CF-gym/101810 AJK题解
CF-gym/101810 AJK题解
[ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Amman Collegiate Programming Contest (2018)]
比赛地址:https://codeforces.com/gym/101810
A. Careful Thief(双指针)
思路:
小偷最优的取法一定是: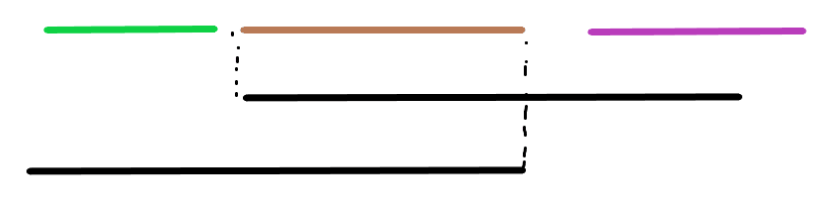
黑色的这两种可能之一。
我们设小偷选择的区间为\(Se\).
即:
要么\(Se\)的起点和一个建筑物区间的起点相等,
要么\(Se\)的终点和一个建筑物区间的终点相等。(可使用贪心思想轻易证明。)
所以我们只需要将建筑区间排序之后,
用双指针正反分别枚举小偷选择的区间起点和终点,同时维护以下答案即可。
代码:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<bitset>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define per(i,n,x) for(int i=n;i>=x;i--)
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define rson mid+1,r,p<<1|1
#define pii pair<pair<ll,ll>,ll>
#define lson l,mid,p<<1
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define se second
#define fi first
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-8;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int N=1e5+10;
const int inf=1e9;
int T;
int m;
ll k;
struct ppo{
ll l,r,v;
bool operator<(const ppo &o) const{
return l<o.l;
}
}a[N];
int main(){
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
//freopen("in","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%lld",&m,&k);
rep(i,1,m){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a[i].l,&a[i].r,&a[i].v);
}
sort(a+1,a+m+1);
int now=1;
ll sum=0,ans=0;
rep(i,1,m){
now=max(now,i);
while(a[now].r-a[i].l+1<=k&&now<=m){
sum+=(a[now].r-a[now].l+1)*a[now].v;
++now;
}
if(now<=m&&a[now].l-a[i].l+1<=k){
ans=max(ans,sum+(k-(a[now].l-a[i].l))*a[now].v);
}else ans=max(ans,sum);
if(k>=a[i].r-a[i].l+1) sum-=(a[i].r-a[i].l+1)*a[i].v;
else sum-=k*a[i].v;
}
sum=0,now=m;
per(i,m,1){
now=min(now,i);
while(a[i].r-a[now].l+1<=k&&now>=1){
sum+=(a[now].r-a[now].l+1)*a[now].v;
--now;
}
if(now>=1&&a[i].r-a[now].r+1<=k){
ans=max(ans,sum+(k-(a[i].r-a[now].r))*a[now].v);
}else ans=max(ans,sum);
if(k>=a[i].r-a[i].l+1) sum-=(a[i].r-a[i].l+1)*a[i].v;
else sum-=k*a[i].v;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
J. T-Shirts Dilemma(二进制处理)
对于
每个数\(num\),
想找到一个最大的\(x,x\le num\)使其\(x| (x+1)|(x+2)|\dots |num>num\)
如果存在这样一个数\(\mathit x\),那么\(num\)的二进制表示中的最低位的一个\(\mathit 0\),\(\mathit x\)在该位置上必须为\(\mathit 1\)。
例如\(num=11011101,x=11011111\),
\(num=11000,x=11001\),
我们记:\(x=F(num)\)。
那么当以\(num\)为最高价格能选择的区间即为\([x+1,num]\),
同时可以证明的是:
对于任意一个\(y\in [x+1,num],x\le F(y)\),忽略这些\(\mathit y\)并不影响答案。
所以我们在进行迭代的时候可以直接令\(num=F(num)\)即可,然后维护最大值的区间长度作为答案。
接下来讲解\(F(num)\)怎么计算,
我们对unsigned long long 类型的\(num\)取反(二进制的每一位flip)得到\(val\),
\(F(num)=num-lowbit(val)\),
\(lowbit()\)就是树状数组中常用的那个函数,即求一个数二进制中的最低位1的数值。
\(lowbit(x)= -x \& x\)
注意求区间的时候,如果\(F(num)<a\),需要将取a作为区间的左端点。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ALL(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define repd(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define pll pair<long long ,long long>
#define gbtb ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define MS0(X) memset((X), 0, sizeof((X)))
#define MSC0(X) memset((X), '\0', sizeof((X)))
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define eps 1e-6
#define chu(x) if(DEBUG_Switch) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]"<<endl
#define du3(a,b,c) scanf("%d %d %d",&(a),&(b),&(c))
#define du2(a,b) scanf("%d %d",&(a),&(b))
#define du1(a) scanf("%d",&(a));
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
ll powmod(ll a, ll b, ll MOD) { if (a == 0ll) {return 0ll;} a %= MOD; ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b & 1) {ans = ans * a % MOD;} a = a * a % MOD; b >>= 1;} return ans;}
