cross_val_score 交叉验证与 K折交叉验证,嗯都是抄来的,自己作个参考
因为sklearn cross_val_score 交叉验证,这个函数没有洗牌功能,添加K 折交叉验证,可以用来选择模型,也可以用来选择特征
sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_score(estimator, X, y=None, groups=None, scoring=None, cv=None, n_jobs=1, verbose=0, fit_params=None, pre_dispatch=‘2*n_jobs’)
这里的cv 可以用下面的kf
关于scoring 参数问题

如果两者都要求高,那就需要保证较高的F1 score
回归类(Regression)问题中
比较常用的是 'neg_mean_squared_error‘ 也就是 均方差回归损失
该统计参数是预测数据和原始数据对应点误差的平方和的均值
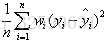
K折交叉验证:sklearn.model_selection.KFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=False, random_state=None)
n_splits:表示划分几等份
shuffle:在每次划分时,是否进行洗牌
random_state:随机种子数
属性:
①get_n_splits(X=None, y=None, groups=None):获取参数n_splits的值
②split(X, y=None, groups=None):将数据集划分成训练集和测试集,返回索引生成器
通过一个不能均等划分的栗子,设置不同参数值,观察其结果
①设置shuffle=False,运行两次,发现两次结果相同
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
...: import numpy as np
# np.arange(起始,终点,步长)
# np.reshape() 是数组对象中的方法,用于改变数组的形状 这里是12维,每组两个元素
...: X = np.arange(24).reshape(12,2)
...: y = np.random.choice([1,2],12,p=[0.4,0.6])
...: kf = KFold(n_splits=5,shuffle=False)
...: for train_index , test_index in kf.split(X):
...: print('train_index:%s , test_index: %s ' %(train_index,test_index))
----------------------------------------------------------------
train_index:[ 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11] , test_index: [0 1 2]
train_index:[ 0 1 2 6 7 8 9 10 11] , test_index: [3 4 5]
train_index:[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 8 9 10 11] , test_index: [6 7]
train_index:[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10 11] , test_index: [8 9]
train_index:[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] , test_index: [10 11]
shuffle=True
train_index:[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 11] , test_index: [ 6 9 10]
train_index:[ 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 11] , test_index: [0 1 7]
train_index:[ 0 1 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11] , test_index: [2 4]
train_index:[ 0 1 2 3 4 6 7 9 10 11] , test_index: [5 8]
train_index:[ 0 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] , test_index: [ 3 11]
n_splits 属性值获取方式



这里的cv 可以是cv
想学就不晚



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号