[转] 20 Command Line Tools to Monitor Linux Performance
It’s really very tough job for every System or Network administrator to monitor and debug Linux System Performance problems every day. After being a Linux Administrator for 5 years in IT industry, I came to know that how hard is to monitor and keep systems up and running. For this reason, we’ve compiled the list of Top 20 frequently used command line monitoring tools that might be useful for every Linux/Unix System Administrator. These commands are available under all flavors of Linux and can be useful to monitor and find the actual causes of performance problem. This list of commands shown here are very enough for you to pick the one that is suitable for your monitoring scenario.
1. Top – Linux Process Monitoring
Linux Top command is a performance monitoring program which is used frequently by many system administrators to monitor Linux performance and it is available under many Linux/Unix like operating systems. The top command used to dipslay all the running and active real-time processes in ordered list and updates it regularly. It display CPU usage, Memory usage, Swap Memory, Cache Size, Buffer Size, Process PID, User, Commands and much more. It also shows high memory and cpu utilization of a running processess. The top command is much userful for system administrator to monitor and take correct action when required. Let’s see top command in action.
# top
For more examples of Top command read : 12 TOP Command Examples in Linux
2. VmStat – Virtual Memory Statistics
Linux VmStat command used to display statistics of virtual memory, kernerl threads, disks, system processes, I/O blocks, interrupts, CPU activity and much more. By default vmstat command is not available under Linux systems you need to install a package called sysstat that includes a vmstat program. The common usage of command format is.
# vmstat procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- --system-- -----cpu----- r b swpd free inact active si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st 1 0 0 810420 97380 70628 0 0 115 4 89 79 1 6 90 3 0
For more Vmstat examples read : 6 Vmstat Command Examples in Linux
3. Lsof – List Open Files
Lsof command used in many Linux/Unix like system that is used to display list of all the open files and the processes. The open files included are disk files, network sockets, pipes, devices and processes. One of the main reason for using this command is when a disk cannot be unmounted and displays the error that files are being used or opened. With this commmand you can easily identify which files are in use. The most common format for this command is.
# lsof COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE NODE NAME init 1 root cwd DIR 104,2 4096 2 / init 1 root rtd DIR 104,2 4096 2 / init 1 root txt REG 104,2 38652 17710339 /sbin/init init 1 root mem REG 104,2 129900 196453 /lib/ld-2.5.so init 1 root mem REG 104,2 1693812 196454 /lib/libc-2.5.so init 1 root mem REG 104,2 20668 196479 /lib/libdl-2.5.so init 1 root mem REG 104,2 245376 196419 /lib/libsepol.so.1 init 1 root mem REG 104,2 93508 196431 /lib/libselinux.so.1 init 1 root 10u FIFO 0,17 953 /dev/initctl
More lsof command usage and examples : 10 lsof Command Examples in Linux
4. Tcpdump – Network Packet Analyzer
Tcpdump one of the most widely used command-line network packet analyzer or packets sniffer program that is used capture or filter TCP/IP packets that received or transferred on a specific interface over a network. It also provides a option to save captured packages in a file for later analysis. tcpdump is almost available in all major Linux distributions.
# tcpdump -i eth0 tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes 22:08:59.617628 IP tecmint.com.ssh > 115.113.134.3.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in.28472: P 2532133365:2532133481(116) ack 3561562349 win 9648 22:09:07.653466 IP tecmint.com.ssh > 115.113.134.3.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in.28472: P 116:232(116) ack 1 win 9648 22:08:59.617916 IP 115.113.134.3.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in.28472 > tecmint.com.ssh: . ack 116 win 64347
For more tcpdump usage read : 12 Tcpdump Command Examples in Linux
5. Netstat – Network Statistics
Netstat is a command line tool for monitoring incoming and outgoing network packets statistics as well as interface statistics. It is very useful tool for every system administrator to monitor network performance and troubleshoot network related problems.
# netstat -a | more Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 *:mysql *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:sunrpc *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:realm-rusd *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:ftp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:ipp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:smtp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:smtp localhost.localdomain:42709 TIME_WAIT tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:smtp localhost.localdomain:42710 TIME_WAIT tcp 0 0 *:http *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:https *:* LISTEN
More Netstat examples : 20 Netstat Command Examples in Linux.
