第一次个人编程作业
一、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 240 | 600 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 5 | 5 |
| Development | 开发 | 600 | 800 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 180 | 300 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 10 | 10 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 60 | 30 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 180 | 120 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 600 | 1440 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 600 | 10 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 70 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 30 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 60 | 120 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 5 | 5 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · 合计 | 2720 | 3600 |
二、计算模块接口
2.1计算模块接口的设计与实现过程。设计包括代码如何组织,比如会有几个类,几个函数,他们之间关系如何,关键函数是否需要画出流程图?说明你的算法的关键,以及独到之处。
-
两个类,一个类用于创建敏感词库,一个类用于执行敏感词检测
- 创建敏感词库的类
- 只包括一个函数,即将中文、拼音、拼音首字母、偏旁部首三者混合
- 执行敏感词检测类
- 包括ac自动机核心算法、敏感词树的建立、读取文件、输出文件函数
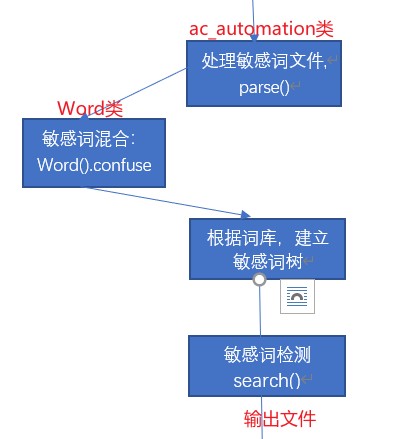
- 包括ac自动机核心算法、敏感词树的建立、读取文件、输出文件函数
- 创建敏感词库的类
-
关键与独到之处
- 并没有啥,本来独到之处可以是那正则表达式一行代码处理一行文本,快速又高效,但是直接批处理后没办法输出原文,这里还在思考;
- 关键之处就在于ac自动机算法、建立敏感词库和查找敏感词函数,查找敏感词时一并处理英文大小写、繁简体、谐音字,在处理英文大小写、繁简体、谐音字时会造成敏感词交叉,这里是关键,也是我现在还没有处理好的一部分,当读取一行文本后,会遍历每一个字,并记录当前字所在位置,如果此字大写就转小写、繁体就转简体,谐音则检测此字的拼音,并在构建的敏感词库中检查是否有相对应的原始敏感词文件中的关键字。
