array
数组容器 array
首先惯例引入头文件
#include <array>
然后定义一个数组
std::array<int,10> a;
表示我创建了一个数组a,含有10个 int 型的元素。
或者可以在声明的同时初始化这个数组
std::array<int,10> a{};
这样数组 a 里面的 10 个值就都被初始化为 0 了。
注意,数组在定义时,必须同时定义元素的个数。并且这里定义为10个之后,数组a 就永远只能有10个空间,不能改变。
或者我们在初始化的同时给其赋值,就像c语言的数组一样
std::array<int,10> a{1,2,3,4,4};
但是我在这个数组里面只写了5个值,也就是说剩下的5个值将被初始化为0。
我们来看一下array的成员函数,在下面这个网站上可以查询到
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/array/array/?kw=array
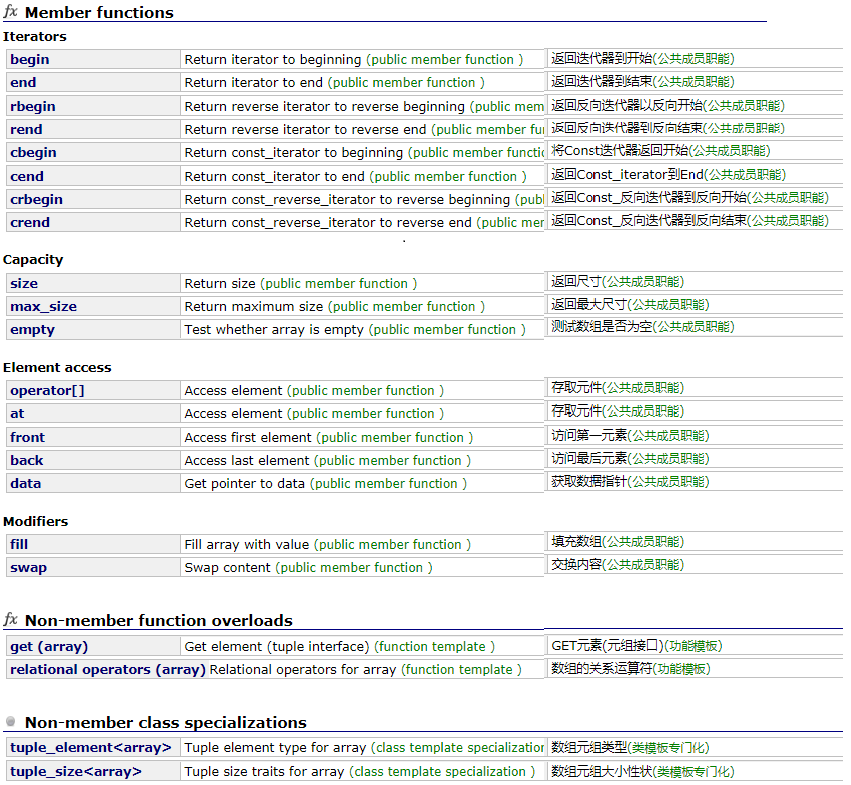
我们用一个例子挨个试一下这些函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { std::array<int,10> a{1,2,3,4,4}; array<int,10> b{}; cout<<a.size()<<endl; //数组长度 cout<<a.max_size()<<endl; //数组可容纳最大容量 if(a.empty()) //判断数组是否为空 cout<<"empty"<<endl; else { cout<<"no empty"<<endl; } for(auto i = a.begin();i != a.end();i++) //返回a的首地址和尾地址 { cout<<*i<<" "; } cout<<endl; cout<<a.at(3)<<endl; //返回第4个元素的值 a[3] cout<<a.front()<<endl; //返回第1个元素的值 a[0] cout<<a.back()<<endl; //返回最后一个元素的值 cout<<&a[0]<<endl; //数组首地址 cout<<a.data()<<endl; //数组首地址 a.fill(19); //用参数填充数组,本代码执行后数组将被初始化为10个19 cout<<"填充后的a: "; for(auto i = a.begin();i != a.end();i++) //返回a的首地址和尾地址 { cout<<*i<<" "; } cout<<endl; b.fill(20); a.swap(b); //交换a和b两个数组的数据 cout<<"交换后的a: "; for(auto i = a.begin();i != a.end();i++) //返回a的首地址和尾地址 { cout<<*i<<" "; } cout<<endl; cout<<"交换后的b: " ; for(auto i = b.begin();i != b.end();i++) //返回a的首地址和尾地址 { cout<<*i<<" "; } cout<<endl; }
输出如下
10 10 no empty 1 2 3 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 4 1 0 0x7ffc199b22f0 0x7ffc199b22f0 填充后的a: 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 交换后的a: 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 交换后的b: 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19



