MNIST手写数字图片识别(线性回归、CNN方法的手工及框架实现)(未完待续)
0-Background
作为Deep Learning中的Hello World 项目无论如何都要做一遍的。
代码地址:Github 练习过程中将持续更新blog及代码。
第一次写博客,很多地方可能语言组织不清,请多多提出意见。。谢谢~
0.1 背景知识:
- Linear regression
- CNN
LeNet-5
AlexNet
ResNet
VGG
- 各种regularization方式
0.2 Catalog
1-Prepare
- Numpy 开源的数值计算库
- matplotlib Python 的 2D绘图库
- TensorFlow 开源的人工智能学习系统
- Keras 基Tensorflow、Theano以及CNTK后端的一个高层神经网络API
2-MNIST
MNIST作为NIST的一个超集,是一个由来自 250 个不同人手写的数字构成。其中包含60,000个训练样本和10,000个测试样本。
加载MNIST
import numpy as np
import os
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class load:
def __init__(self,
path='mnist'):
self.path = path
def load_mnist(self):
"""Read train and test dataset and labels from path"""
train_image_path = 'train-images.idx3-ubyte'
train_label_path = 'train-labels.idx1-ubyte'
test_image_path = 't10k-images.idx3-ubyte'
test_label_path = 't10k-labels.idx1-ubyte'
with open(os.path.join(self.path, train_label_path), 'rb') as labelpath:
magic, n = struct.unpack('>II', labelpath.read(8))
labels = np.fromfile(labelpath, dtype=np.uint8)
train_labels = labels.reshape(len(labels), 1)
with open(os.path.join(self.path, train_image_path), 'rb') as imgpath:
magic, num, rows, cols = struct.unpack('>IIII', imgpath.read(16))
images = np.fromfile(imgpath,
dtype=np.uint8).reshape(len(train_labels), 784)
train_images = images
with open(os.path.join(self.path, test_label_path), 'rb') as labelpath:
magic, n = struct.unpack('>II', labelpath.read(8))
labels = np.fromfile(labelpath,
dtype=np.uint8)
test_labels = labels.reshape(len(labels), 1)
with open(os.path.join(self.path, test_image_path), 'rb') as imgpath:
magic, num, rows, cols = struct.unpack('>IIII', imgpath.read(16))
images = np.fromfile(imgpath, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(len(test_labels), 784)
test_images = images
return train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels = load().load_mnist()
print('train_images shape:%s' % str(train_images.shape))
print('train_labels shape:%s' % str(train_labels.shape))
print('test_images shape:%s' % str(test_images.shape))
print('test_labels shape:%s' % str(test_labels.shape))
np.random.seed(1024)
trainImage = np.random.randint(60000, size=4)
testImage = np.random.randint(10000, size=2)
img1 = train_images[trainImage[0]].reshape(28, 28)
label1 = train_labels[trainImage[0]]
img2 = train_images[trainImage[1]].reshape(28, 28)
label2 = train_labels[trainImage[1]]
img3 = train_images[trainImage[2]].reshape(28, 28)
label3 = train_labels[trainImage[2]]
img4 = train_images[trainImage[3]].reshape(28, 28)
label4 = train_labels[trainImage[3]]
img5 = test_images[testImage[0]].reshape(28, 28)
label5 = test_labels[testImage[0]]
img6 = test_images[testImage[1]].reshape(28, 28)
label6 = test_labels[testImage[1]]
plt.figure(num='mnist', figsize=(2, 3))
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.title(label1)
plt.imshow(img1)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.title(label2)
plt.imshow(img2)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.title(label3)
plt.imshow(img3)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.title(label4)
plt.imshow(img4)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.title(label5)
plt.imshow(img5)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.title(label6)
plt.imshow(img6)
plt.show()
运行得到输出:
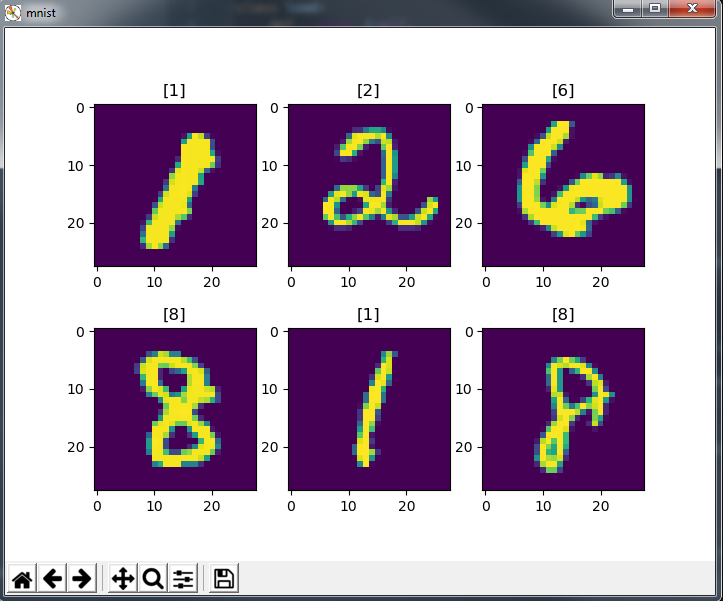
3-LinearRegression
采用线性回归的方式对MNIST数据集训练识别。
采用2层网络,hidden layer具有四个神经元,激活函数分别使用Tanh和ReLu。
由于MNIST是一个多分类问题,故输出层采用Softmax作为激活函数,并使用cross entropy作为Loss Function。
3.1 使用Numpy实现
3.1.1 通过Tran data、label获取 layer size
Code:
def layer_size(X, Y):
"""
Get number of input and output size, and set hidden layer size
:param X: input dataset's shape(m, 784)
:param Y: input labels's shape(m,1)
:return:
n_x -- the size of the input layer
n_h -- the size of the hidden layer
n_y -- the size of the output layer
"""
n_x = X.T.shape[0]
n_h = 4
n_y = Y.T.shape[0]
return n_x, n_h, n_y
3.1.2 初始化参数
初始化W1、b1、W2、b2*
W初始化为非0数字
b均初始化为0
Code:
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Initialize parameters
:param n_x: the size of the input layer
:param n_h: the size of the hidden layer
:param n_y: the size of the output layer
:return: dictionary of parameters
"""
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2
}
return parameters
3.1.3 Forward Propagation
ReLu采用\((|Z|+Z)/2\)的方式实现
def ReLu(Z):
return (abs(Z) + Z) / 2
def forward_propagation(X, parameters, activation="tanh"):
"""
Compute the forword propagation
:param X: input data (m, n_x)
:param parameters: parameters from initialize_parameters
:param activation: activation function name, has "tanh" and "relu"
:return:
cache: caches of forword result
A2: sigmoid output
"""
X = X.T
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
if activation == "tanh":
A1 = np.tanh(Z1)
elif activation == "relu":
A1 = ReLu(Z1)
else:
raise Exception('Activation function is not found!')
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-Z2))
cache = {"Z1": Z1,
"A1": A1,
"Z2": Z2,
"A2": A2}
return A2, cache



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步