R-CNN, Fast R-CNN, Faster R-CNN, YOLO — Object Detection Algorithms(目标检测教程)
原文出自https://towardsdatascience.com/r-cnn-fast-r-cnn-faster-r-cnn-yolo-object-detection-algorithms-36d53571365e
原文为2018年7月10日终稿
Introduction
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary field that has been gaining huge amounts of traction in the recent years(since CNN) and self-driving cars have taken centre stage. Another integral part of computer vision is object detection. Object detection aids in pose estimation, vehicle detection, surveillance etc. The difference between object detection algorithms and classification algorithms is that in detection algorithms, we try to draw a bounding box around the object of interest to locate it within the image. Also, you might not necessarily draw just one bounding box in an object detection case, there could be many bounding boxes representing different objects of interest within the image and you would not know how many beforehand.
计算机视觉是一个跨学科的领域,近年来得到了极大的关注(自CNN以来),自动驾驶汽车也成为了研究的中心。计算机视觉的另一个组成部分是目标检测。目标检测有助于姿态估计、车辆检测、监控等。目标检测算法和分类算法的区别在于,在检测算法中,我们试图在感兴趣的目标周围画一个边界框,以便在图像中定位目标。另外,在对象检测的情况下,您可能不一定只绘制一个边界框,图像中可能有许多表示不同感兴趣对象的边界框,并且您不知道事先有多少个边界框。
The major reason why you cannot proceed with this problem by building a standard convolutional network followed by a fully connected layer is that, the length of the output layer is variable — not constant, this is because the number of occurrences of the objects of interest is not fixed. A naive approach to solve this problem would be to take different regions of interest from the image, and use a CNN to classify the presence of the object within that region. The problem with this approach is that the objects of interest might have different spatial locations within the image and different aspect ratios. Hence, you would have to select a huge number of regions and this could computationally blow up. Therefore, algorithms like R-CNN, YOLO etc have been developed to find these occurrences and find them fast.
无法通过构建标准卷积网络和完全连接的层来处理此问题的主要原因是,输出层的长度是可变的,而不是恒定的,这是因为感兴趣对象的出现次数不是固定的。解决这个问题的一个简单方法是从图像中提取不同的感兴趣区域,并使用CNN对该区域中存在的对象进行分类。这种方法的问题是,感兴趣的对象在图像中可能具有不同的空间位置和不同的纵横比。因此,您将不得不选择大量的区域,这可能会在计算上爆炸。因此,诸如R-CNN、YOLO等算法已经被开发出来,以发现这些事件并快速找到它们。
R-CNN
To bypass the problem of selecting a huge number of regions, Ross Girshick et al. proposed a method where we use selective search to extract just 2000 regions from the image and he called them region proposals. Therefore, now, instead of trying to classify a huge number of regions, you can just work with 2000 regions. These 2000 region proposals are generated using the selective search algorithm which is written below.
为了绕过选择大量区域的问题,Ross-Girshick等人提出了一种方法,使用选择性搜索从图像中只提取2000个区域,他称之为区域建议。因此,现在,不用尝试对大量区域进行分类,只需使用2000个区域即可。这2000个区域建议是使用下面介绍的选择性搜索算法生成的。
Selective Search:
- Generate initial sub-segmentation, we generate many candidate regions
- Use greedy algorithm to recursively combine similar regions into larger ones
- Use the generated regions to produce the final candidate region proposals
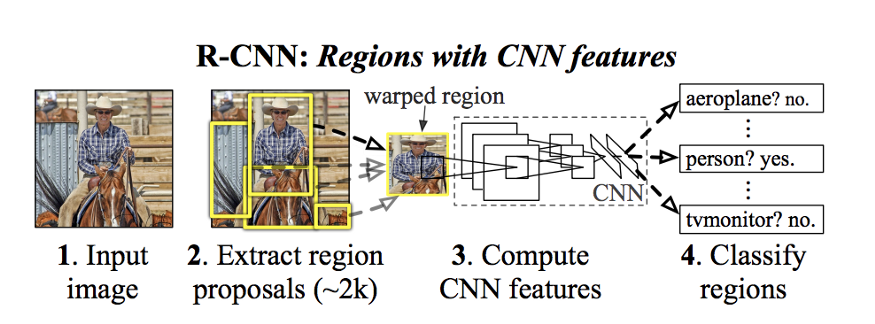
To know more about the selective search algorithm, follow this link. These 2000 candidate region proposals are warped into a square and fed into a convolutional neural network that produces a 4096-dimensional feature vector as output. The CNN acts as a feature extractor and the output dense layer consists of the features extracted from the image and the extracted features are fed into an SVM to classify the presence of the object within that candidate region proposal. In addition to predicting the presence of an object within the region proposals, the algorithm also predicts four values which are offset values to increase the precision of the bounding box. For example, given a region proposal, the algorithm would have predicted the presence of a person but the face of that person within that region proposal could’ve been cut in half. Therefore, the offset values help in adjusting the bounding box of the region proposal.
