axios源码学习记录
带着问题读源码,主要解决以下几个问题
1、为什么 axios 既可以当函数调用,也可以当对象使用
2、 axios 调用流程及原理
3、有用过拦截器吗?原理是怎样的?
4、axios取消请求及原理。
5、为什么支持浏览器中发送请求也支持node发送请求?
一、为什么 axios 既可以当函数调用,也可以当对象使用
axios调用了Axios函数,Axios函数的原型上绑定了很多方法。本质上两种方法最终都是调用了Axios。prototype.request同一个函数
// Provide aliases for supported request methods utils.forEach(['delete', 'get', 'head', 'options'], function forEachMethodNoData(method) { /*eslint func-names:0*/ Axios.prototype[method] = function(url, config) { return this.request(utils.merge(config || {}, { method: method, url: url })); }; }); utils.forEach(['post', 'put', 'patch'], function forEachMethodWithData(method) { /*eslint func-names:0*/ Axios.prototype[method] = function(url, data, config) { return this.request(utils.merge(config || {}, { method: method, url: url, data: data })); }; });
二、axios的调用流程

流程中最关键的的有三点
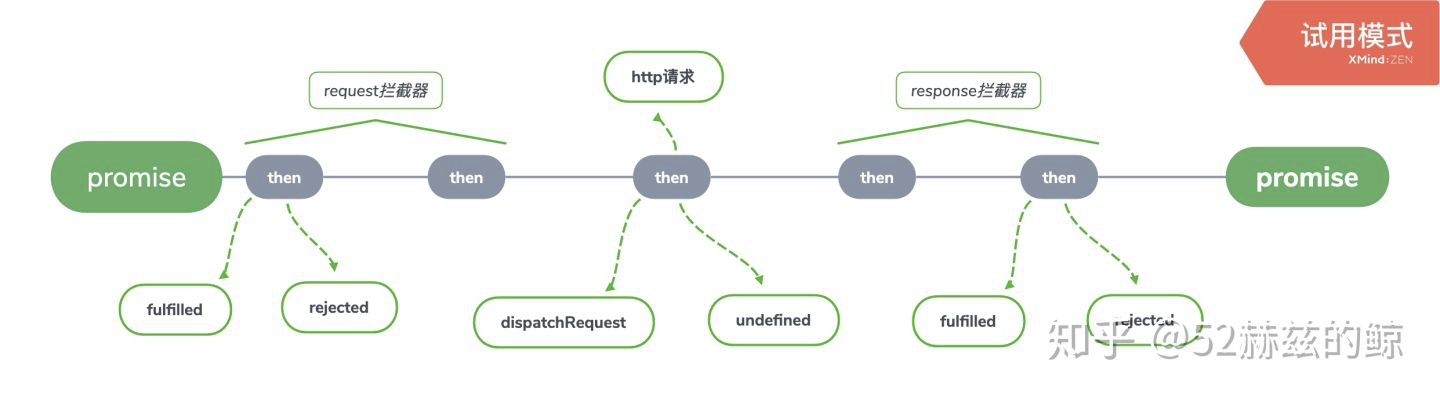
1、promise链式调用
var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined]; var promise = Promise.resolve(config); this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(interceptor) { chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected); }); this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(interceptor) { chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected); }); while (chain.length) { promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift()); }
promise链式调用最明显的就是这几行代码。
首先新建一个chain数组,一个为dispatchRequest方法,一个是为了对称加入的undefined
然后通过拦截器的forEach依次在头部加入请求拦截器的成功和失败函数。
再依次在数组尾部加入响应拦截器的成功和失败还是。
最后通过while函数循环从首部依次执行,请求拦截器=》请求=》响应拦截器,形成一个promise链
2、dispatchRequest函数
dispatchRequest函数用来真正发送请求。
它通过适配器函数adapter来判断是在浏览器环境还是node环境,以便使用xhr或者http来发送请求。
主要流程是每次执行时先判断是否有取消请求动作,如果有直接取消执行,如果没有接着向下执行
function dispatchRequest(config) { throwIfCancellationRequested(config); // Support baseURL config if (config.baseURL && !isAbsoluteURL(config.url)) { config.url = combineURLs(config.baseURL, config.url); } // 确保 config.header 存在。 config.headers = config.headers || {}; // Transform request data config.data = transformData( config.data, config.headers, config.transformRequest ); // 拍平 config.header。 config.headers = utils.merge( config.headers.common || {}, config.headers[config.method] || {}, config.headers || {} ); //删除一些 config.header。 utils.forEach( ['delete', 'get', 'head', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'common'], function cleanHeaderConfig(method) { delete config.headers[method]; } ); var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter; //返回适配器adapter(Promise实例)执行后 then执行后的 Promise实例。 //返回结果传递给响应拦截器处理。 return adapter(config).then(function onAdapterResolution(response) { //判断是否取消请求 throwIfCancellationRequested(config); // Transform response data response.data = transformData( response.data, response.headers, config.transformResponse ); return response; }, function onAdapterRejection(reason) { if (!isCancel(reason)) { throwIfCancellationRequested(config); // Transform response data if (reason && reason.response) { reason.response.data = transformData( reason.response.data, reason.response.headers, config.transformResponse ); } } return Promise.reject(reason); }); };