6. Htop – Linux Process Monitoring
Htop is a much advanced interactive and real time Linux process monitoring tool. This is much similar to Linux top command but it has some rich features like user friendly interface to manage process, shortcut keys, vertical and horizontal view of the processes and much more. Htop is a third party tool and doesn’t included in Linux systems, you need to install it using YUM package manager tool. For more information on installation read our article below.
# htop
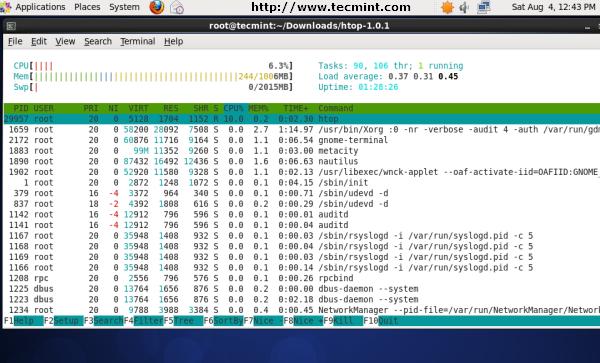
Htop Command Example Screenshot
For Htop installation read : Install Htop (Linux Process Monitoring) in Linux
7. Iotop – Monitor Linux Disk I/O
Iotop is also much similar to top command and Htop program, but it has accounting function to monitor and display real time Disk I/O and processes. This tool is much useful for finding the exact process and high used disk read/writes of the processes.
# iotop
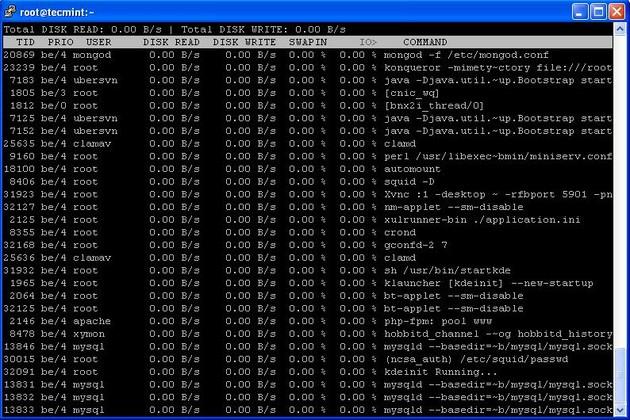
Iotop Command Example Screenshot
For Ioptop installation and usage read : Install Iotop in Linux
8. Iostat – Input/Output Statistics
IoStat is simple tool that will collect and show system input and output storage device statistics. This tool is often used to trace storage device performance issues including devices, local disks, remote disks such as NFS.
# iostat
Linux 2.6.18-238.9.1.el5 (tecmint.com) 09/13/2012
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
2.60 3.65 1.04 4.29 0.00 88.42
Device: tps Blk_read/s Blk_wrtn/s Blk_read Blk_wrtn
cciss/c0d0 17.79 545.80 256.52 855159769 401914750
cciss/c0d0p1 0.00 0.00 0.00 5459 3518
cciss/c0d0p2 16.45 533.97 245.18 836631746 384153384
cciss/c0d0p3 0.63 5.58 3.97 8737650 6215544
cciss/c0d0p4 0.00 0.00 0.00 8 0
cciss/c0d0p5 0.63 3.79 5.03 5936778 7882528
cciss/c0d0p6 0.08 2.46 2.34 3847771 3659776
For more Iostat usage and examples visit : 6 Iostat Command Examples in Linux
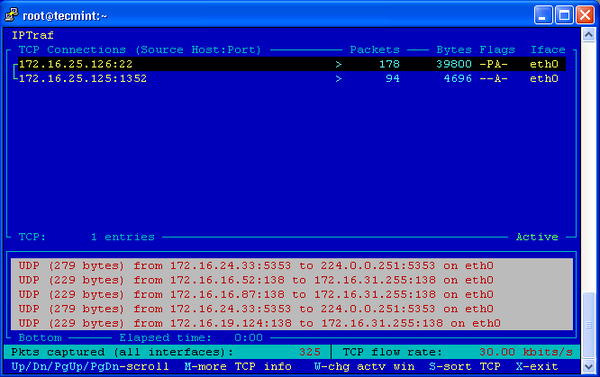
9. IPTraf – Real Time IP LAN Monitoring
IPTraf is an open source console-based real time network (IP LAN) monitoring utility for Linux. It collects a variety of information such as IP traffic monitor that passes over the network, including TCP flag information, ICMP details, TCP/UDP traffic breakdowns, TCP connection packet and byne counts. It also gathers information of general and detaled interface statistics of TCP, UDP, IP, ICMP, non-IP, IP checksum errors, interface activity etc.
