算法——排序(选择排序)
选择排序是最不抽象的排序
算法——排序(选择排序)
选择排序是通过选择某个极值放置到序位的排序方法。所以选择排序每次的选取必将改变相对次序。
《算法导论》书中没有讲授简单选择排序。因为其和冒泡排序都是非常不实用的排序。
但是这两者的同类排序堆排序和快速排序,却非常强大。
简单选择排序
核心是选择最值,然后排序。
堆排序(基于比较的选择排序)
更多内容可以看
https://www.cnblogs.com/qianxinn/p/15705731.html
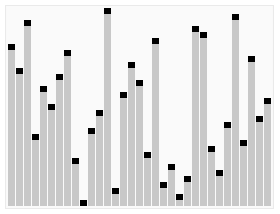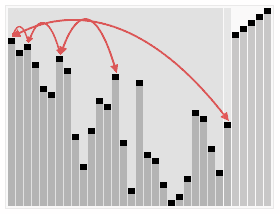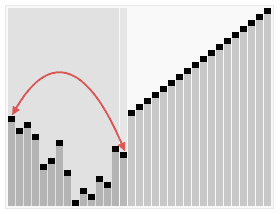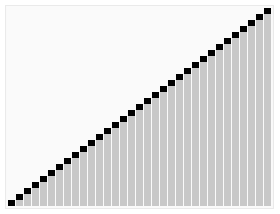
In computer science, heapsort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm. Heapsort can be thought of as an improved selection sort: like selection sort, heapsort divides its input into a sorted and an unsorted region, and it iteratively shrinks the unsorted region by extracting the largest element from it and inserting it into the sorted region. Unlike selection sort, heapsort does not waste time with a linear-time scan of the unsorted region; rather, heap sort maintains the unsorted region in a heap data structure to find the largest element in each step more quickly.
堆排序是基于二叉堆(binary heap)的排序,二叉堆是一种优先队列,满足
- L(i) >= L(2i) 且 L(i) >= L(2i+1) 大根堆
- L(i) <= L(2i) 且 L(i) <= L(2i+1) 小根堆
堆排序最后一定会形成大根堆或小根堆。
(二叉)堆数据结构可以看作完全二叉树,但是树的每个结点对应数组中的一个元素。因此,堆和BST完全不同。
下面我给出堆排序的代码。好多书上这里都是错的。
本代码已精校,性能已尽可能优化。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void heapMaxAdjust(vector<int>& heap, int root, int size)
{
heap[0] = heap[root];
for (int child = 2*root; child < size; child*=2)
{
if (heap[child] < heap[child+1])
++child;
if (heap[0] < heap[child])
{
heap[root] = heap[child];
root = child;
} else break;
}
heap[root] = heap[0];
}
void buildMaxHeap(vector<int>& heap, int size)
{
for (int root = size/2; root > 0; --root)
heapMaxAdjust(heap, root, size);
}
int main()
{
vector<int> heap = {0, 53, 17, 78, 9, 45, 65, 87, 32};
buildMaxHeap(heap, heap.size());
for (int i : heap)
std::cout << i << "\t";
std::cout << "\n";
}
纯算法部分。
void heapMaxAdjust(vector<int>& heap, int root, int size)
{
heap[0] = heap[root];
for (int child = 2*root; child < size; child*=2)
{
if (heap[child] < heap[child+1])
++child;
if (heap[0] < heap[child])
{
heap[root] = heap[child];
root = child;
} else break;
}
heap[root] = heap[0];
}
void buildMaxHeap(vector<int>& heap, int size)
{
for (int root = size/2; root > 0; --root)
heapMaxAdjust(heap, root, size);
}
堆排序的核心是维护子树形成大根堆,并最终形成整个树的大根堆。
二叉树的最后一个结点必然是第[n/2]个结点的子结点。
于是,堆排序通过对[n/2]处结点(每个大根堆子树的根结点)往前依次进行heapMaxAdjust,维护这些子树形成大根堆,并最终递归形成大根堆。
void buildMaxHeap(vector<int>& heap, int size)
{
for (int root = size/2; root > 0; --root)
heapMaxAdjust(heap, root, size);
}
而子树通过以下方式形成大根堆。其中heap[0]在国内一般称为哨兵位,是为了提高性能使用的交换变量。
子树形成大根堆的方法,有点类似于DP中的自下而上的DP方法。
void heapMaxAdjust(vector<int>& heap, int root, int size)
{
// 基本情况: a(1) = heap[root]
heap[0] = heap[root];
// 归纳步骤: a(n+1) = a(n)*2,递归为子结点的子结点
for (int child = 2*root; child < size; child*=2)
{
// 归纳步骤1:child = max(左结点,右结点)
if (heap[child] < heap[child+1])
++child;
// 归纳步骤2:
// heap[0]和child结点对比,然后root变为其子结点,child在child*=2中又变为root子结点。
if (heap[0] < heap[child])
{
heap[root] = heap[child];
root = child;
} else break;
}
// 终止情况:最终的root值即为开始heap[0]暂存应放置的位置
heap[root] = heap[0];
}