要了解有关选择性搜索算法的更多信息,请访问以下链接。这2000个候选区域建议被扭曲成一个正方形,并输入一个卷积神经网络,产生一个4096维的特征向量作为输出。CNN作为一个特征抽取器,输出的稠密层由从图像中提取的特征组成,将提取的特征输入到SVM中,对候选区域内的目标进行分类。该算法除了预测区域内是否存在物体外,还预测了四个偏移值,以提高边界框的精度。例如,给定一个区域建议,算法本来可以预测一个人的存在,但该区域建议中该人的脸可能被切成两半。因此,偏移值有助于调整区域建议的边界框。
Problems with R-CNN
-
它仍然需要大量的时间来训练网络,因为你将不得不分类2000个地区的建议,每幅图像。
-
它不能实时实现,因为每个测试映像大约需要47秒。
-
选择搜索算法是一种固定的算法。因此,在那个阶段没有学习。这可能导致产生不好的候选区域提案。
-
It still takes a huge amount of time to train the network as you would have to classify 2000 region proposals per image.
-
It cannot be implemented real time as it takes around 47 seconds for each test image.
-
The selective search algorithm is a fixed algorithm. Therefore, no learning is happening at that stage. This could lead to the generation of bad candidate region proposals.
Fast R-CNN
The same author of the previous paper(R-CNN) solved some of the drawbacks of R-CNN to build a faster object detection algorithm and it was called Fast R-CNN. The approach is similar to the R-CNN algorithm. But, instead of feeding the region proposals to the CNN, we feed the input image to the CNN to generate a convolutional feature map. From the convolutional feature map, we identify the region of proposals and warp them into squares and by using a RoI pooling layer we reshape them into a fixed size so that it can be fed into a fully connected layer. From the RoI feature vector, we use a softmax layer to predict the class of the proposed region and also the offset values for the bounding box.
前一篇论文的作者(R-CNN)解决了R-CNN的一些缺点,提出了一种快速的目标检测算法,称之为快速R-CNN。该方法类似于R-CNN算法。但是,我们没有将区域建议反馈给CNN,而是将输入图像反馈给CNN以生成卷积特征图。从卷积特征图中,我们识别提议的区域并将它们扭曲成正方形,通过使用RoI池层,我们将它们重塑为固定大小,以便可以将其输入到完全连接的层中。从RoI特征向量出发,我们使用softmax层来预测建议区域的类别以及边界框的偏移值。
The reason “Fast R-CNN” is faster than R-CNN is because you don’t have to feed 2000 region proposals to the convolutional neural network every time. Instead, the convolution operation is done only once per image and a feature map is generated from it.
“快速R-CNN”比R-CNN快的原因是你不必每次都向卷积神经网络提供2000个区域建议。相反,卷积运算只在每幅图像上进行一次,并从中生成特征图。
From the above graphs, you can infer that Fast R-CNN is significantly faster in training and testing sessions over R-CNN. When you look at the performance of Fast R-CNN during testing time, including region proposals slows down the algorithm significantly when compared to not using region proposals. Therefore, region proposals become bottlenecks in Fast R-CNN algorithm affecting its performance.