For more information and usage of IPTraf tool, please visit : IPTraf Network Monitoring Tool
10. Psacct or Acct – Monitor User Activity
psacct or acct tools are very useful for monitoring each users activity on the system. Both daemons runs in the background and keeps a close watch on the overall activity of each user on the system and also what resources are being consumed by them.
These tools are very useful for system administrators to track each users activity like what they are doing, what commands they issued, how much resources are used by them, how long they are active on the system etc.
For installation and example usage of commands read the article on Monitor User Activity with psacct or acct
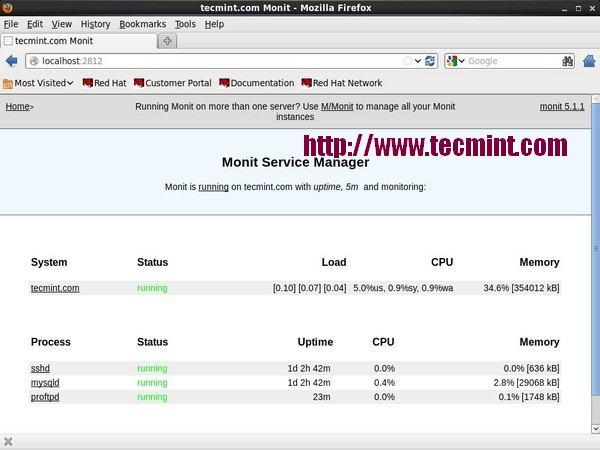
11. Monit – Linux Process and Services Monitoring
Monit is a free open source and web based process supervision utility that automatically monitors and managers system processes, programs, files, directories, permissions, checksums and filesystems.
It monitors services like Apache, MySQL, Mail, FTP, ProFTP, Nginx, SSH and so on. The system status can be viewed from the command line or using it own web interface.
Read More : Linux Process Monitoring with Monit
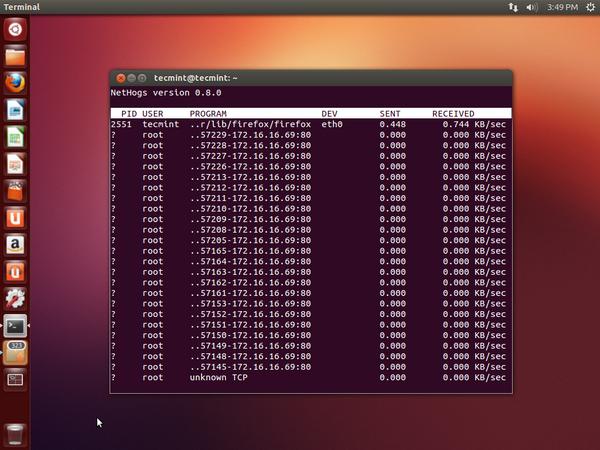
12. NetHogs – Monitor Per Process Network Bandwidth
NetHogs is an open source nice small program (similar to Linux top command) that keeps a tab on each process network activity on your system. It also keeps a track of real time network traffic bandwidth used by each program or application.
Read More : Monitor Linux Network Bandwidth Using NetHogs
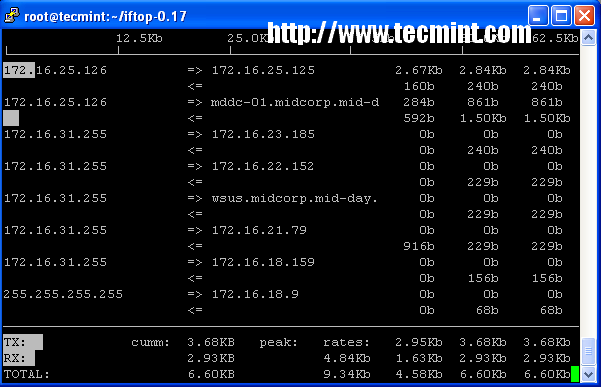
13. iftop – Network Bandwidth Monitoring
iftop is another terminal-based free open source system monitoring utility that displays a frequently updated list of network bandwidth utilization (source and destination hosts) that passing through the network interface on your system. iftop is considered for network usage, what ‘top‘ does for CPU usage. iftop is a ‘top‘ family tool that monitor a selected interface and displays a current bandwidth usage between two hosts.