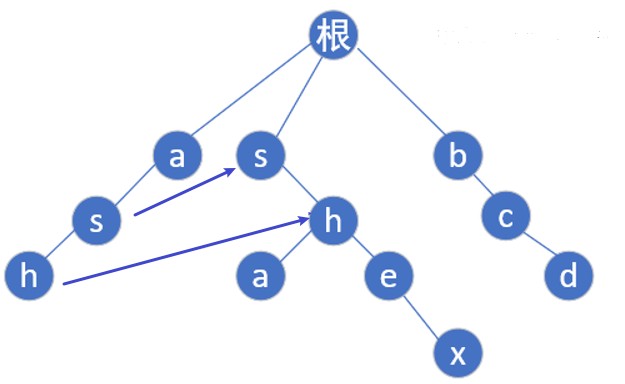
- ac自动机算法就是在tire树的基础上,增加一个fail指针,如果当前点匹配失败,则将指针转移到fail指针指向的地方,这样就不用回溯,而可以路匹配下去了。当前模式串后缀和fail指针指向的模式串部分前缀相同,如ash和shex,我们找到h发现下一个要找的是x,就跳到shex中的e处,看看此处的下一个字符(x)是不是应该找的那一个,同时这也是一个特例,反应最短匹配和最长匹配的差别,最长匹配也是本人一直致力于努力要做到的方法,基本情况如下:
2.2计算模块接口部分的性能改进。记录在改进计算模块性能上所花费的时间,描述你改进的思路,并展示一张性能分析图,并展示你程序中消耗最大的函数。
性能分析图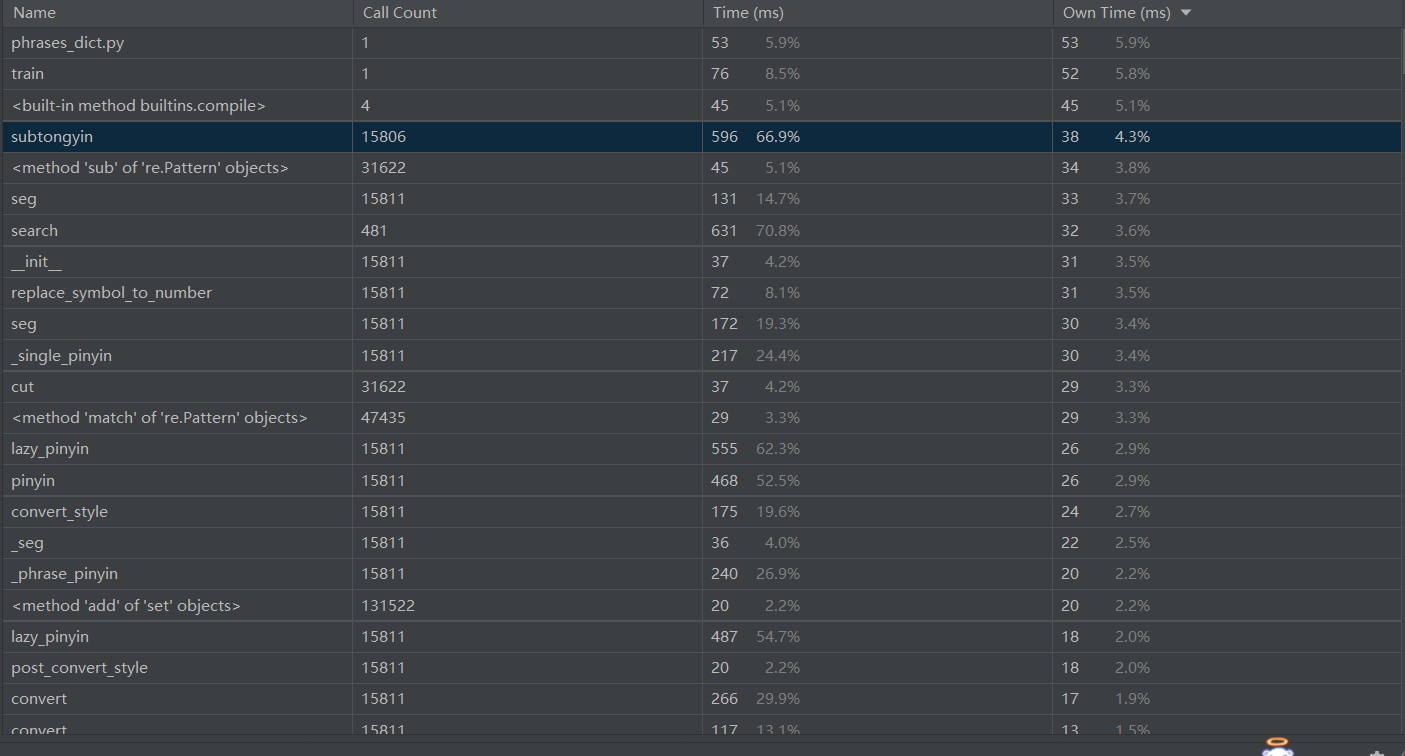
程序中函数消耗分析图
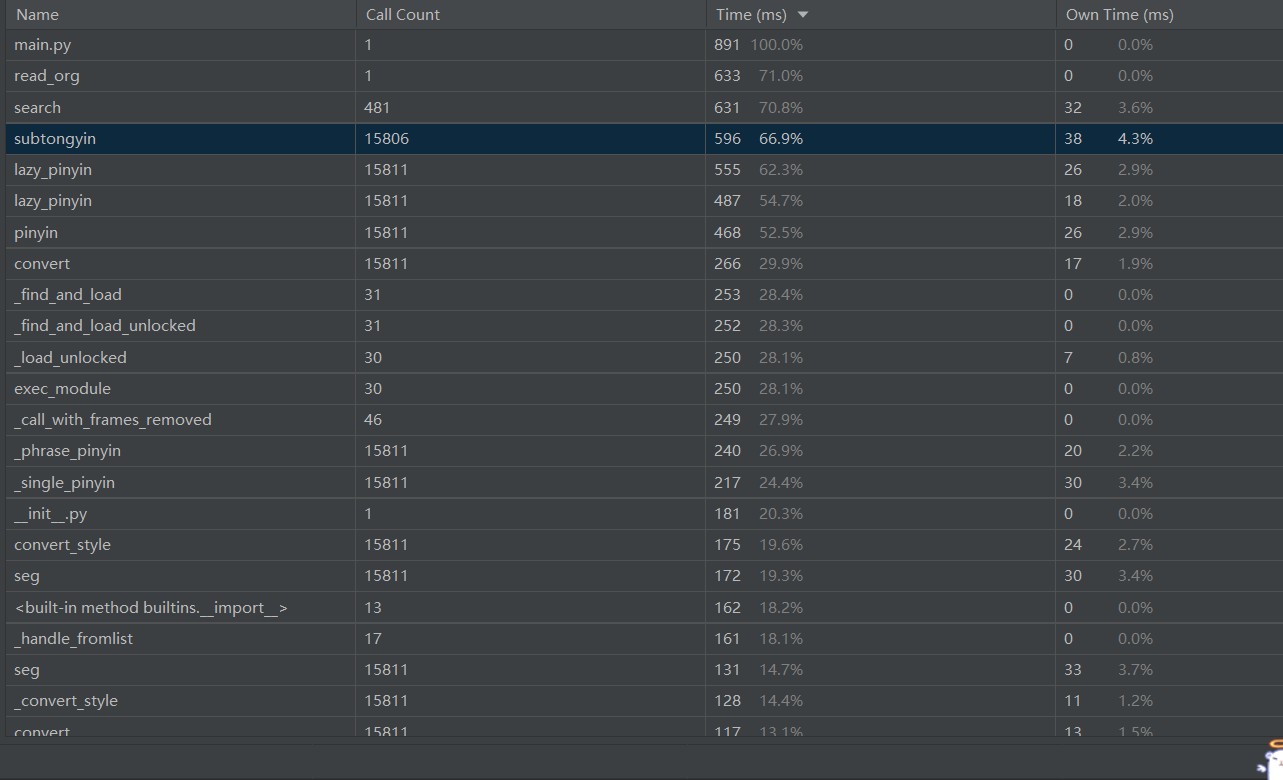
消耗时间最长的search()函数(即是敏感词检测函数,此函数期间调用了subtongyin()函数,这个函数遍历所有文字判断是否是同音字,所以调用次数较多,消耗时间较长),嵌套调用、依次遍历导致时间过长,改进思路是避免依次遍历,试图寻找正则表达式方法每行过滤从而避免嵌套调用、反复调用,并进一步修改在写出文件时,如何记录敏感词在原文所处形态,但是还未成功……
2.3计算模块部分单元测试展示。展示出项目部分单元测试代码,并说明测试的函数,构造测试数据的思路。并将单元测试得到的测试覆盖率截图,发表在博客中。
代码如下,测试查找敏感词函数
# 查找敏感词函数
def search(self, content):
p = self.root
result = []
currentposition = 0
forme = []
s=[]
gap=''
flag=False
while currentposition < len(content):
word1 = content[currentposition]
if (u'\u4e00' <= word1 <= u'\u9fa5'):
word = self.subtongyin(content[currentposition-1],word1)
elif ('a'<=word1<='z'):
word=word1
elif (u'\u3400' <= word1 <= u'\u4db5'):
word= Converter('zh-hans').convert(word1)
elif ('A'<=word1<='Z'):
word=word1.lower()
else:
if flag:
s.append(word1)
currentposition += 1
continue
while word in p.next == False and p != self.root:
p = p.fail
if word in p.next:
p = p.next[word]
if flag==False:
s.append(word1)
flag=True
else:
s.append(word1)
else:
p = self.root
s=[]
if p.isWord:
result.append(p.word)
result.append(self.__line_cnt)
temp=gap.join(s)
result.append(temp)
self.result.append(result)
result=[]
s=[]
flag=False
p = self.root
self.total+=1
currentposition += 1
return result
测试建立敏感词树函数
# 加载敏感词库函数
def parse(self, path):
confused_word_list=[]
with open(path,encoding='utf-8') as f:
for keyword in f: #跳去构建扩大敏感词树
confuse = Word(str(keyword).strip())
confused_word_list.append(confuse.confuse())
gap = ''
for words in confused_word_list:
for keyword in words:
self.addword(gap.join(keyword))
self.confused_words=confused_word_list
def confuse(self):
confuenum = []
word = list(self.original_word)
for i in range(len(word)):
c = word[i]
# 汉字
if (u'\u4e00' <= c <= u'\u9fa5') or (u'\u3400' <= c <= u'\u4db5'):#常见字、繁体字、不常见字
li = []
# pinyin
pin = pypinyin.lazy_pinyin(c)
gap=''
#print(self.pinandzi)
li.append(c)
li.append(pin) #全拼
pin = pin[0]
li.append(pin[0]) #首字母
if is_leftandright(c):
hanzi_part = getRadical(c)
li.append(hanzi_part)
word[i] = li #一个词添加完毕
pinandzi.append([c,gap.join(pin),pin[0]]+hanzi_part)
else:
pass
for c in word:
#开始混合
if not isinstance(c, list):
if len(confuenum) == 0:
confuenum.append([c])
else:
for li in confuenum:
li.append(c)
else:
if len(confuenum) == 0:
for alist in c:
if not isinstance(alist, list):
confuenum.append([alist])
else:
confuenum.append(alist)
else:
temp = confuenum
