day-15 用opencv怎么扫描图像,利用查找表和计时
一、本节知识预览
1、 怎样遍历图像的每一个像素点?
2、 opencv图像矩阵怎么被存储的?
3、 怎样衡量我们算法的性能?
4、 什么是查表,为什么要使用它们?
二、什么是查表,为什么要使用它们?
假设一张三通道RGB图像,每个像素通道有256种不同颜色取值,那么一个像素点可能有256*256*256(1600多万)种可能颜色取值,这对于实际计算来说,开销是相当大的。而实际计算中,只需要少量的颜色值就能达到相同的效果。常用的一种方法是进行颜色空间缩减。用如下方法,我们可以将颜色空间取值减少10倍:

然而如果对每个像素点,都应用一次公式减少颜色空间取值,开销仍然很大,因此我们引入一个新方法:查表。
//定义查表
uchar table[256];
int divideWidth = 10;
for (int i = 0;i < 256; ++i)
{
table[i] = (uchar)(divideWidth*(i/divideWidth));
}
divideWith可以简单理解为取值减少的倍数,例如取值为10,颜色取值由256种可能变成25种。单个像素也只有25*25*25(15625)种可能,较之前1600多万种,计算量极大减少。然后将某个像素点某个通道的值,作为查表的数组索引,可以直接获取到最后的颜色值,避免了数学运算的工作量。
三、怎样衡量我们算法的性能?
opencv中,我们需要经常衡量一个接口/算法的时间,通过使用Opencv两个自带的函数cv::getTickCount()和cv::getTickFrequency()可以实现,前者记录从系统启动开始CPU计数次数,后者记录CPU计数频率,可用如下代码实现时间衡量:
double t = (double)getTickCount(); // do something ... t = ((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency(); cout << "Times passed in seconds: " << t << endl;
四、opencv图像矩阵怎么被存储的?
再来回顾下之前的问题,图像是怎么在内存中被存储的。假设我们的图像是一张n*m的灰度图像,在内存中的存储方式将会是这样的:
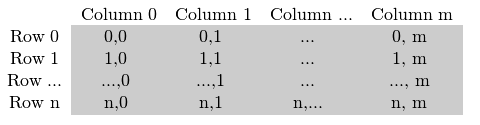
如果图像是一张RGB多通道图像,实际在内存中存储是这样的:
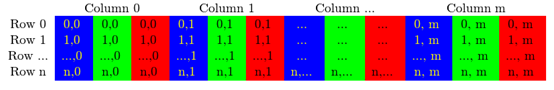
可以注意到,通道顺序是BGR而不是原有的RGB。另外由于我们的内存足够大,我们的矩阵可以一行接一行连续被存储,这样可以加快图像扫描的速度,通过cv::Mat::isContinuous()函数确认图像是否被连续存储。
五、怎样遍历图像的每一个像素点?
一谈到性能,没有什么能比C 风格的[]数组访问操作更高效了,因此可以用如下高效的方式实现查表法减少颜色空间取值:
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I,const uchar* const table)
{
//accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows;
int nCols = I.cols*channels;
if(I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
int i,j;
uchar *p;
for ( i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);
for(j = 0;j < nCols;++j)
{
p[j] = table[p[j]];
}
}
return I;
}
此外,我们还可以通过opencv提供的递归方法实现图像的遍历:
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I,const uchar* const table)
{
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
MatIterator_<uchar> it,end;
for( it = I.begin<uchar>(),end = I.end<uchar>();it != end;++it)
{
*it = table[*it];
}
break;
}
case 3:
{
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it,end;
for(it = I.begin<Vec3b>(),end = I.end<Vec3b>();it != end;++it)
{
(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];
(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];
(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];
}
break;
}
}
return I;
}
同时,还可以使用at方法实时计算图像坐标实现图像的遍历,新定义Mat_<Vec3b> _I是为了编码偷懒的方式,可以直接使用()运算符而不是at函数:
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I,const uchar * const table)
{
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
for (int i = 0;i < I.rows;++i)
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j)
{
I.at<uchar>(i,j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i,j)];
}
break;
}
case 3:
{
Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;
for (int i = 0;i < I.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0;j < I.cols; ++j)
{
//_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0] = table[_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0]];
//_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1] = table[_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1]];
//_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2] = table[_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2]];
_I(i,j)[0] = table[_I(i,j)[0]];
_I(i,j)[1] = table[_I(i,j)[1]];
_I(i,j)[2] = table[_I(i,j)[2]];
}
I = _I;
break;
}
}
return I;
}
OpenCV库也为我们提供一个快速查表的库函数:
Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U);
uchar* p = lookUpTable.ptr();
for( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
p[i] = table[i];
LUT(I, lookUpTable, J);
最后,我们附上整个程序源码,通过调用摄像头,获取图像,然后对前100帧图像利用查表法进行颜色空间缩减:
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<cv.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I,const uchar* const table)
{
//accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows;
int nCols = I.cols*channels;
if(I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
int i,j;
uchar *p;
for ( i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);
for(j = 0;j < nCols;++j)
{
p[j] = table[p[j]];
}
}
return I;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I,const uchar* const table)
{
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
MatIterator_<uchar> it,end;
for( it = I.begin<uchar>(),end = I.end<uchar>();it != end;++it)