Read More : iftop – Monitor Network Bandwidth Utilization
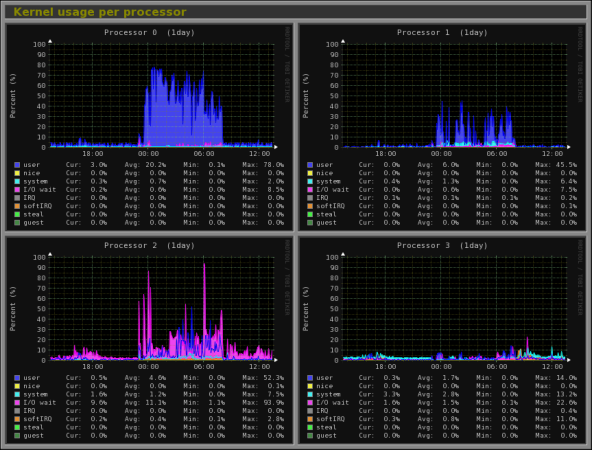
14. Monitorix – System and Network Monitoring
Monitorix is a free lightweight utility that is designed to run and monitor system and network resources as many as possible in Linux/Unix servers. It has a built in HTTP web server that regularly collects system and network information and display them in graphs. It Monitors system load average and usage, memory allocation, disk driver health, system services, network ports, mail statistics (Sendmail, Postfix, Dovecot, etc), MySQL statistics and many more. It designed to monitor overall system performance and helps in detecting failures, bottlenecks, abnormal activities etc.
Read More : Monitorix a System and Network Monitoring Tool for Linux
15. Arpwatch – Ethernet Activity Monitor
Arpwatch is a kind of program that is designed to monitor Address Resolution (MAC and IP address changes) of Ethernet network traffic on a Linux network. It continuously keeps watch on Ethernet traffic and produces a log of IP and MAC address pair changes along with a timestamps on a network. It also has a feature to send an email alerts to administrator, when a pairing added or changes. It is very useful in detecting ARP spoofing on a network.
Read More : Arpwatch to Monitor Ethernet Activity
16. Suricata – Network Security Monitoring
Suricata is an high performance open source Network Security and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Monitoring System for Linux, FreeBSD and Windows.It was designed and owned by a non-profit foundation OISF (Open Information Security Foundation).
Read More : Suricata – A Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention System
17. VnStat PHP – Monitoring Network Bandwidth
VnStat PHP a web based frontend application for most popular networking tool called “vnstat“. VnStat PHP monitors a network traffic usage in nicely graphical mode. It displays a total IN and OUT network traffic usage in hourly, daily, monthly and full summary report.
Read More : VnStat PHP – Monitoring Network Bandwidth
18. Nagios – Network/Server Monitoring
Nagios is an leading open source powerful monitoring system that enables network/system administrators to identify and resolve server related problems before they affect major business processes. With the Nagios system, administrators can able to monitor remote Linux, Windows, Switches, Routers and Printers on a single window. It shows critical warnings and indicates if something went wrong in your network/server which indirectly helps you to begin remediation processes before they occur.
Read More : Install Nagios Monitoring System to Monitor Remote Linux/Windows Hosts
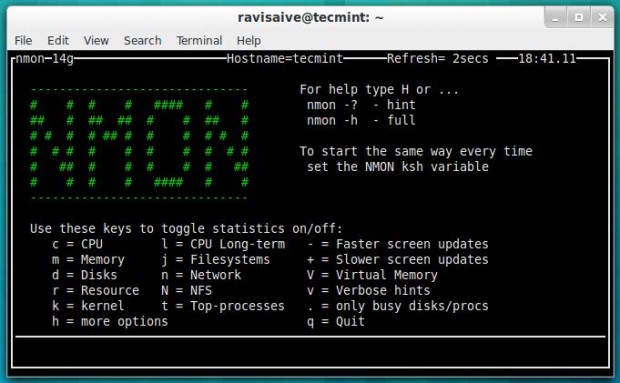
19. Nmon: Monitor Linux Performance
Nmon (stands for Nigel’s performance Monitor) tool, which is used to monitor all Linux resources such as CPU, Memory, Disk Usage, Network, Top processes, NFS, Kernel and much more. This tool comes in two modes: Online Mode and Capture Mode.
The Online Mode, is used for real-time monitoring and Capture Mode, is used to store the output in CSV format for later processing.
Read More: Install Nmon (Performance Monitoring) Tool in Linux
20. Collectl: All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool
Collectl is a yet another powerful and feature rich command line based utility, that can be used to gather information about Linux system resources such as CPU usage, memory, network, inodes, processes, nfs, tcp, sockets and much more.
Read More: Install Collectl (All-in-One Performance Monitoring) Tool in Linux
21. Glances – Real Time System Monitoring
Glances is a monitoring tool built to present as much information as possible in any terminal size, it automatically takes the terminal window size it runs on, in other words, it’s a responsive monitoring tool.
Features
- Licensed under LGPL and written in Python.
- Cross-platform, it works on Windows, Mac, BSD and Linux.
- Available in most Linux official repositories.
- A It gives a lot of information about your system.
- Built using curses.
Read More: Install Glances on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Ubuntu/Debian
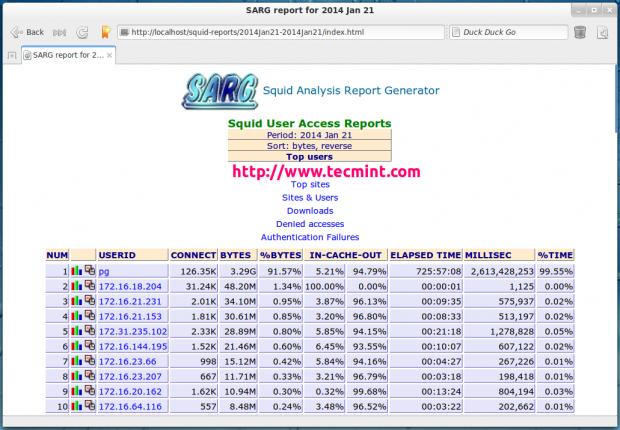
22. Sarg – Squid Bandwidth Monitoring
Sarg (Squid Analysis Report Generator) is a free & open-source tool which act as a monitoring tool for your Squid proxy server, it creates reports about your Squid proxy server users, IP addresses, the sites they visit beside some other information.
Features of Sarg
- Licensed under GPL 2 and available in many languages.
- Works under Linux & FreeBSD.
- Generates report in HTML format.
- Very easy to install & use.
Read More: Install Sarg “Squid Bandwidth Monitoring” Tool in Linux
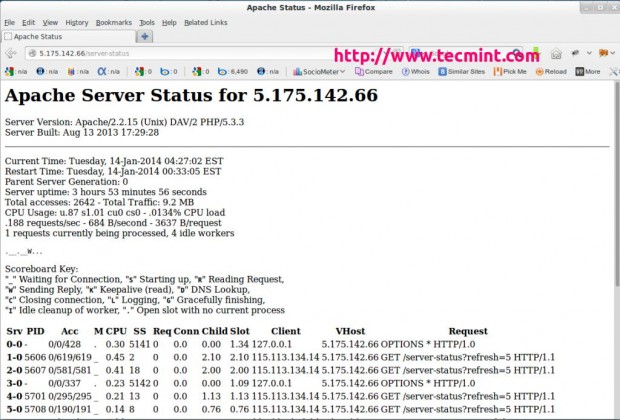
23. Apache Status Monitoring
Apache Module mod_status is an Apache server module that allows you to monitor the workers status of the Apache server. It generates a report in an easy to read HTML format. It shows you the status of all the workers, how much CPU each one using, and what requests are currently handled and number of working and not working workers.