从上面的图表中,你可以推断快速的R-CNN在训练和测试过程中明显快于R-CNN。当您在测试期间查看快速R-CNN的性能时,与不使用区域建议相比,包括区域建议会显著减慢算法的速度。因此,区域建议成为影响快速R-CNN算法性能的瓶颈。
Faster R-CNN
Both of the above algorithms(R-CNN & Fast R-CNN) uses selective search to find out the region proposals. Selective search is a slow and time-consuming process affecting the performance of the network. Therefore, Shaoqing Ren et al. came up with an object detection algorithm that eliminates the selective search algorithm and lets the network learn the region proposals.
Similar to Fast R-CNN, the image is provided as an input to a convolutional network which provides a convolutional feature map. Instead of using selective search algorithm on the feature map to identify the region proposals, a separate network is used to predict the region proposals. The predicted region proposals are then reshaped using a RoI pooling layer which is then used to classify the image within the proposed region and predict the offset values for the bounding boxes.
上述两种算法(R-CNN和Fast R-CNN)都使用选择性搜索来找出区域建议。选择性搜索是一个缓慢而耗时的过程,会影响网络的性能。因此,任少青等人提出了一种目标检测算法,消除了选择性搜索算法,让网络学习区域。
与Fast R-CNN类似,图像作为卷积网络的输入,卷积网络提供卷积特征图。在特征图上不使用选择性搜索算法来识别区域建议,而是使用单独的网络来预测区域建议。然后使用RoI池层对预测的区域建议进行重塑,然后使用RoI池层对建议区域内的图像进行分类并预测边界框的偏移值。
From the above graph, you can see that Faster R-CNN is much faster than it’s predecessors. Therefore, it can even be used for real-time object detection.
从上图中,你可以看到更快的R-CNN比它的前身快得多。因此,它甚至可以用于实时目标检测。
YOLO — You Only Look Once
All of the previous object detection algorithms use regions to localize the object within the image. The network does not look at the complete image. Instead, parts of the image which have high probabilities of containing the object. YOLO or You Only Look Once is an object detection algorithm much different from the region based algorithms seen above. In YOLO a single convolutional network predicts the bounding boxes and the class probabilities for these boxes.
以前的所有目标检测算法都使用区域来定位图像中的目标。网络看不到完整的图像。取而代之的是图像中包含物体的概率很高的部分。YOLO或You Only Look Once是一种与上述基于区域的算法有很大不同的目标检测算法。在YOLO中,一个卷积网络可以预测这些框的边界框和类概率。
How YOLO works is that we take an image and split it into an SxS grid, within each of the grid we take m bounding boxes. For each of the bounding box, the network outputs a class probability and offset values for the bounding box. The bounding boxes having the class probability above a threshold value is selected and used to locate the object within the image.
YOLO的工作原理是,我们拍摄一幅图像,并将其分割成一个SxS网格,在每个网格内我们拍摄m个边界框。对于每个边界框,网络输出边界框的类概率和偏移值。选择具有高于阈值的类概率的边界框并用于在图像中定位对象。
YOLO is orders of magnitude faster(45 frames per second) than other object detection algorithms. The limitation of YOLO algorithm is that it struggles with small objects within the image, for example it might have difficulties in detecting a flock of birds. This is due to the spatial constraints of the algorithm.
YOLO比其他目标检测算法快几个数量级(每秒45帧)。YOLO算法的局限性在于它很难处理图像中的小对象,例如,它可能很难检测到一群鸟。这是由于算法的空间限制。
Conclusion
Computer vision conferences have been viewing new radical concepts each year and step by step I guess we are moving towards jaw-dropping performances from AI(if not already!). It only gets better. I hope the concepts were made lucid in this article, thank you 😃
计算机视觉会议每年都会看到新的激进概念,我想我们正一步步走向人工智能令人瞠目结舌的表现(如果还没有的话!)。它只会变得更好。我希望这篇文章中的概念清晰明了,谢谢:)


