栈和队列
栈
栈就像一个弹匣,一个个往里放子弹,你最后放进去的子弹,最先打出来,如果不打出后面的子弹,那你先放的子弹就打不出来。
如图所示:
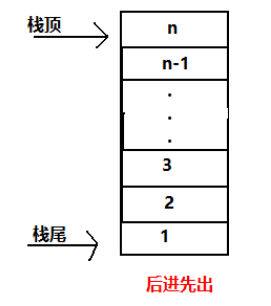
后来者居上,后存入的数据放在栈顶,先存入的数据放于栈底,只有把栈顶部的数据拿出来,才能拿到下面 先存入的数据。
我们用链表写一个链栈,因为基本都是前面单向链表的知识,所以这里不单独列出每个函数的功能了。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> typedef struct node { int data; struct node *next; }stack; /***************函数声明*****************/ stack *BuildStack(); int PushStack(stack *p_stack,int data); int ReadStackTop(stack *p_stack); void ReadStackData(stack *p_stack); int PopStack(stack *p_stack); void FreeStatic(stack *p_stack); stack *CreateStack(stack *p_stack); int EmptyStack(stack *p_stack); /***************************************** *函数作用:创建一个节点 *输入参数:节点数据 *返 回 值:头节点 *备 注: *****************************************/ stack *BuildStack(int data) { stack *p_creat = NULL; p_creat = (stack *)malloc(sizeof(stack)); if (p_creat == NULL) { printf("ERROR:BuildStack创建节点失败\n"); exit(0); } memset(p_creat,0,sizeof(stack)); p_creat->data = data; p_creat->next = NULL; return p_creat; } /***************************************** *函数作用:创建一个栈 *输入参数:栈 第一个元素值 *返 回 值:栈内第一个(最后一个元素) *备 注: *****************************************/ stack *CreateStack(stack *p_stack) { stack *p_tmp = BuildStack(0); p_stack = p_tmp; p_tmp->next = NULL; return p_tmp; } /***************************************** *函数作用:压栈(入栈) *输入参数:栈指针,加入的数据 *返 回 值:成功1 失败0 *备 注:在栈顶存入数据(链表尾) *****************************************/ int PushStack(stack *p_stack,int data) { stack *p_creat = BuildStack(data); stack *p_tmp = p_stack; if (p_stack == NULL) { printf("ERROR:PushStack该栈未初始化\n"); return 1; } else { while(p_tmp->next != NULL) { p_tmp = p_tmp->next; } p_tmp->next = p_creat; if (data == ReadStackTop(p_stack)) { printf("存入栈顶成功\n"); return 1; } else { printf("ERROR:PushStack存入栈顶失败\n"); return 0; } } } /***************************************** *函数作用:读栈顶元素值 *输入参数:栈 *返 回 值:栈顶数据 *备 注: *****************************************/ int ReadStackTop(stack *p_stack) { stack *p_tmp = p_stack; if (EmptyStack(p_stack) == 0) { printf("ERROR:ReadStackTop 空栈 读取栈顶元素失败\n"); return; } else { while(p_tmp->next != NULL) { p_tmp = p_tmp->next; } printf("栈顶的值为%d\n",p_tmp->data); return p_tmp->data; } } /***************************************** *函数作用:读栈里所有值 *输入参数:栈 *返 回 值: *备 注: *****************************************/ void ReadStackData(stack *p_stack) { stack *p_tmp = p_stack->next; int i = 0; printf("------------------------\n"); while(p_tmp != NULL) { printf("%d\t",p_tmp->data); p_tmp = p_tmp->next; i++; } printf("\n------------------------\n"); } /***************************************** *函数作用:出栈 *输入参数:栈 *返 回 值:成功1 失败0 *备 注: *****************************************/ int PopStack(stack *p_stack) { stack *p_tmp = p_stack,*p_free = p_stack; if (EmptyStack(p_stack) == 0) { printf("ERROR:PopStack 空栈 出栈失败\n"); return 0; } else { while(p_free->next != NULL) { p_tmp = p_free; p_free = p_free->next; } p_tmp->next = NULL; free(p_free); return 1; } } /***************************************** *函数作用:清空栈 *输入参数:栈 *返 回 值: *备 注: *****************************************/ void FreeStatic(stack *p_stack) { //p_tmp从头节点开始一路往后指,遇到不为空(需要free)的节点便将该节点交给p_free释放 stack *p_tmp = p_tmp,*p_free = NULL; while(p_tmp != NULL) { p_free = p_tmp; p_tmp = p_tmp->next; free(p_free); } } /***************************************** *函数作用:判断栈是否为空 *输入参数:栈 *返 回 值:0为空 1非空 *备 注: *****************************************/ int EmptyStack(stack *p_stack) { stack *p_tmp = p_stack; if (p_stack->next == NULL) { return 0; } return 1; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { //创建一个栈 stack *p_stack = CreateStack(p_stack); //依次从栈顶加入数个数据 PushStack(p_stack,5); ReadStackData(p_stack); PushStack(p_stack,10); ReadStackData(p_stack); PushStack(p_stack,15); ReadStackData(p_stack); //出栈 PopStack(p_stack); ReadStackData(p_stack); //读栈顶元素 ReadStackTop(p_stack); //一个一个全扔出去 PopStack(p_stack); PopStack(p_stack); ReadStackData(p_stack); //空栈时出栈 PopStack(p_stack); FreeStatic(p_stack); return 0; }
运行结果如下,充分说明我们的代码的正确:

队列
队列就类似于我们排队买票。
先来排队的人就先买票,后来的人在后面排队,只有前面的买完票了,离开之后,后面的人才可以买到票。
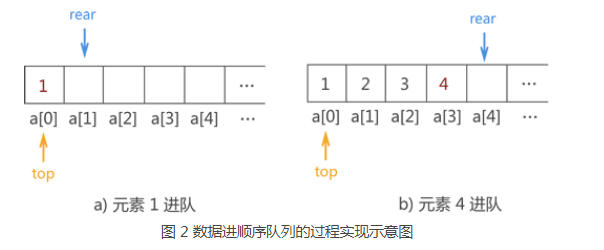
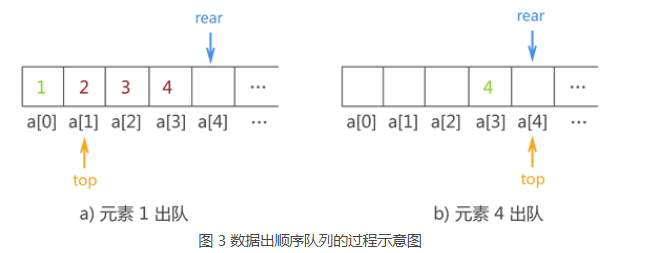
下面我们用一个数组当做队列,两个指针分别指向队列的头和队列尾,将他们封进一个结构体里
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct Queue { int a[10]; int head; //指向数组头 int tail; //指向数组尾 }queue; /************函数声明************/ queue *QueueInit(void); int InQueue(queue *p_queue,int data); int OutQueue(queue *p_queue); void PrintfQueue(queue *p_queue); /******************** *函数功能:队列初始化 *输入参数: *返 回:新建队列名 *********************/ queue *QueueInit(void) { queue *p_creat = NULL; p_creat = (queue *)malloc(sizeof(queue)); if (p_creat == NULL) { printf("ERROR:QueueInit队列初始化失败\n"); exit(0); } p_creat->head = 0; p_creat->tail = 0; return p_creat; } /******************** *函数功能:在队里末尾插入新数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 data 新加入数据 *返 回: *********************/ int InQueue(queue *p_queue,int data) { p_queue->a[p_queue->tail] = data; p_queue->tail++; return data; } /******************** *函数功能:队列头删除一个数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 *返 回: *********************/ int OutQueue(queue *p_queue) { p_queue->a[p_queue->head] = 0; p_queue->head++; return 0; } /******************** *函数功能:打印队列全部数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 *返 回: *********************/ void PrintfQueue(queue *p_queue) { int i = 0; int tmp = p_queue->head; printf("--------------------\n"); for (i = 0; i < 20; ++i) { if (tmp+i != p_queue->tail) { printf("%d\t",p_queue->a[tmp+i]); } else{break;} } printf("\n--------------------\n"); } int main() { queue *p_queue = QueueInit(); InQueue(p_queue,1); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,2); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,3); PrintfQueue(p_queue); OutQueue(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); OutQueue(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); return 0; }
运行结果如下:

看上去十分美好,就是我想要的结果,但是如果我打印整个数组,就会发现问题
//打印整个数组 for ( i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { printf("%d\t", p_queue->a[i]); }

对,数组前面OutQueue的两个元素是没了,但是这个坑还留着,浪费了空间
而且我定义结构体时也只给了数组10个坑,这10个坑用完了就没了
针对这种情况,我们对刚才的队列做如下改动:
首先define定义一个CUBAGE 替代数组容量