{
*it = table[*it];
}
break;
}
case 3:
{
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it,end;
for(it = I.begin<Vec3b>(),end = I.end<Vec3b>();it != end;++it)
{
(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];
(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];
(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];
}
break;
}
}
return I;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I,const uchar * const table)
{
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
for (int i = 0;i < I.rows;++i)
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j)
{
I.at<uchar>(i,j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i,j)];
}
break;
}
case 3:
{
Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;
for (int i = 0;i < I.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0;j < I.cols; ++j)
{
//_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0] = table[_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0]];
//_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1] = table[_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1]];
//_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2] = table[_I.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2]];
_I(i,j)[0] = table[_I(i,j)[0]];
_I(i,j)[1] = table[_I(i,j)[1]];
_I(i,j)[2] = table[_I(i,j)[2]];
}
I = _I;
break;
}
}
return I;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceLut(Mat& I,Mat& J,const uchar * const table)
{
Mat lookUpTable(1,256,CV_8U);
uchar* p = lookUpTable.ptr();
for ( int i = 0;i < 256; ++i)
p[i] = table[i];
LUT(I,lookUpTable,J);
return J;
}
int main( )
{
Mat frame_input,frame_src,frame_reduce_c,frame_reduce_iterator,frame_reduce_random_access,frame_reduce_lut;
VideoCapture capture(0);
if(capture.isOpened())
{
printf("打开摄像头成功\n");
capture >> frame_input;
printf("图像分辨率为:%d * %d,通道数为%d\n",frame_input.rows,frame_input.cols,frame_input.channels());
}
//定义查表
uchar table[256];
int divideWidth = 30;
for (int i = 0;i < 256; ++i)
{
table[i] = (uchar)(divideWidth*(i/divideWidth));
}
float time_cnts_c = 0,time_cnts_iterator = 0,time_cnts_random_access = 0,time_cnts_lut = 0;
double tick = 0,number = 0;
while(number < 100){
++number;
printf("读取第%f帧图像\n",number);
capture >> frame_input;
if(frame_input.empty()){
printf("--(!) No captured frame -- Break!");
}
else{
frame_src = frame_input.clone();
frame_reduce_c = frame_input.clone();
frame_reduce_iterator = frame_input.clone();
frame_reduce_random_access = frame_input.clone();
tick = getTickCount();
ScanImageAndReduceC(frame_reduce_c,table);
time_cnts_c += ((double)getTickCount()- tick)*1000 / getTickFrequency();
tick = getTickCount();
ScanImageAndReduceIterator(frame_reduce_iterator,table);
time_cnts_iterator += ((double)getTickCount()- tick)*1000 / getTickFrequency();
tick = getTickCount();
ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(frame_reduce_random_access,table);
time_cnts_random_access += ((double)getTickCount()- tick)*1000 / getTickFrequency();
tick = getTickCount();
ScanImageAndReduceLut(frame_src,frame_reduce_lut,table);
time_cnts_lut += ((double)getTickCount()- tick)*1000 / getTickFrequency();
imshow("原始图像", frame_src);
imshow("ScanImageAndReduceC",frame_reduce_c);
imshow("ScanImageAndReduceIterator",frame_reduce_iterator);
imshow("ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess",frame_reduce_random_access);
imshow("ScanImageAndReduceLut",frame_reduce_lut);
}
waitKey(10);
}
printf("time_cnts_c:%f\n",time_cnts_c/100);
printf("time_cnts_iterator:%f\n",time_cnts_iterator/100);
printf("time_cnts_random_access:%f\n",time_cnts_random_access/100);
printf("time_cnts_lut:%f\n",time_cnts_lut/100);
waitKey(1000000);
return 0;
}
六、实验结果
opencv教程给出的时间参考如下:
https://docs.opencv.org/master/db/da5/tutorial_how_to_scan_images.html
|
Method |
Time |
|
Efficient Way |
79.4717 milliseconds |
|
Iterator |
83.7201 milliseconds |
|
On-The-Fly RA |
93.7878 milliseconds |
|
LUT function |
32.5759 milliseconds |
实际在我们环境上(480*640,3通道)测试的结果如下:
|
Method |
Time |
|
Efficient Way |
4.605026 milliseconds |
|
Iterator |
92.846123 milliseconds |
|
On-The-Fly RA |
240.321487 milliseconds |
|
LUT function |
3.741437 milliseconds |
实验结果表明,使用opencv自带的LUT函数,效率最高。这是因为OpenCV内建的多线程原因。其次是c语言高效的[]数组访问方式。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号