ll poww(ll a, ll b) { if (a == 0ll) {return 0ll;} ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b & 1) {ans = ans * a ;} a = a * a ; b >>= 1;} return ans;}
void Pv(const vector<int> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%d", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("\n");}}}
void Pvl(const vector<ll> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%lld", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("\n");}}}
inline long long readll() {long long tmp = 0, fh = 1; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') {if (c == '-') fh = -1; c = getchar();} while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') tmp = tmp * 10 + c - 48, c = getchar(); return tmp * fh;}
inline int readint() {int tmp = 0, fh = 1; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') {if (c == '-') fh = -1; c = getchar();} while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') tmp = tmp * 10 + c - 48, c = getchar(); return tmp * fh;}
void pvarr_int(int *arr, int n, int strat = 1) {if (strat == 0) {n--;} repd(i, strat, n) {printf("%d%c", arr[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');}}
void pvarr_LL(ll *arr, int n, int strat = 1) {if (strat == 0) {n--;} repd(i, strat, n) {printf("%lld%c", arr[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');}}
const int maxn = 1000010;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*** TEMPLATE CODE * * STARTS HERE ***/
#define DEBUG_Switch 0
typedef unsigned long long ull;
ull lowbit(ull x)
{
return -x & x;
}
int main()
{
#if DEBUG_Switch
freopen("C:\\code\\input.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
//freopen("C:\\code\\output.txt","w",stdout);
int t;
t = readint();
while (t--)
{
ull a = readll();
ull b = readll();
ull v = readll();
ull ans = 0;
// chu(ans);
ull r = v;
ull l;
int id1, id2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 62; ++i)
{
if ((1ll << i)&v)
id1 = i;
if ((1ll << i)&b)
id2 = i;
}
if (id1 > id2)
{
printf("%llu\n", b - a + 1 );
continue;
}
if (v < a)
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
while (1)
{
ull x = lowbit(~r);
if (x > r)
l = a - 1;
else
l = r - x;
if(min(r, b)>=max(l, a - 1))
ans = max(ans, min(r, b) - max(l, a - 1));
r = l;
if (r < a)
break;
}
// chu(ans);
printf("%llu\n", ans );
}
return 0;
}
K. League of Demaciasi
思路:
我们枚举每一个士兵作为激光炮的边界:
- 对于每一个士兵,根据它的位置确定和原点的距离,如果距离大于\(z/2\),那么该士兵就可以作激光炮的左右边界,那么让把激光炮的左边界恰好靠在该士兵的位置上即可(右边界也行,同质的,选择其一即可)。
- 否则只能作激光炮的下边界。
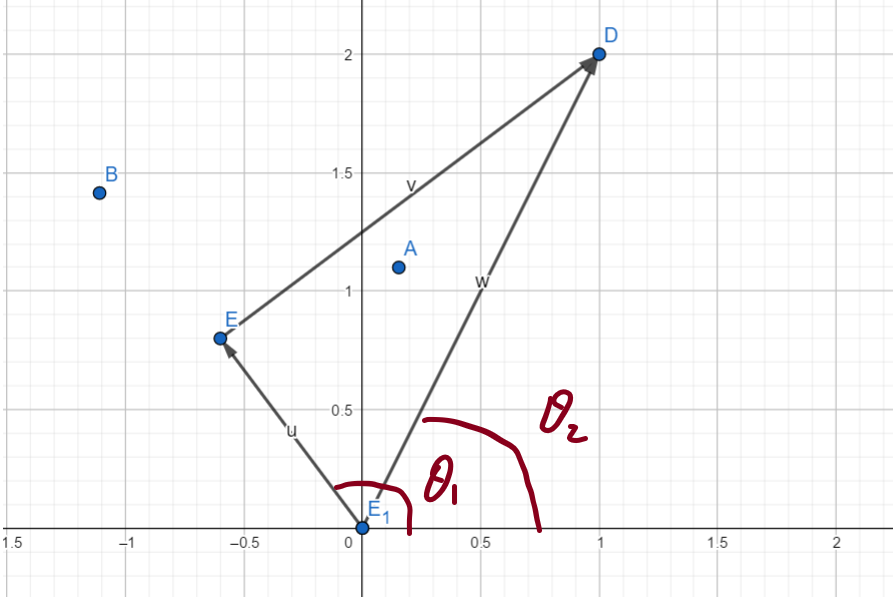
看图表示一个左边界靠在点\(\mathit D\)上的激光炮的左下角部分图,可以明显的发现,当角度\(\theta_1\)确定后,因为向量\(\mathit u\)的模长为\(z/2\),即可表示出一个唯一的激光炮。
角度\(\theta_1\)也很好求,因为\(|DE_1|\)很好求得,从而可以得到\(\angle DE_1E\),\(\theta_2\)是\(E_1D\)的斜率角,
所以:\(\theta_1=\theta_2+\ang DE_1E\)。
判断一个点是否在激光炮内
满足以下两个条件即可:
1、在\(E_1E\)上的投影的绝对值不大于\(Z/2\)
2、在下边界的右方,即\(0\le \overrightarrow{E_1D}\times\overrightarrow{E_1E}\)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ALL(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define repd(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define pll pair<long long ,long long>
#define gbtb ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define MS0(X) memset((X), 0, sizeof((X)))
#define MSC0(X) memset((X), '\0', sizeof((X)))
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define eps 1e-6
#define chu(x) if(DEBUG_Switch) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]"<<endl
#define du3(a,b,c) scanf("%d %d %d",&(a),&(b),&(c))