Read More: Apache Web Server Load and Page Statistics Monitoring
24. Monit – Linux Process and Services Monitoring
Monit is a nice program that monitors your Linux & Unix server, it can monitor everything you have on your server, from the main server (Apache, Nginx..) to files permissions, files hashes and web services. Plus a lot of things.
Features of Monit
- Free & open-source, released under AGPL and written in C.
- It can be started from the command line interface or via its special web interface.
- Very effective in monitoring all the software on your system and services.
- A nice web interface with beautiful charts for CPU and RAM usage.
- Monit can automatically take actions in emergency situations.
- A lot more..
Read More: Install Monit Tool in RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Ubuntu/Debian
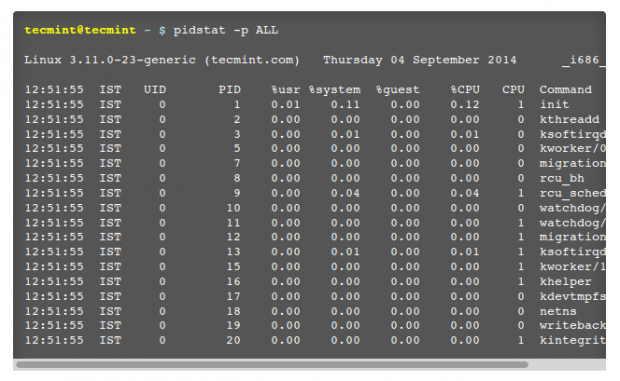
25. Sysstat – All-in-One System Performance Monitoring
Another monitoring tool for your Linux system. Sysstat is not a real command in fact, it’s just the name of the project, Sysstat in fact is a package that includes many performance monitoring tools like iostat, sadf, pidstat beside many other tools which shows you many statistics about your Linux OS.
Features of Sysstat
- Available in many Linux distributions repositories by default.
- Ability to create statistics about RAM, CPU, SWAP usage. Beside the ability to monitor Linux kernel activity, NFS server, Sockets, TTY and filesystems.
- Ability to monitor input & output statistics for devices, tasks.. etc.
- Ability to output reports about network interfaces and devices, with support for IPv6.
- Sysstat can show you the power statistics (usage, devices, the fans speed.. etc) as well.
- Many other features..
Read More: Install Sysstat in Linux and 20 Useful Commands of Sysstat
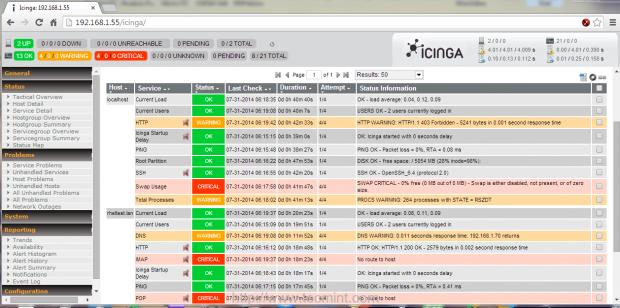
26. Icinga – Next Generation Server Monitoring
Unlike the other tools, Icinga is a network monitoring program, it shows you many options and information about your network connections, devices and processes, it’s a very good choice for those who are looking for a good tool to monitor their networking stuffs.
Features of Icinga
- Icinga is also free and open-source.
- Very functional in monitoring everything you may have in networking.
- Support for MySQL and PostgreSQL is included.
- Real-time monitoring with A nice web interface.
- Very expendable with modules and extensions.
- Icinga supports applying services and actions to hosts.
- A lot more to discover..
Read More: Install Icinga in RHEL/CentOS 7/6
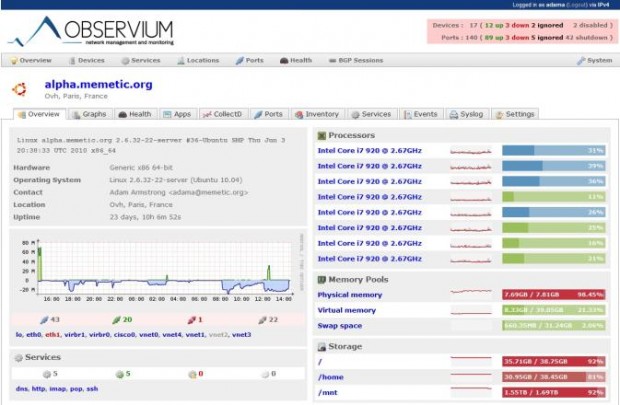
27. Observium – Network Management and Monitoring
Observium is also a network monitoring tool, it was designed to help you manage your network of servers easily, there are 2 versions from it; Community Edition which is free & open-source and Commercial version which costs £150/year.
Features of Observium
- Written in PHP with MySQL database support.
- Has a nice web interface to output information and data.
- Ability to manage and monitor hundreds of hosts worldwide.
- The community version from it is licensed under QPL license.
- Works on Windows, Linux, FreeBSD and more.
Read More: Observium – Network Management and Monitoring Tool for RHEL/CentOS
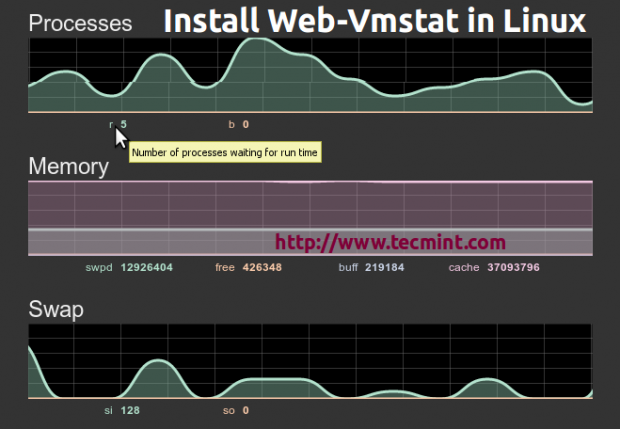
28. Web VMStat – System Statistics Monitoring
Web VMStat is a very simple web application programmer, that provides a real time system information usage, from CPU to RAM, Swap and input/output information in html format.
Read More: Web VMStat: A Real Time System Statistics Tool for Linux
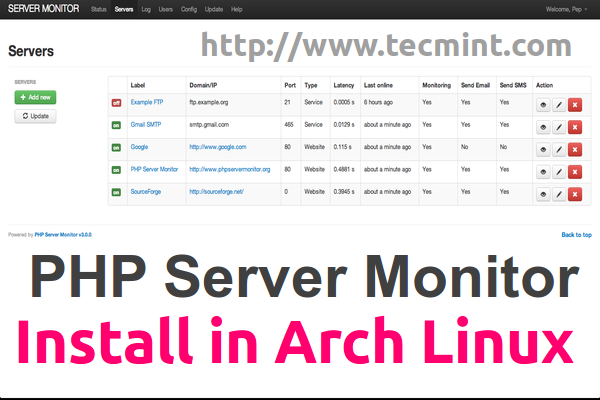
29. PHP Server Monitoring
Unlike the other tools on this list, PHP Server Monitoring is a web script written in PHP that helps you to manage you websites and hosts easily, it supports MySQL database and is released under GPL 3 or later.
Features
- A nice web interface.
- Ability to send notifications to you via Email & SMS.
- Ability to view the most important information about CPU and RAM.
- A very modern logging system to log connection errors and emails that are sent.
- Support for cronjob services to help you monitor your servers and websites automatically.
Read More: Install PHP Server Monitoring Tool in Arch Linux
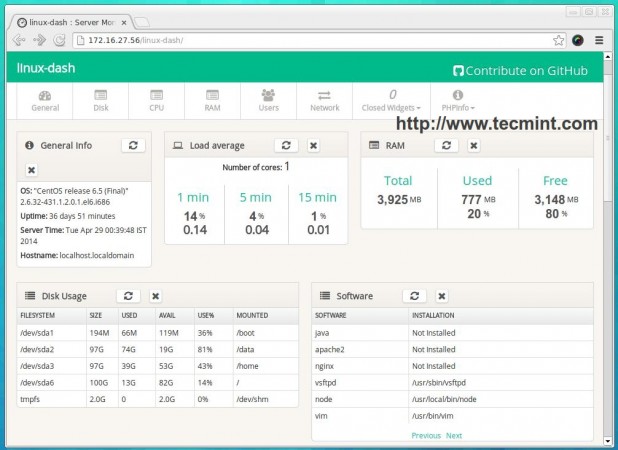
30. Linux Dash – Linux Server Performance Monitoring
From its name, “Linux Dash” is a web dashboard that shows you the most important information about your Linux systems such as RAM, CPU, file-system, running processes, users, bandwidth usage in real time, it has a nice GUI and it’s free & open-source.
