算法分析——排序的分析
不容易变质的思想,只有纸张能承载。 ————qianxin
本文是讲述思想的算法分析文章,并没有严谨的数学,以及客观的代码说明
算法分析——排序的分析
引子
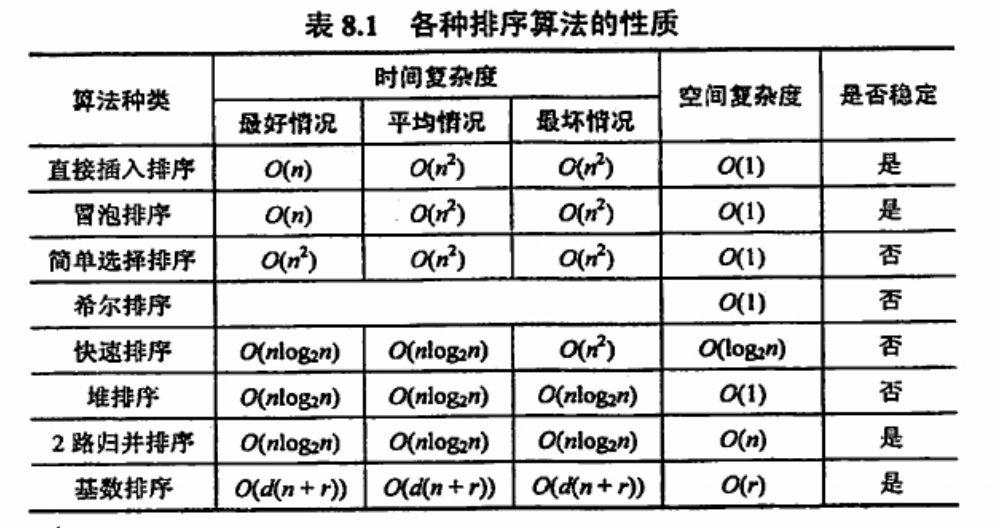
关于这张图,学编程的估计都很头疼。
是否稳定(stable)
IBM (Insertion, Bubble, Merge)是三个稳定的排序。基数排序属于另一个范畴,也是稳定排序。
稳定指的是,The order of equal elements is guaranteed to be preserved.
比如排行榜,稳定的排序会维持先后相对次序,从而使只浏览一次的人不会得到完全错误的提示。
而不稳定的排序,其中的相对次序总是不断变化,从而无法一次就可以得到信息。
稳定的排序,通常特点是对元素的移动操作尽可能地不剧烈,(因为不剧烈的稳定部分排序)而不改变相对次序。这也导致性能受到限制。
而稳定的排序,最适合处理基本有序的数据(整理图书之类的)。
分治排序
平均时间复杂度达到\(O(log_2n)\)的排序,都是分治的。堆排序的分治思想基于优先队列(\(L(i)与L(2i),L(i)与L(2i+1)\)维持两个相同的偏序关系)。
排序思想
核心是确定某个元素最终位置的排序(排序的最终目的)
交换排序(冒泡,快速),简单选择排序
核心是使子序列有序的排序(通过子序列慢慢达到排序的目的,通常会比较稳定)
插入排序,堆排序,归并排序,(基数排序)
最简单地确定某个元素最终位置的排序
简单选择排序,\(n(n-1)/2\)次选择,时间复杂度\(O(n^2)\)
排序方法的细分
通常能用最短的时间复杂度确定某个元素最终位置的排序(排序的最终目的)
快速排序,达到排序的最终目的,且可以快速交换
适合基本有序的排序表,数据量不要太大,《算法导论》上只随便提了一嘴的排序
希尔排序 这个排序很具有限定性,n在特定范围是,时间复杂度可以达到\(O(n^2)\),比较复杂的排序
最好地体现了分而治之的排序
归并排序
基于优先队列的排序
堆排序 堆排序是所有排序中,在应用方面最特别的排序。虽然不像快速排序一样快,不像希尔排序一样难,不像归并排序那样分治,不像插入排序那样稳定
这个排序需要专门的篇幅,在此就简单地提一下。
堆排序
堆排序在一般情况下比快速排序慢,但是比其他排序都要快。比快速排序好在,它的最坏情况也是\(O(log_2n)\)而不是\(O(n^2)\)
In computer science, heapsort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm. Heapsort can be thought of as an improved selection sort: like selection sort, heapsort divides its input into a sorted and an unsorted region, and it iteratively shrinks the unsorted region by extracting the largest element from it and inserting it into the sorted region. Unlike selection sort, heapsort does not waste time with a linear-time scan of the unsorted region; rather, heap sort maintains the unsorted region in a heap data structure to find the largest element in each step more quickly.
堆数据结构通常可以用来做高效的优先队列。
(二叉)堆数据结构可以看作完全二叉树,但是树的每个结点对应数组中的一个元素。因此,堆和BST完全不同。BST是通过中序遍历可以得到有序数组,而堆排序是一种通过将输入(数组)看成堆,从而使输入(数组)数据有序的方法。而堆又可以看作完全二叉树。
Heapsort's primary advantages are its simple, non-recursive code, minimal auxiliary storage requirement, and reliably good performance: its best and worst cases are within a small constant factor of each other, and of the theoretical lower bound on comparison sorts. While it cannot do better than O(n log n) for pre-sorted inputs, it does not suffer from quicksort's O(n2) worst case, either. (The latter can be avoided with careful implementation, but that makes quicksort far more complex, and one of the most popular solutions, introsort, uses heapsort for the purpose.)
Its primary disadvantages are its poor locality of reference and its inherently serial nature; the accesses to the implicit tree are widely scattered and mostly random, and there is no straightforward way to convert it to a parallel algorithm.
This makes it popular in embedded systems, real-time computing, and systems concerned with maliciously chosen inputs, such as the Linux kernel. It is also a good choice for any application which does not expect to be bottlenecked on sorting.
堆排序的最坏情况\(O(log_2n)\),使得大多数操作系统不会因为异常输入而发生故障。
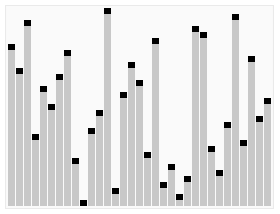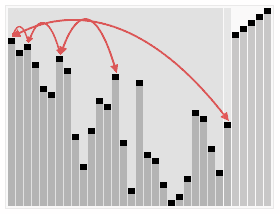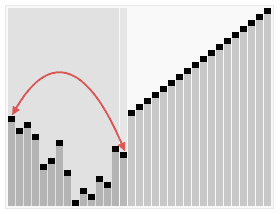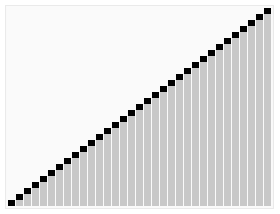
代码可以看这块:
https://www.cnblogs.com/qianxinn/p/15669334.html
ChangeLog
12月18日 18:58 这篇文章很好用。不过还是再补充一点吧。最多写3次得了。
12月21日 18:06 本文完结。文章应该没什么要修改的了,


