Spring学习笔记1
一、Spring介绍
Spring 是一个开源框架,是为了解决企业应用程序开发复杂性而创建的。框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许您选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 J2EE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。
简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EE full-stack(一站式)轻量级开源框架
spring有两个核心模块:
1.控制反转 (Inversion Of Control)(IOC)容器
(或者叫做依赖注入dependency injection(DI ))
2.Spring 面向切面编程(AOP)
spring 框架是一个分层架构,由 7 个定义良好的模块组成。Spring 模块构建在核心容器之上,核心容器定义了创建、配置和管理 bean 对象的方式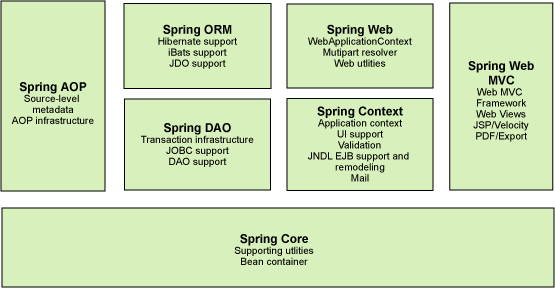
spring在项目中的地位
二、Spring使用
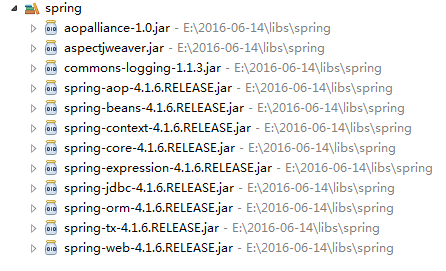
1、导入jar包
2、配置文件
在根目录下新建一个xml配置文件,名字没有限制,一般为spring.xml(和SpringMVC可使用同一个配置文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- 把需要管理的bean配置在 DI IOC 依赖注入/控制反转 (这个类的控制权就交由spring管壁,统一管理 反转权利)--> <!-- <bean name="udao" class="dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean> <bean name="udao2" class="dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean> Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type [dao.UserDao] is defined: expected single matching bean but found 2: udao,udao2 <bean name="uservice" class="service.impl.UserServiceImpl" autowire="byType"> 配置属性值,非简单类型用ref引用 ,简单类型(基本数据类型)用value赋值 <property name="ud" ref="udao"></property> 如果不 手动实例化,,提供了自动方式1byName 2byType <property name="aaa" value="999"></property> <property name="score"> <array> <value>99</value> <value>88.5</value> <value>77</value> <value>66</value> </array> </property> <property name="animals"> <list> <value>东北虎</value> <value>北极熊</value> <value>南极企鹅</value> </list> </property> <property name="people"> <set> <value>张三</value> <value>李四</value> <value>王五</value> </set> </property> <property name="weather"> <map> <entry key="郑州" value="多云" /> <entry key="北京" value="晴" /> <entry key="上海" value="暴雨" /> </map> </property> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="a">100</prop> <prop key="b">200</prop> <prop key="c">300</prop> </props> </property> </bean> --> <!-- 之前类与类之间的交互,需要通过在对方类中new对象的方式实现 --> <!-- 现在类与类之间的交互,把类交给spring,把控制权完全交给spring --> <!-- 注解方式完成dao层和service层的自动注入 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zy"></context:component-scan> </beans>
3、生成对象
UserDaoImpl
package com.zy.dao.impl; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.zy.dao.UserDao; @Component //这个注解就相当于在spring.xml配置了该bean public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ //1探究spring怎么管理bean @Override public void login(String name, String pwd) { System.out.println("用户名:"+name+"密码:"+pwd); } }
UserServiceImpl
package com.zy.service.impl; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.zy.dao.UserDao; import com.zy.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl; import com.zy.service.UserService;
@Component //把该类纳入spring管理 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ //service层要调用dao层,需要创建dao层对象,调用dao层方法 // UserDao ud = new UserDaoImpl();//不要自己动手实例化对象---会通过spring实现 @Autowired //通过spring自动实例化该对象 先按byName再按byType UserDao ud; //若不给getter setter会报 // Bean property 'ud' is not writable or has an invalid setter method public UserDao getUd() { return ud; } public void setUd(UserDao ud) { this.ud = ud; }
String aaa; public String getAaa() { return aaa; } public void setAaa(String aaa) { this.aaa = aaa; } //-----------------------集合属性---数组------------------------ private double[] score; public double[] getScore() { return score; } public void setScore(double[] score) { this.score = score; } //-----------------------集合属性---List------------------------ private List<String> animals; public List<String> getAnimals() { return animals; } public void setAnimals(List<String> animals) { this.animals = animals; } //-----------------------集合属性---Set------------------------ private Set<String> people; public Set<String> getPeople() { return people; } public void setPeople(Set<String> people) { this.people = people; } //-----------------------集合属性---Map------------------------ private Map<String, String> weather; public Map<String, String> getWeather() { return weather; } public void setWeather(Map<String, String> weather) { this.weather = weather; } //-----------------------集合属性---Properties------------------------ private Properties properties;// 集合 键a=100 值b=200,现在基本被Map取代了 public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Override public void login(String name, String pwd) { ud.login(name, pwd); } }
4、对象属性赋值,单例/原型模式
上面2中xml
DI_Scope
scope:
1).singleton单例模式(默认)
一个bean标签只会生成一个对象,每次在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中通过getBean方法获取的时候都是同一个对象
2).prototype原型模式
一个bean标签只会生成多个对象,每次在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中通过getBean方法获取的时候都是同一新的对象
三、注解方式(二中的3)
自动注入(给某个类中的属性实例化对象)
<bean autowire="byType"></bean>
按类型在spring所有的bean中找合适的bean去实例化对象
注意:如果再bean集合中发现两个及以上可用的bean就会报错
<bean autowire="byName"></bean>
按名字在spring所有的bean中找与属性同名的bean去实例化对象
<!-- 注解方式完成dao层和service层的自动注入 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zy"></context:component-scan>

类上使用
|
@Component //这个注解就相当于在spring.xml中配置了该bean---把该类纳入spring管理 |
属性上使用
|
@Autowired //通过spirng自动实例化该对象 UserDao ud; |
类上 控制对象的单例/原型模式
|
@Scope("prototype") @Scope("singleton") 默认 |
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.zy.service.impl.UserServiceImpl; public class MyTest2 { @Test public void show(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext cxc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); UserServiceImpl bean = cxc.getBean("userServiceImpl", UserServiceImpl.class); //注解方式默认名称为类名首字母小写 bean.login("小白", "123456"); } }
//总结下,如果三层中,service调用dao层对象,controller调用service对象
采用spring的控制反转/依赖注入 实现三层中的对象实例化
Ioc最大的好处,把控制权交于spring,利于项目的解耦