new_confuse_enum = []
for alist in c:
new_confuse = copy.deepcopy(temp)
if not isinstance(alist, list):
for existed_confuse in new_confuse:
existed_confuse.append(alist)
else:
for existed_confuse in new_confuse:
for x in alist:
existed_confuse.append(x)
new_confuse_enum = new_confuse_enum + new_confuse
confuenum = new_confuse_enum
return confuenum
测试数据来自作业样例words.txt与org.txt,样例类型齐全,包括繁简体、中英文、拼音混合、谐音、英文大小写等等例子。
测试覆盖率截图
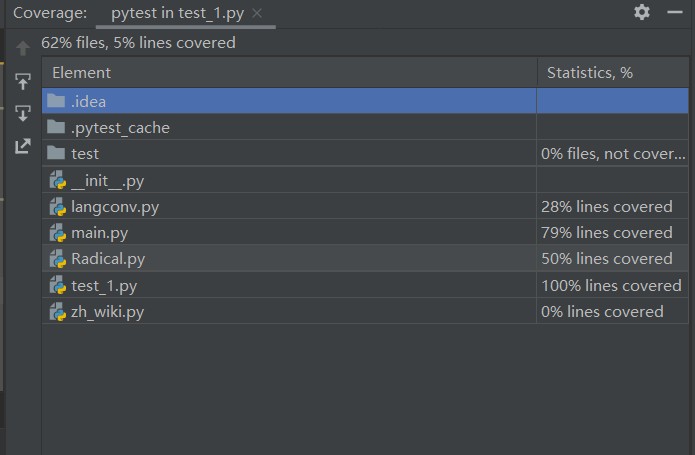
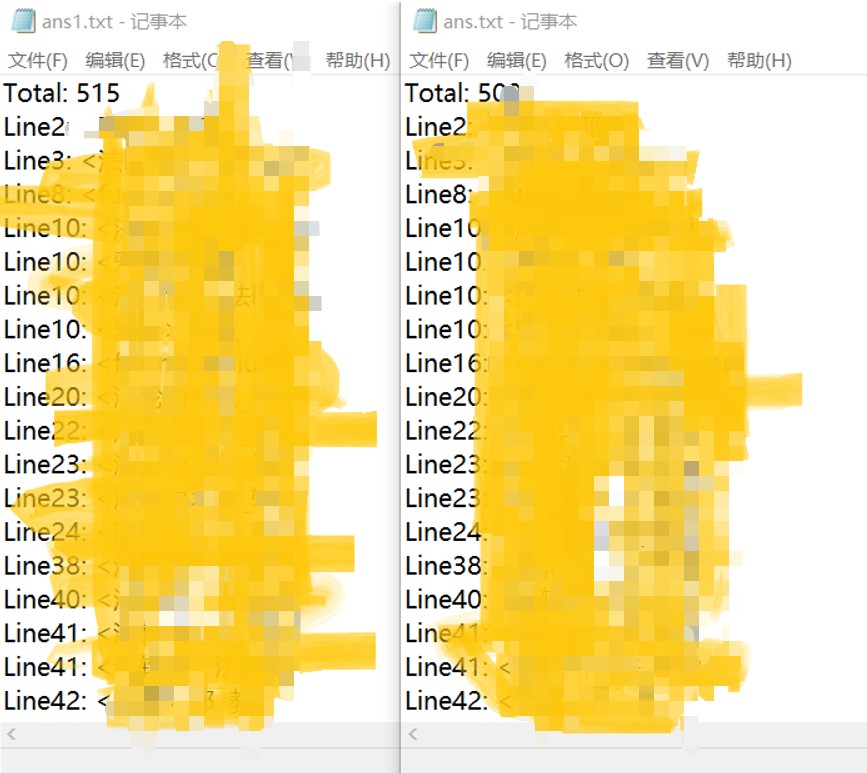
展示一张最终测试结果图,基本答案相同,和原答案相比多出几个,貌似比大家做的检测出来少了一个。
2.4计算模块部分异常处理说明。在博客中详细介绍每种异常的设计目标。每种异常都要选择一个单元测试样例发布在博客中,并指明错误对应的场景。
异常处理只在文件读入读出时进行了处理。
IO异常:输入文件不存在时、无法写到指定文件时,引发错误“Unable to open the file to be detected”和“Unable to open ans file”
def read_org(self, path): #读取文本处理文字
try: #异常处理
with open(path, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as org:
lines = org.readline
except IOError:
raise IOError("Unable to open the file to be detected")
def out_ans(self,path):
try:
with open(path, 'w+', encoding='utf-8') as ans:
print("Total: {}".format(self.total), file=ans)
except IOError:
raise IOError("Unable to open ans file")
三、心得
在这次作业完成过程中,因为上星期在准备其他比赛事情而基本上没有太投入到其中,只是构思了一部分,等这个星期再来时,发现这就是极限挑战,代码整体完成的还是比较粗糙,很多地方还来不及细化改进,但也收获颇丰,提高了疯狂搜索查阅资料的能力??基本按照一个正常开发的流程来完成整个作业,也了解到如何完成单元测试,最大的收获也就是学会了一堆包,并学习了AC自动机算法,耗费许多时间和精力,编程的思维也更熟练了些。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号