就需要保留各个局部区域score最大的bounding box,两个bounding box的重叠程度一般用IOU的值作为衡量,
IOU = 两个bounding box的围成的区域的交集 / 两个bounding box围成区域的并集。
1 function pick = nms(boxes, overlap) 2 % top = nms(boxes, overlap) 3 % Non-maximum suppression. (FAST VERSION) 4 % Greedily select high-scoring detections and skip detections 5 % that are significantly covered by a previously selected 6 % detection. 7 %################################################################ 8 % input ----- boxes: object detection window 9 % size(boxes) = (n,5) 10 % n --- the number of window 11 % (xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax, score) 12 % overlap: suppression threshold 13 % 14 % output ----- pick:the index of reserved window 15 if isempty(boxes) 16 pick = []; 17 return; 18 end 19 20 x1 = boxes(:,1); 21 y1 = boxes(:,2); 22 x2 = boxes(:,3); 23 y2 = boxes(:,4); 24 s = boxes(:,end); 25 26 % calculate the area of all detections 27 area = (x2-x1+1) .* (y2-y1+1); 28 % vals is the sorted elments in ascending order, I is the corresponding index 29 [vals, I] = sort(s); 30 31 pick = s*0; 32 counter = 1; 33 while ~isempty(I) 34 last = length(I); 35 i = I(last); 36 pick(counter) = i; 37 counter = counter + 1; 38 39 xx1 = max(x1(i), x1(I(1:last-1))); 40 yy1 = max(y1(i), y1(I(1:last-1))); 41 xx2 = min(x2(i), x2(I(1:last-1))); 42 yy2 = min(y2(i), y2(I(1:last-1))); 43 44 w = max(0.0, xx2-xx1+1); 45 h = max(0.0, yy2-yy1+1); 46 47 inter = w.*h; 48 o = inter ./ (area(i) + area(I(1:last-1)) - inter); 49 50 I = I(find(o<=overlap)); 51 end 52 53 pick = pick(1:(counter-1));
越努力,越幸运