#define CUBAGE 10 //队列数组容量
当尾指针指向数组的末尾时,如果前面还有空间,则尾指针指向数组首地址,让前面已经走掉的坑位重复利用
在调试到这里时,我遇到一个问题:
我采取判断队列是否满员的方式是 p_queue->tail == p_queue->head
这就有了麻烦,就是在初始化队列的时候头尾指针确实是相等的,所以如果加入了这个条件,必须想办法让他跳过初始化之后第一次给队列赋值的判断,所以这里我放了一个标志位flg,初始化的时候 flg = 1,第一次赋值过后flg变为0,所以在判断满员的同时判断flg,若 flg = 0 则已经完成了第一次的赋值 这个时候再用头尾指针相等就可以判断是否满员了。
所以插入数据函数更改为:
/******************** *函数功能:在队里末尾插入新数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 data 新加入数据 *返 回:data 成功 0失败 *********************/ int InQueue(queue *p_queue,int data) { //尾指针走到最后 然后返回队列头 if(p_queue->tail == CUBAGE) { p_queue->tail = 0; } //尾指针再一次和头指针相等时 判断为满 if (p_queue->tail == p_queue->head && flg == 0) { printf("ERROR:InQueue队列已满加入失败\n"); return 0; } p_queue->a[p_queue->tail] = data; p_queue->tail++; flg = 0; return data; }
全部代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define CUBAGE 5 //队列数组容量 int flg; typedef struct Queue { int a[CUBAGE]; int head; //指向数组头 int tail; //指向数组尾 }queue; /************函数声明************/ queue *QueueInit(void); int InQueue(queue *p_queue,int data); int OutQueue(queue *p_queue); void PrintfQueue(queue *p_queue); /******************** *函数功能:队列初始化 *输入参数: *返 回:新建队列名 *********************/ queue *QueueInit(void) { queue *p_creat = NULL; p_creat = (queue *)malloc(sizeof(queue)); if (p_creat == NULL) { printf("ERROR:QueueInit队列初始化失败\n"); exit(0); } memset(p_creat,0,sizeof(p_creat)); p_creat->head = 0; p_creat->tail = 0; flg = 1; return p_creat; } /******************** *函数功能:在队里末尾插入新数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 data 新加入数据 *返 回:data 成功 0失败 *********************/ int InQueue(queue *p_queue,int data) { //尾指针走到最后 然后返回队列头 if(p_queue->tail == CUBAGE) { p_queue->tail = 0; } //尾指针再一次和头指针相等时 判断为满 if (p_queue->tail == p_queue->head && flg == 0) { printf("ERROR:InQueue队列已满加入失败\n"); return 0; } p_queue->a[p_queue->tail] = data; p_queue->tail++; flg = 0; return data; } /******************** *函数功能:队列头删除一个数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 *返 回: *********************/ int OutQueue(queue *p_queue) { p_queue->a[p_queue->head] = 0; p_queue->head++; if (p_queue->head == CUBAGE) { p_queue->head = 0; } return 0; } /******************** *函数功能:打印队列全部数据 *输入参数: queue 队列名 *返 回: *********************/ void PrintfQueue(queue *p_queue) { int i = 0; printf("--------------------\n"); for (i = 0; i < CUBAGE; ++i) { printf("%d\t",p_queue->a[i]); } printf("\n--------------------\n"); } int main() { queue *p_queue = QueueInit(); InQueue(p_queue,1); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,2); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,3); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,4); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,5); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InQueue(p_queue,6); PrintfQueue(p_queue); return 0; }
测试暂时没有什么问题,接下来我们看一下熟悉的链表操作。。。
熟悉的malloc熟悉的memset熟悉的末尾增加熟悉的释放。。。
