ES6 - 基础学习(11): Map 和 WeakMap 数据结构
Map 数据结构
JavaScript的对象(Object),本质上是键值对的集合(Hash结构),但是键 传统上还是只能用字符串表示,这就给对象的使用带来了诸多的限制和不便。而 ES6为此提供了新的数据结构 Map,Map数据结构同样保存键值对(类似于对象),但任何值(对象或原始值) 都可以作为一个键或一个值,不再像传统对象那样受到约束。可以理解为 Object结构提供了“字符串—值”的对应,Map 数据结构提供了“值—值”的对应,是一种更完善的 Hash结构实现。
Maps 和 Objects 的区别
1、一个 Object的键只能是字符串或者 Symbols,但一个 Map的键可以是任意值。
2、Map中的键值是有序的(FIFO原则),而添加到对象中的键值则不是(对象中的键值是无序的)。
3、Map中的键值对个数可以从 size属性获取,而 Object的键值对个数只能手动计算。
4、Object都有自己的原型,原型链上的键名有可能和对象上自己设置的键名产生冲突。
Map 数据结构基本用法
// Map是一种简单、灵活的适合一对一查找的数据结构,其效率和灵活性比传统Object更好
// key是数字、字符串、null、undefined、NaN
let testMap = new Map();
testMap.set(-123, "+123"); // 键: -123,值: "+123"
testMap.set("Test Map", "和键'Test Map'对应的值"); // 键: "Test Map",值: "和键'Test Map'对应的值"
testMap.set(null, NaN); // 键: null,值: NaN
testMap.set(undefined, 1234); // 键: undefined,值:1234
testMap.set(NaN, 10 * 10); // 键: NaN,值:10*10 虽然 NaN和任何值甚至和它自己都不相等(NaN !== NaN 返回true),但 NaN作为 Map的键来说是没有区别的。
console.log(testMap); // Map(5) {-123 => "+123", "Test Map" => "和键'Test Map'对应的值", null => NaN, undefined => 1234, NaN => 100}
// key是对象
let testMap = new Map();
testMap.set({'Test':'Map'}, {'Test':'Map'}); // 键: {'Test':'Map'},值: {'Test':'Map'}
console.log(testMap); // Map(1) {{…} => {…}}
// key是数组
let testMap = new Map();
testMap.set([1,2,'TestMap'], [1,2,'TestMap']); // 键: [1,2,'TestMap'],值: [1,2,'TestMap']
console.log(testMap); // Map(1) {Array(3) => Array(3)}
// key是函数
let testMap = new Map();
testMap.set(function () { // 键: function方法,值: [1,2,'TestMap']
console.log('new Map');
}, [1,2,'TestMap']);
console.log(testMap); // Map(1) {ƒ => Array(3)}


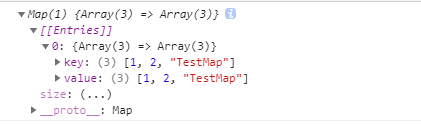

图1:key是数字、字符串、null、undefined、NaN 图2:key是对象 图3:key是数组 图4:key是方法
// Map作为构造函数,Map也可以接受一个数组(二维数组)作为参数。该数组内的成员(成员也是数组)是一个个表示键值对的数组。
let testMap = new Map([
[-123, '+123'],
[undefined, null],
[NaN, NaN]]);
console.log(testMap); // Map(3) {-123 => "+123", undefined => null, NaN => NaN}
// 如果Map实例的键是一个基本数据类型(字符串、数字、布尔值,null,undefined,Symbol),则只要两个值严格相等,Map数据结构就将其视为同一个键。如0和-0是一个键,布尔值true和字符串true则是两个不同的键,undefined 和 null是两个不同的键。
// 另外,虽然NaN不严格相等于自身,但 Map数据结构将其视为同一个键。
// Map构造函数传入数组作为参数初始化,实际上相当于执行了以下三步。
let parList = [
[-123, '+123'],
[undefined, null],
[NaN, NaN]
];
let testMap = new Map();
parList.forEach(
([key, value]) => testMap.set(key, value)
);
Map 实例的属性和方法
Map 实例具有以下原型属性:
1、Map.prototype.constructor:构造函数,即默认的 Map函数。
2、Map.prototype.size:返回 Map实例的成员数量总数。
Map 实例具有以下原型方法,主要分为:操作方法(用于操作数据) 和 遍历方法(用于遍历成员)。
1、Map.prototype.set(key, value):设置键名key对应的键值value,然后返回整个 Map实例。若key存在,则更新该键对应的值,否则就新生成该键,并进行赋值。
2、Map.prototype.get(key):获取 Map实例内 key键对应的值,键存在则返回该键对应的值,不存在则返回undefined。
3、Map.prototype.has(key):返回一个布尔值,表示该键是否在当前 Map实例内。
4、Map.prototype.delete(key):删除 Map实例内某个键,返回一个布尔值。true表示删除成功;false删除失败,或者该键不存在。
5、Map.prototype.clear():清除所有成员(清空当前 Map实例),没有返回值。
6、Map.prototype.keys():返回键名的遍历器。
7、Map.prototype.values():返回键值的遍历器。
8、Map.prototype.entries():返回所有成员的遍历器。
9、Map.prototype.forEach():遍历每个成员的回调函数,可以遍历当前 Map实例内每个成员。
Map 实例原型方法 - 操作方法:set(key, value)、get(key)、has(key)、delete(key)、clear()
// size属性
let testMap = new Map([
[-123, '+123'],
[undefined, null],
]);
console.log(testMap.size); // 2
// set(key,value)
testMap.set('setFunc', ['setFunc', 1234]); // Map(3) {-123 => "+123", undefined => null, "setFunc" => Array(2)}
testMap.set('setFunc', true); // Map(3) {-123 => "+123", undefined => null, "setFunc" => true} 'setFunc'存在,更新'setFunc'对应的值
testMap.set(NaN, NaN); // Map(4) {-123 => "+123", undefined => null, "setFunc" => true, NaN => NaN} NaN不存在,新生成 NaN键 并进行赋值
