异常处理——课后作业
2017-11-16 23:15 默默不语 阅读(252) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报1. 请阅读并运行AboutException.java示例,然后通过后面的几页PPT了解Java中实现异常处理的基础知识。
程序源代码
public class EmbededFinally { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }
结果截图

2. 请尝试解释以下奇怪的现象

jvm在处理浮点数时,生成的是ddiv字节码指令,i/0,0转化为浮点数0.0,而0.0是double类型的,并不精确,所以不会抛出异常。
jvm在处理整数时,生成的是idiv字节码指令,整数除0就是除0,会抛出异常。
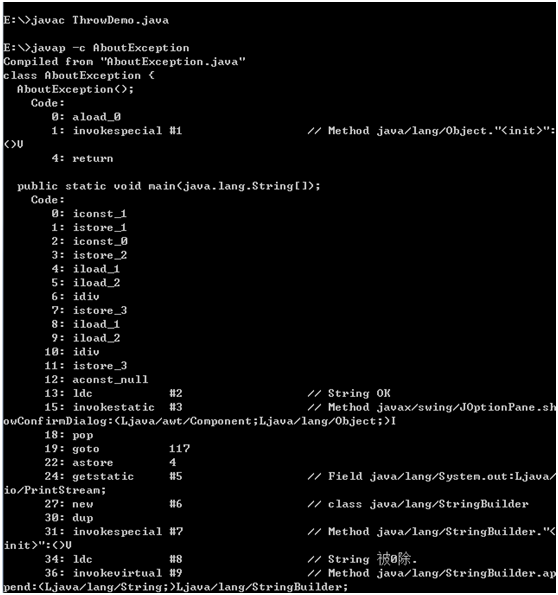

3. 阅读以下代码(CatchWho.java),写出程序运行结果:
程序源代码
public class CatchWho { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
运行结果
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/内层try-catch
发生ArithmeticException
原因分析
注意其结构,里面的try抛出异常一,对应的catch(紧跟着的catch)接收一并执行,外层的try抛出异常二,对应的catch接收二并执行,抛出异常和接收异常这执行可以看成是一个单一的动作操作,最后的catch就没有抛出这一动作执行,所以不运行(因为抛出异常一已被接住)。
4.写出CatchWho2.java程序运行的结果
程序源代码
public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
运行结果
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/外层try-catch
原因分析
此例题和上面例题的区别就在于,里面的catch所接住的方向变了。
按着程序顺序分析下来,当里面的try抛出异常时,只有外面的catch能接住,那么开始执行外面的catch,顺序就从刚才执行的语句之下执行下去了,即便是外面的catch交换顺序,结果一样不变。
由两题总结:try catch这一模式,是有顺序依据的,当执行try语句是,紧接着的就是所对应的catch来执行,然后接着catch继续执行下去。
5. 请先阅读 EmbedFinally.java示例,再运行它,观察其输出并进行总结。
程序源代码
public class EmbededFinally { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }
结果截图

原因分析
finally是无论是否出现异常都会执行的,在第三个try中出现异常,紧跟着的catch已经接收到,但此并不算第二个try出现异常,因为异常已经解决,那么之后就不会显示第二个和第一个catch的内容了。
6. 辨析:finally语句块一定会执行吗?
请通过 SystemExitAndFinally.java示例程序回答上述问题
程序源代码
public class SystemExitAndFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0); } finally { System.out.println("in finally"); } } }
结果截图

分析
JVM是java虚拟机,finally是由JVM保证执行,而System.exit(0)是正常退出程序,结束JVM的运行,那么最后finally就不再执行。
finally语句不被执行的唯一情况是先执行了用于终止程序的System.exit()方法。
7.编写一个程序,此程序在运行时要求用户输入一个整数,代表某门课的考试成绩,程序接着给出“不及格”、“及格”、“中”、“良”、“优”的结论。
要求程序必须具备足够的健壮性,不管用户输入什么样的内容,都不会崩溃。
程序源代码
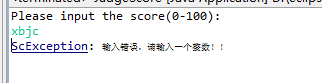
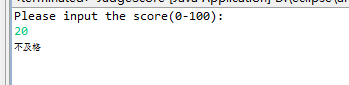
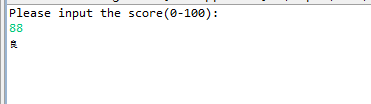
import java.util.Scanner; public class JudgeScore { /** * @param args */ //信1605-2 20163691 陈美琪 public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("Please input the score(0-100):");//提示用户输入成绩 try { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String score=input.nextLine();//以字符串形式输入成绩 int flag=0; boolean result=score.matches("[0-9]+"); if(result==true)//用户输入的均为整数 { int sc=Integer.parseInt(score);//将字符串类型转换为整数 //用户输入的数据为整数 if (sc<0||sc>100) { throw new ScException("输入范围不正确!"); } else if(sc>=90&&sc<=100)//90-100 优 { System.out.println("优"); } else if(sc>=80&sc<90)//80-90 良 { System.out.println("良"); } else if(sc>=70&&sc<80)//70-80 中 { System.out.println("中"); } else if(sc>=60&&sc<=70)//60-70 及格 { System.out.println("及格"); } else//0-60 不及格 { System.out.println("不及格"); } } else { throw new ScException("输入错误,请输入一个整数!!"); } } catch(ScException e) { System.out.println(e); } } } class ScException extends Exception//定义异常处理类 { public ScException(String msg)//构造函数 { super(msg); } }
结果截图






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!