#define du2(a,b) scanf("%d %d",&(a),&(b))
#define du1(a) scanf("%d",&(a));
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
ll powmod(ll a, ll b, ll MOD) { if (a == 0ll) {return 0ll;} a %= MOD; ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b & 1) {ans = ans * a % MOD;} a = a * a % MOD; b >>= 1;} return ans;}
ll poww(ll a, ll b) { if (a == 0ll) {return 0ll;} ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b & 1) {ans = ans * a ;} a = a * a ; b >>= 1;} return ans;}
void Pv(const vector<int> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%d", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("\n");}}}
void Pvl(const vector<ll> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%lld", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("\n");}}}
inline long long readll() {long long tmp = 0, fh = 1; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') {if (c == '-') fh = -1; c = getchar();} while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') tmp = tmp * 10 + c - 48, c = getchar(); return tmp * fh;}
inline int readint() {int tmp = 0, fh = 1; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') {if (c == '-') fh = -1; c = getchar();} while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') tmp = tmp * 10 + c - 48, c = getchar(); return tmp * fh;}
void pvarr_int(int *arr, int n, int strat = 1) {if (strat == 0) {n--;} repd(i, strat, n) {printf("%d%c", arr[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');}}
void pvarr_LL(ll *arr, int n, int strat = 1) {if (strat == 0) {n--;} repd(i, strat, n) {printf("%lld%c", arr[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');}}
const int maxn = 10010;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*** TEMPLATE CODE * * STARTS HERE ***/
#define DEBUG_Switch 0
// const double eps = 1e-6;
int sgn(double x)
{
if (fabs(x) < eps)return 0;
if (x < 0)return -1;
else return 1;
}
struct Point
{
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double _x, double _y)
{
x = _x; y = _y;
}
Point operator -(const Point &b)const
{
return Point(x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point &b)const
{
return Point(x + b.x, y + b.y);
}
void operator /=(const double &b)
{
x /= b;
y /= b;
}
//叉积
double operator ^(const Point &b)const
{
return x * b.y - y * b.x;
}
//点积
double operator *(const Point &b)const
{
return x * b.x + y * b.y;
}
//绕原点旋转角度B(弧度值),后x,y的变化
void transXY(double B)
{
double tx = x, ty = y;
x = tx * cos(B) - ty * sin(B);
y = tx * sin(B) + ty * cos(B);
}
double distance(Point & bb)
{
return sqrt((x - bb.x) * (x - bb.x) + (y - bb.y) * (y - bb.y));
}
void show()
{
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
};
int n, m;
double z;
Point a[maxn];
const double pi = acos(-1);
int main()
{
#if DEBUG_Switch
freopen("C:\\code\\input.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
//freopen("C:\\code\\output.txt","w",stdout);
int t;
t = readint();
while (t--)
{
n = readint();
m = readint();
scanf("%lf", &z);
repd(i, 1, n)
{
a[i].x = readint();
a[i].y = readint();
}
double c;
Point o = Point(0, 0);
int isok = 0;
z /= 2;
repd(i, 1, n)
{
c = o.distance(a[i]);
Point base = a[i];
if (c > z )
{
base.transXY(acos(z / c));// 旋转
}
base /= o.distance(base);// 单位化
int cnt = 1;
repd(j, 1, n)
{
if (i == j)
continue;
if (abs( a[j]*base) <= z)
{
if ((a[j]^base) >= 0)
{
cnt++;
}
}
}
if (cnt >= m)
{
isok = 1;
break;
}
}
if (isok)
{
printf("Yes\n");
} else
{
printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}



