day-11 python自带库实现2层简单神经网络算法
深度神经网络算法,是基于神经网络算法的一种拓展,其层数更深,达到多层,本文以简单神经网络为例,利用梯度下降算法进行反向更新来训练神经网络权重和偏向参数,文章最后,基于Python 库实现了一个简单神经网络算法程序,并对异或运算和0-9字符集进行预测。
一、问题引入
利用如下图像结构,通过训练集对其参数进行训练,当有新的测试数据时,通过更新函数,获得正确的预测值,更新函数方程为:
Oij = activation(sum(xi*wij)+bij)
图中为简单的两层神经网络结构,4,5对应的为隐藏层,6为输出层,
activation代表激活函数,常用的有logistic和tanh函数,b称为偏向。
二、神经网络正向更新和反向更新规则介绍
对于正向更新:
Oij = activation(sum(xi*wij)+bij)
对于反向更新:
对于输出层:Errj = activation_derivate(Oj)*(Tj-Oj)
对于隐藏层:Errj = activation_derivate(Oj)*sum(Errk*Wjk)
delta(Wij) = l*Errj*Oij
delta(bj) = l*Errj
wij = wij + delta(wij)
bj = bj + delta(bj)
其中:
j代表第j层
k代表输出层
T代表实际标记值
O代表输出值
activation代表激活函数,常用的有logistic和tanh函数
activation_derivate代表激活函数的倒数
三、一个简单神经网络的数学运算实例
我们以一个3×2×1神经网络为例,说明如何利用正向更新和反向更新来训练神经网络,完成一次更新:
|
x1 |
x2 |
x3 |
w14 |
w15 |
w24 |
w25 |
w34 |
w35 |
w46 |
w56 |
b4 |
b5 |
b6 |
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
0.2 |
-0.3 |
0.4 |
0.1 |
-0.5 |
0.2 |
-0.3 |
-0.2 |
-0.4 |
-0.2 |
0.1 |
同时,我们设定学习率l=0.9,实际输出值为1
import numpy as np x1 = 1 x2 = 0 x3 = 1 w14 = 0.2 w15 = -0.3 w24 = 0.4 w25 = 0.1 w34 = -0.5 w35 = 0.2 w46 = -0.3 w56 = -0.2 b4 = -0.4 b5 = 0.2 b6 = 0.1 l = 0.9 t = 1 # 定义activation函数和倒数 def logistic(x): return 1/(1+np.exp(-x)) def logistic_derivate(x): return x*(1-x) # 正向更新 z4 = x1*w14 + x2*w24 + x3*w34 + b4 z5 = x1*w15 + x2*w25 + x3*w35 + b5 O4 = logistic(z4) O5 = logistic(z5) z6 = O4*w46 + O5 * w56 + b6 O6 = logistic(z6) print(O4,O5,O6) 结果:0.331812227832 0.524979187479 0.473888898824
# 求取各个神经元节点误差值 E6 = logistic_derivate(O6)*(t-O6) E5 = logistic_derivate(O5)*E6*w56 E4 = logistic_derivate(O4)*E6*w46 print(E6,E5,E4) 结果:0.131169078214 -0.00654208506417 -0.00872456196543
# 反向更新权重和偏向 w46 = w46 + l*E6*O4 w56 = w56 + l*E6*O5 w14 = w14 + l*E4*x1 w24 = w14 + l*E4*x2 w34 = w34 + l*E4*x3 w15 = w15 + l*E5*x1 w25 = w25 + l*E5*x2 w35 = w35 + l*E5*x3 print(w46,w56,w14,w15,w24,w25,w34,w35) 结果:-0.260828846342 -0.138025067507 0.192147894231 -0.305887876558 0.192147894231 0.1 -0.507852105769 0.194112123442
b4 = b4 + l*E4 b5 = b5 + l*E5 b6 = b6 + l*E6 print(b4,b5,b6)
结果:-0.407852105769 0.194112123442 0.21805217039
四、简单神经网络算python实现程序
介绍程序前,首先引入一个矩阵点乘基本运算

import numpy as np # 一维矩阵 a = np.arange(0,9) print(a) b = a[::-1] print(b) print(np.dot(a,b)) # 二维矩阵 a = np.arange(1,5).reshape(2,2) print(a) b = np.arange(5,9).reshape(2,2) print(b) c = np.dot(a,b) print(c) 结果: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8] [8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0] 84 [[1 2] [3 4]] [[5 6] [7 8]] [[19 22] [43 50]]
在实际编程过程中,引入7,8节点来代替偏向的作用,省去了计算偏向的过程,此时所有其它节点偏向为0,简化代码编程实现,下面式代码实例:
import numpy as np # 定义两个sigmoid函数及其倒数 def tanh(x): return np.tanh(x) def tanh_derivative(x): return 1.0 - np.tanh(x)*np.tanh(x) def logistic(x): return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x)) def logistic_derivative(x): return logistic(x)*(1-logistic(x)) # 定义一个简单神经网络类 class NeuralNetwork: def __init__(self,layers,activation = 'tanh'): ''' layers:定义神经网络各层神经元的个数,例如[10,10,3]表示3层神经网络,第一层10个神经元,以此类推 activation:定义神经网络的激活函数,可选值(tanh,logistic) ''' if activation == 'logistic': self.activation = logistic self.activation_deriv = logistic elif activation == 'tanh': self.activation = tanh self.activation_deriv = tanh_derivative # 定义并初始化权重,怎么初始化? self.weights = [] for i in range(1,len(layers) - 1): self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i-1] + 1,layers[i] + 1))-1)*0.25) self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i] + 1,layers[i+1]))-1)*0.25) # 训练 def fit(self,X,y,learning_rate = 0.2,epochs = 10000): X = np.atleast_2d(X) temp = np.ones([X.shape[0],X.shape[1] + 1]) temp[:,0:-1] = X X = temp y = np.array(y) # 使用抽样梯度算法 for k in range(epochs): # 从所有样本中,随机取一行 i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0]) a = [X[i]] # 完成正向的所有更新 for l in range(len(self.weights)): a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l],self.weights[l]))) # 计算输出层错误率 error = y[i] - a[-1] deltas = [error*self.activation_deriv(a[-1])] # 计算隐藏层 for l in range(len(a) -2,0,-1): deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T)*self.activation_deriv(a[l])) deltas.reverse() # 反向更新权重 for i in range(len(self.weights)): layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i]) delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i]) self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta) # 预测,即正向更新过程 def predict(self,x): x = np.array(x) temp = np.ones(x.shape[0] + 1) temp[0:-1] = x a= temp for l in range(0,len(self.weights)): a = self.activation(np.dot(a,self.weights[l])) return a
五、利用神经网络进行异或运算预测
from SimplyNeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork import numpy as np nn = NeuralNetwork([2,2,1],'tanh') # 验证异或逻辑 x = np.array([[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]) y = np.array([0,1,1,0]) nn.fit(x,y) for i in [0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]: print(i,nn.predict(i))
如下倒数4行为预测结果,根据异或运算,和实际结果一致:
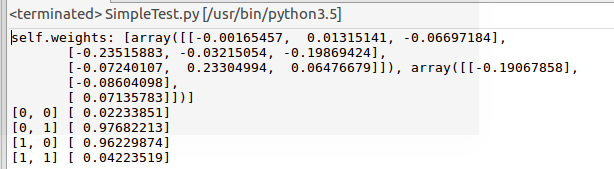
六、利用神经网络进行0-9数字预测
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_digits from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer from SimplyNeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split digits = load_digits() X = digits.data y = digits.target # 将测试样本值转换为0-1之间的值 X -=X.min() X /= X.max() nn = NeuralNetwork([64,100,10],'logistic') X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y) labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train) print(y_train) print(labels_train) labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test) print("start fitting") nn.fit(X_train,labels_train,epochs = 3000) predictions = [] for i in range(X_test.shape[0]): o = nn.predict(X_test[i]) predictions.append(np.argmax(o)) print(confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions)) print(classification_report(y_test, predictions))
如下对角线表示预测成功的记录数,最下方表示预测成功率统计数据,数据显示,成功率93%,预测效果已经很好:
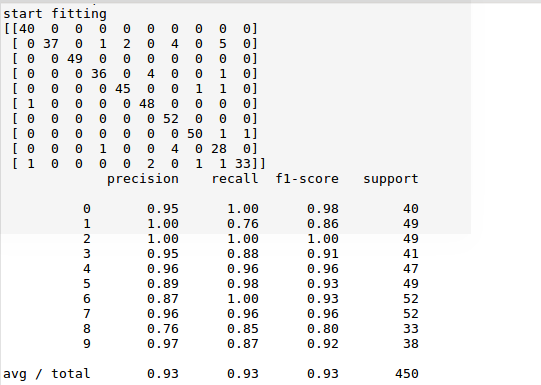




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号