3、取消请求函数
function CancelToken(executor) { if (typeof executor !== 'function') { throw new TypeError('executor must be a function.'); } var resolvePromise; this.promise = new Promise(function promiseExecutor(resolve) { resolvePromise = resolve; }); var token = this; executor(function cancel(message) { if (token.reason) { // Cancellation has already been requested return; } token.reason = new Cancel(message); resolvePromise(token.reason); }); } /** * Throws a `Cancel` if cancellation has been requested. */ CancelToken.prototype.throwIfRequested = function throwIfRequested() { if (this.reason) { throw this.reason; } }; /** * Returns an object that contains a new `CancelToken` and a function that, when called, * cancels the `CancelToken`. */ CancelToken.source = function source() { var cancel; var token = new CancelToken(function executor(c) { cancel = c; }); return { token: token, cancel: cancel }; }; module.exports = CancelToken;
axios的取消使用方法:
// 第一种取消方法 axios.get(url, { cancelToken: new axios.CancelToken(cancel => { if (/* 取消条件 */) { cancel('取消请求'); } }) }); // 第二种取消方法 const CancelToken = axios.CancelToken; const source = CancelToken.source(); axios.get(url, { cancelToken: source.token }); source.cancel('取消请求');
两种方法都是调用的 new CancelToken里的executor函数
axios在每次发送请求时都会判断是否已经执行了executor函数,如果在发送请求前已经执行,直接throw error,停止发送请求。
如果已经执行到request函数,则直接返回reject(reason),这时,xhrpromise链直接执行xhr.abort(),并且返回reject
//xhr.js if (config.cancelToken) { // Handle cancellation config.cancelToken.promise.then(function onCanceled(cancel) { if (!request) { return; } request.abort(); reject(cancel); // Clean up request request = null; }); }
4、拦截器构造函数
function InterceptorManager() { this.handlers = []; } /** * Add a new interceptor to the stack * * @param {Function} fulfilled The function to handle `then` for a `Promise` * @param {Function} rejected The function to handle `reject` for a `Promise` * * @return {Number} An ID used to remove interceptor later */ InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function use(fulfilled, rejected) { this.handlers.push({ fulfilled: fulfilled, rejected: rejected }); return this.handlers.length - 1; }; /** * Remove an interceptor from the stack * * @param {Number} id The ID that was returned by `use` */ InterceptorManager.prototype.eject = function eject(id) { if (this.handlers[id]) { this.handlers[id] = null; } }; /** * Iterate over all the registered interceptors * * This method is particularly useful for skipping over any * interceptors that may have become `null` calling `eject`. * * @param {Function} fn The function to call for each interceptor */ InterceptorManager.prototype.forEach = function forEach(fn) { utils.forEach(this.handlers, function forEachHandler(h) { if (h !== null) { fn(h); } }); }; module.exports = InterceptorManager;
拦截器构造函数只有三个方法,添加拦截器,注销拦截器,执行所有的拦截器
前端笔记0-0