#include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }node; typedef struct Queue { int size_queue; struct Queue *head; struct Queue *tail; }queue; /*******函数初始化********/ node *CreatNode(int data); queue *CreatQueue(void); int InsertQueueData(queue *p_queue,int data); void PrintfQueue(queue *p_queue); void DeleteQueueData(queue *p_queue); void FreeQueue(queue *p_queue); /******************** *函数功能:新建节点 *输入参数:新数据 *返回值 :新节点指针 *********************/ node *CreatNode(int data) { node *p_creat = NULL; p_creat = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node)); if (p_creat == NULL) { printf("ERROR:CreatNode 新建节点失败\n"); exit(0); } memset(p_creat,0,sizeof(node)); p_creat->data = data; p_creat->next = NULL; return p_creat; } /******************** *函数功能:新建队列 *输入参数: *返回值 :新队列指针 *********************/ queue *CreatQueue(void) { queue *p_creat = NULL; p_creat = (queue *)malloc(sizeof(queue)); if (p_creat == NULL) { printf("ERROR:CreatQueue 新建队列失败\n"); exit(0); } memset(p_creat,0,sizeof(queue)); p_creat->size_queue = 0; p_creat->head = NULL; p_creat->tail = NULL; return p_creat; } /******************** *函数功能:在队列尾加入新数据 *输入参数: p_queue 队列 data 要加入的数据 *返回值 : *********************/ int InsertQueueData(queue *p_queue,int data) { node *p_tmp = p_queue->tail; node *p_creat = CreatNode(data); if (p_tmp != NULL) { p_tmp->next = p_creat; } p_queue->tail = p_creat; p_queue->size_queue++; if (p_queue->head == NULL) { p_queue->head = p_creat; } return 0; } /******************** *函数功能:打印整个队列 *输入参数:队列名 *返回值 : *********************/ void PrintfQueue(queue *p_queue) { node *tmp = p_queue->head; printf("队列共有%d元素\t", p_queue->size_queue); while(tmp != NULL) { printf("%d\t",tmp->data); tmp = tmp->next; } printf("\n-----------------\n"); } /******************** *函数功能:删除头数据 *输入参数:队列名 *返回值 : *********************/ void DeleteQueueData(queue *p_queue) { node *tmp = p_queue->head; if (p_queue->head == NULL) { printf("ERROR:DeleteQueueData 队列为空 删除失败\n"); } else { if (tmp->next != NULL) { p_queue->head = tmp->next; p_queue->size_queue--; free(tmp); } else { free(tmp); p_queue->head = NULL; p_queue->tail = NULL; p_queue->size_queue = 0; } } return; } /******************** *函数功能:释放队列 数据全部清除 *输入参数:队列名 *返回值 : *********************/ void FreeQueue(queue *p_queue) { int i ; for ( i = 0; i < p_queue->size_queue; ++i) { DeleteQueueData(p_queue); } free(p_queue); return; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { queue *p_queue = CreatQueue(); InsertQueueData(p_queue,1); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InsertQueueData(p_queue,2); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InsertQueueData(p_queue,3); PrintfQueue(p_queue); DeleteQueueData(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); DeleteQueueData(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InsertQueueData(p_queue,4); PrintfQueue(p_queue); DeleteQueueData(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); DeleteQueueData(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); DeleteQueueData(p_queue); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InsertQueueData(p_queue,1); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InsertQueueData(p_queue,2); PrintfQueue(p_queue); InsertQueueData(p_queue,3); PrintfQueue(p_queue); FreeQueue(p_queue); return 0; }
运行结果如下:






