线程五大状态
1. 线程的五大状态
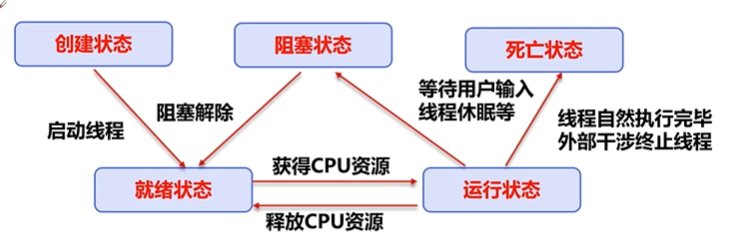
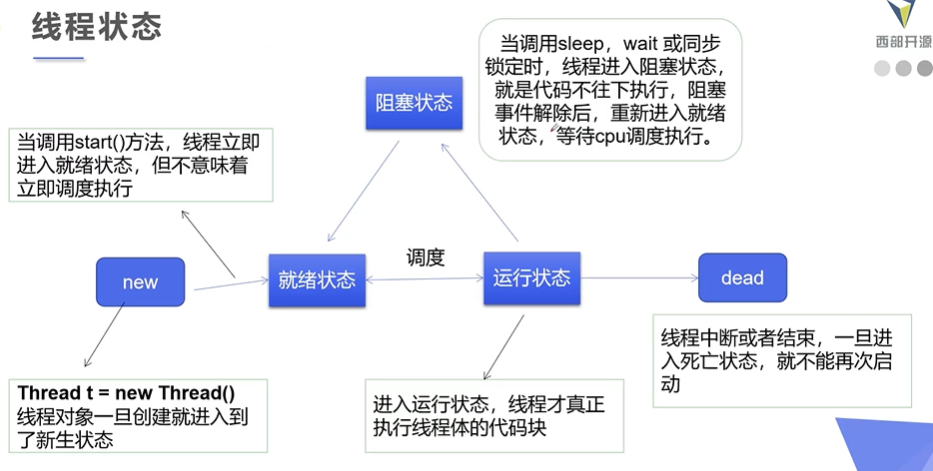
2. 线程停止stop
- 建议线程正常停止,-->利用次数,不建议死循环
2 .建议使用标志位 - 不要使用stop或destroy等JDK不建议使用的方法
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
//1.设置一个标志位
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i =0;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("run...Thread" + i++);
}
}
//2.设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop() {
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();
new Thread(testStop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("main "+ i);
if (i == 80) {
testStop.stop();
System.out.println("线程停止了");
}
}
}
}
3. 线程休眠sleep

public class TestSleep {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
tenDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//获取系统当前时间
Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
int count = 10;
while (count >= 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));
startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
count--;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//模拟倒计时
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if (num <= 0) break;;
}
}
}
4. 线程礼让yield
礼让不一定成功,看CPU心情
public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield = new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield,"a").start();
new Thread(myYield,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行");
Thread.yield(); //线程礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程停止执行");
}
}

5. join合并线程
代此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞,可以理解为插队
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("VIP来了" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动线程
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
//主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
System.out.println("main" + i);
if (i == 200) {
thread.join();
}
}
}
}
6. 测试线程状态
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {//等待5s
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("---------");
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //NEW
//启动后
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //RUN
//只要线程不终止,一直输出状态
while (state!=Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //更新线程状态
}
}
}
7. 测试优先级
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10
先设置优先级,再启动start()
public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程默认优先级
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority,"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority,"t2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority,"t3");
Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority,"t4");
Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority,"t5");
//先设置优先级,再启动
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(6);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(1);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(8);
t5.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
8. 守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 如垃圾回收机制gcc
//测试守护线程
//上帝守护你
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
YouAndMe ym = new YouAndMe();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true);//默认false是用户线程,正常线程都是用户线程
thread.start();//上帝守护线程启动
new Thread(ym).start();//用户线程启动
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("上帝保佑着你我");
}
}
}
class YouAndMe implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("你我活着");
}
System.out.println("Goodbye World------");
}
}