testMap.set('setFunc', true).set(NaN, NaN); // Map(4) {-123 => "+123", undefined => null, "setFunc" => true, NaN => NaN} set方法 链式操作
// get(key)
testMap.get(undefined); // null
testMap.get(456789); // undefined
// has(key)
testMap.has(undefined); // true
testMap.has(456789); // false
// delete(key)
testMap.delete(undefined); // true
testMap.delete(456789); // false 该键不存在,在删除时也会返回false。所以在数据操作要求比较严格时,应先判断该键是否存在,再视情况决定是否进行删除操作
// clear()
console.log(testMap.size); // 3
testMap.clear(); // 没有返回值,故显示 undefined
testMap.size; // 0
Map 实例原型方法 - 遍历方法:keys()、values()、entries()、forEach()
// Map的遍历顺序就是成员的添加顺序。Map数据结构的迭代,以 for...of 和 forEach()最优
let testMap = new Map([
[-123, '+123'],
[undefined, null],
['setFunc', ['setFunc', 1234]],
]);
testMap.set(NaN, {'test': '17:40'});
// keys()
for (let item of testMap.keys()) {
console.log(item);
}
// -123
// undefined
// setFunc
// NaN
// values()
for (let item of testMap.values()) {
console.log(item);
}
// +123
// null
// ["setFunc", 1234]
// {test: "17:40"}
// entries():entries方法返回的遍历器都是以数组的形式呈现,同时包括键名和键值(前是名后是值)。
for (let item of testMap.entries()) {
console.log(item);
}
// 或
for (let [key, value] of testMap.entries()) {
console.log([key, value]);
}
// [-123, "+123"]
// [undefined, null]
// ["setFunc", Array(2)]
// [NaN, {…}]
// Map数据结构的默认遍历器接口(Symbol.iterator属性)就是entries方法,所以 for...of等同于调用 entries()方法
for (let [key, value] of testMap) {
console.log([key, value]);
}
// [-123, "+123"]
// [undefined, null]
// ["setFunc", Array(2)]
// [NaN, {…}]
console.log(testMap[Symbol.iterator] === testMap.entries); // true
// forEach():Map实例也可以使用forEach方法,用于对每个成员执行指定操作,没有返回值。
testMap.forEach(function (value, key) {
console.log([key, value]);
});
// [-123, "+123"]
// [undefined, null]
// ["setFunc", Array(2)]
// [NaN, {…}]
WeakMap 数据结构
WeakMap 数据结构 与 Map 数据结构类似,也是键值对的集合,但它与 Map有两个区别。
1、WeakMap 只接受对象作为键名 (null 除外),不接受其他类型的值作为键名。
2、WeakMap 实例内键名所指向的对象,不计入垃圾回收机制,和 WeakSet实例内的成员一样。
// WeakMap本身也是一个构造函数,用来生成 WeakMap数据结构实例。WeakMap可以接受一个数组(二维数组)作为构造函数的初始化参数,但该数组内(外层数组)各个成员数组(内层数组)第一项必须是对象或者数组
let testWeakMap = new WeakMap([[{}, '+123'], [{}, null]]);
console.log(testWeakMap); // WeakMap {{…} => "+123", {…} => null}
let testWeakMap = new WeakMap([[[1, 2, 3], '[1, 2, 3]'], [[4, 5, 6], '[4, 5, 6]']]);
console.log(testWeakMap); // WeakMap {Array(3) => "[4, 5, 6]", Array(3) => "[1, 2, 3]"}
console.log(testWeakMap.get([1, 2, 3])); // undefined 两次引用数组[1, 2, 3],内存地址不一样,[1, 2, 3]和[1, 2, 3]不是同一个数组,所以获取不到值
testWeakMap.set(123, 456);
console.log(testWeakMap); // Uncaught TypeError: Invalid value used as weak map key
testWeakMap.set(null, undefined);
console.log(testWeakMap); // Uncaught TypeError: Invalid value used as weak map key
和 WeakSet一样,WeakMap数据结构也没有size属性(WeakMap实例内某个键名某个时刻是否存在完全不可预测,跟垃圾回收机制何时运行有关),故不能进行keys()、values()、entries()、forEach()等遍历操作。
WeakMap实例只有四个原型方法:set(key, value)、get(key)、has(key),delete(key)、功能和 Map数据结构一样
let tempObj = {'a': 1};
let testWeakMap = new WeakMap();
testWeakMap.set(tempObj, 123);
console.log(testWeakMap); // WeakMap {{…} => 123}
testWeakMap.get(tempObj); // 123
testWeakMap.get({'a': 1}); // undefined
testWeakMap.has(tempObj); // true
testWeakMap.has({'a': 1}); // false
testWeakMap.size; // undefined size属性不存在
testWeakMap.clear(); // Uncaught TypeError: testWeakMap.clear is not a function 也没有clear方法
testWeakMap.delete(tempObj); // true
testWeakMap.delete({'a': 1}); // false
总结:和 Set数据结构一样,Map数据结构在实际开发过程中也经常被用到,它的灵活性和高效性以及代码的简洁性都给开发人员带来了诸多便利。



