hashMap--1.8和1.7的区别。阈值为什么是8,泊松分布。
JDK1.8
只说与1.7不同的地方,相同的看1.7 https://www.cnblogs.com/q540973436/p/13227018.html
1、 1.8是数组+链表+红黑树,1.7是数组+链表。红黑树查找时,比较的是hash值和key是否equal
2 、 1.8是尾插法,1.7是头插法。为什么使用尾插法?
原因:1、1.8是链表+红黑树,需要判断链表是否>=8,因此要遍历链表,刚好使用尾插法。尾插法,避免了扩容后元素倒叙的问题
为什么会线程不安全:1.7头插法会导致死循环。1.8尾插法会导致数值的覆盖
3、 计算hashcode的方法不同:1.7经过4次位移运算和5次异或运算,得到hashcode。 1.8只经过1次位移和1次异或运算得到hashcode
1 | h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16) |
4、 扩容时重新计算元素的位置方法不同。 1.7是按照(length-1)&hashcode重新计算得到数组位置,没有利用规律。
1.8判断Hash值的新增参与运算的位是0还是1就直接迅速计算出了扩容后的储存
规律:要么在原位置,要么在扩容前的原始位置+扩容的大小值
5、 1.8是先插入,再扩容,1.7是先扩容再插入.
1.7先扩容再插入是为了减少一次hash&(length-1)的位置运算。
1.8扩容的位置运算简单多了,值计算高位是否为1,0则在原位置,1则在old+oldlength
6、 链表长度达到8也不一定变成红黑树,如果数组长度小于64,则进行扩容。64是值数组长度,而不是hashMap中的元素个数
红黑树个数达到6的时候,退变成链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) hd.treeify(tab); } } |
7.1.8的put流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; } |
先判断数组是否为空,空则先初始化为16
计算key的hash,(n - 1) & hash位置是null,则直接put
不是null,则先判断改位置结点是树节点还是链表结点。是树节点,接插入红黑树,相同的key时覆盖
是链表,则遍历链表,若找打相同的Key且hashcode相同则覆盖。长度不到8,则尾插法
插入后,链表长度达到8,则进行红黑树转换。若长度<64则先扩容,再判断是否需要转成红黑树。
符合条件,则转换成红黑树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) hd.treeify(tab); } } |
阈值为什么是8,
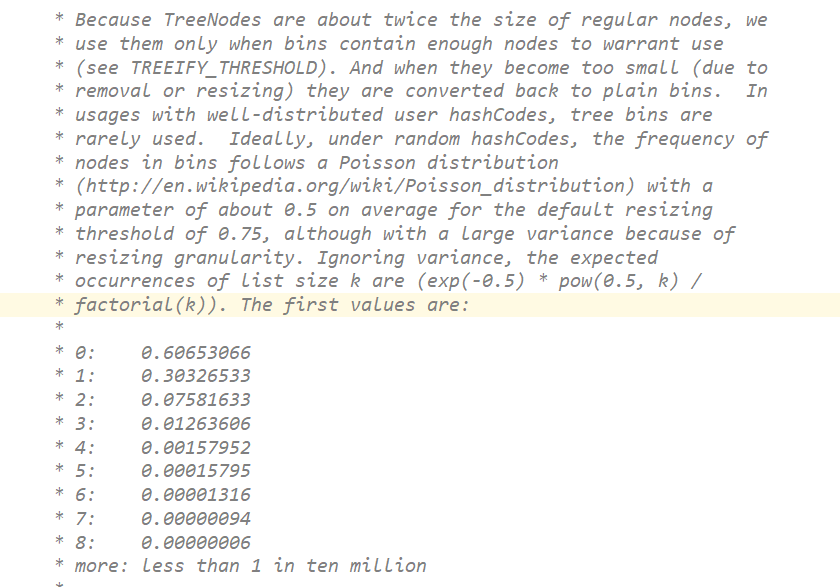
泊松分布,亿分之八的概率转换成红黑树




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)