C语言中的字符和字符串
C语言在中常常出现字符和字符串,而一串字符或者字符串其实就是数组
字符数组的定义
char arr[]={'h','e','l','l','o','\0'};
而定义字符串:
char arr1[]="HELLO";
字符的输入和输出可以向一维数组那样用scanf和printf,而字符也可以用自己特定输入和输出函数gerchar和putchar,而用getchar和putchar输入一串字符
char arr[1000]; int i=0,j=0; char ch; while ((ch=getchar())!='\n') { arr[i]=ch; i++; } arr[i]='\0'; while (arr[j]!='\0') { putchar(arr[j]); j++; } printf("\n");
输出结果:

字符串也有自己特定的输入和输出函数
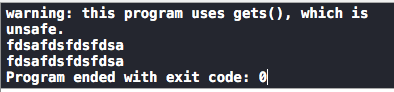
// gets和puts 字符串的输入和输出 char ch[100]; gets(ch); puts(ch);
字符串的相关库函数部分:需要导入头文件
#include <string.h>
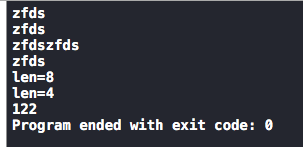
char str1[30]="wfds"; char str2[]="zfds"; strcpy(str1, str2);//把str2复制到str1中,str1的长度要比str2大 puts(str1); puts(str2); strcat(str1,str2);//把str2链接到str1中,总长度空间大于两个的空间 puts(str1); puts(str2); printf("len=%lu\n",strlen(str1));//计算字符串的长度 printf("len=%lu\n",strlen(str2));//不包括'\0' printf("%d\n",strcmp(str1, str2)) ;
结果:
字符函数部分:需要导入头文件
#include <ctype.h>
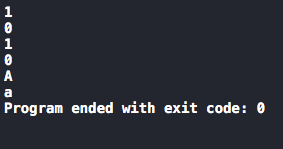
char ch='a',ch1='A'; printf("%d\n",isalpha(ch));//是否为字母 printf("%d\n",isupper(ch));//是否为大写 printf("%d\n",islower(ch));//是否为小写 printf("%d\n",isdigit(ch));//是否为数字 printf("%c\n",toupper(ch));//转变为大写 printf("%C\n",tolower(ch1));//转变为小写
字符串大写变小写,小写变大写
char ch[100],ch1; gets(ch); int i=0; while (ch[i]!='\0') { ch1=ch[i]; if (isupper(ch1)==1) { ch1= tolower(ch1); }else{ ch1=toupper(ch1); } putchar(ch1); i++; } printf("\n");
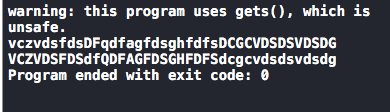
字符串转为整型或浮点型
需要导入头文件
#include <stdlib.h>
//字符串转 char *chs="11.52"; printf("chs=%s\n",chs); double d=atof(chs); int a=atoi(chs); printf("%f\n",d); printf("%d\n",a);
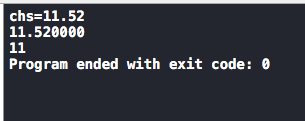
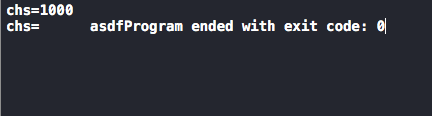
数字转字符串
int num=1000; char chs[100]; //将num按照%d的格式存储到chs中 sprintf(chs,"%d",num); printf("chs=%s\n",chs); //将字符串按照指定的格式存储 sprintf(chs, "%10s","asdf"); printf("chs=%s",chs);