Read More: Install Linux Dash (Linux Performance Monitoring) Tool in Linux
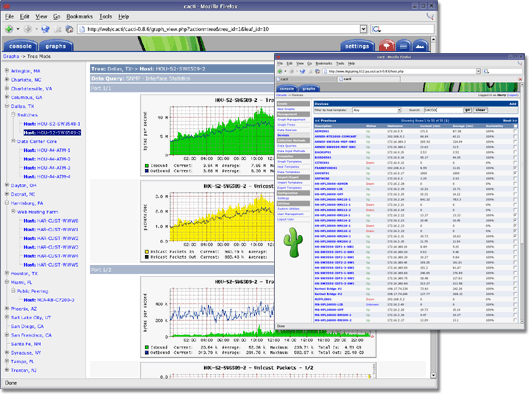
31. Cacti – Network and System Monitoring
Cacti is nothing more than a free & open-source web interface for RRDtool, it is used often to monitor the bandwidth using SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), it can be used also to monitor CPU usage.
Features of Cacti
- Free & open-source, released under GPL license.
- Written in PHP with PL/SQL.
- A cross-platform tool, it works on Windows and Linux.
- User management; you may create different users accounts for Cacti.
Read More: Install Cacti Network and System Monitoring Tool in Linux
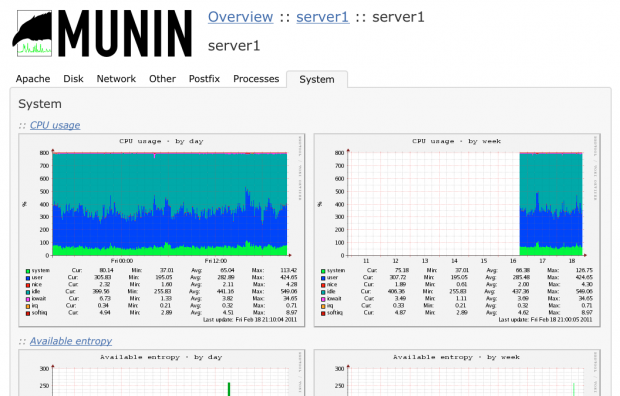
32. Munin – Network Monitoring
Munin is also a web interface GUI for RRDtool, it was written in Perl and licensed under GPL, Munin is a good tool to monitor systems, networks, applications and services. It works on all Unix-like operating systems and has a nice plugin system; there are 500 different plugin available to monitor anything you want on your machine. A notifications system is available to send messages to the administrator when there’s an error or when the error is resolved.
Read More: Install Munin Network Monitoring Tool in Linux
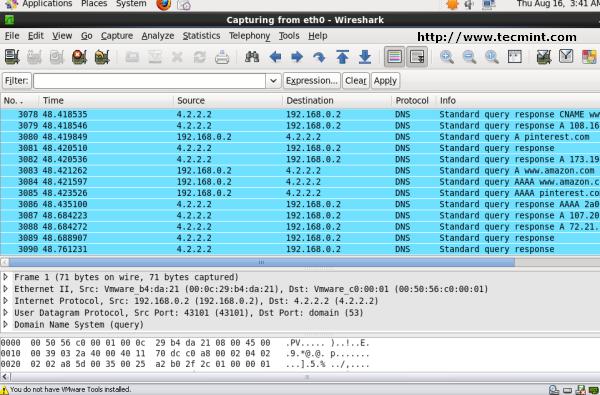
33. Wireshark – Network Protocol Analyzer
Also, unlike all the other tools on our list, Wireshark is an analyzer desktop program which is used to analyze network packets and to monitor network connections. It’s written in C with the GTK+ library and released under the GPL license.
Features
- Cross-platform: it works on Linux, BSD , Mac OS X and Windows.
- Command line support: there’s a command line based version from Wireshark to analyze data.
- Ability to capture VoIP calls, USB traffic, network data easily to analyze it.
- Available in most Linux distributions repositories.
Read More: Install Wireshark – Network Protocol Analyzer Tool in Linux




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号