常用模块-re正则表达式
import re
re模块
正则表达式就是字符串的匹配规则,在多数编程语言里都有相应的支持,python里对应的模块是re
常用的表达式规则
'.' 默认匹配除\n之外的任意一个字符,若指定flag DOTALL,则匹配任意字符,包括换行
'^' 匹配字符开头,若指定flags MULTILINE,这种也可以匹配上(r"^a","\nabc\neee",flags=re.MULTILINE)
'$' 匹配字符结尾, 若指定flags MULTILINE ,re.search('foo.$','foo1\nfoo2\n',re.MULTILINE).group() 会匹配到foo1
'*' 匹配*号前的字符0次或多次, re.search('a*','aaaabac') 结果'aaaa'
'+' 匹配前一个字符1次或多次,re.findall("ab+","ab+cd+abb+bba") 结果['ab', 'abb']
'?' 匹配前一个字符1次或0次 ,re.search('b?','alex').group() 匹配b 0次
'{m}' 匹配前一个字符m次 ,re.search('b{3}','alexbbbs').group() 匹配到'bbb'
'{n,m}' 匹配前一个字符n到m次,re.findall("ab{1,3}","abb abc abbcbbb") 结果'abb', 'ab', 'abb']
'|' 匹配|左或|右的字符,re.search("abc|ABC","ABCBabcCD").group() 结果'ABC'
'(...)' 分组匹配, re.search("(abc){2}a(123|45)", "abcabca456c").group() 结果为'abcabca45'
'\A' 只从字符开头匹配,re.search("\Aabc","alexabc") 是匹配不到的,相当于re.match('abc',"alexabc") 或^
'\Z' 匹配字符结尾,同$
'\d' 匹配数字0-9
'\D' 匹配非数字
'\w' 匹配[A-Za-z0-9]
'\W' 匹配非[A-Za-z0-9]
'\s' 匹配空白字符、\t、\n、\r , re.search("\s+","ab\tc1\n3").group() 结果 '\t'
'(?P<name>...)' 分组匹配 re.search("(?P<province>[0-9]{4})(?P<city>[0-9]{2})(?P<birthday>[0-9]{4})","371481199306143242").groupdict("city") 结果{'province': '3714', 'city': '81', 'birthday': '1993'}
re的匹配语法有以下几种
- re.match 从头开始匹配。从字符串的第一个字符开始匹配
- re.search 匹配包含。搜索全局,但是只返回匹配到的第一个值
- re.findall 把所有匹配到的字符放到以列表中的元素返回
- re.split 以匹配到的字符当做列表分隔符
- re.sub 匹配字符并替换
- re.fullmatch 全部匹配
re.compile(pattern, flags=0)
Compile a regular expression pattern into a regular expression object, which can be used for matching using its match(), search() and other methods, described below.
The sequence
prog = re.compile(pattern)
result = prog.match(string)
is equivalent to
result = re.match(pattern, string)
but using re.compile() and saving the resulting regular expression object for reuse is more efficient when the expression will be used several times in a single program.
re.match(pattern, string, flags=0)
从起始位置开始根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容,匹配单个
- pattern 正则表达式
- string 要匹配的字符串
- flags 标志位,用于控制正则表达式的匹配方式
import re
obj = re.match('\d+', '123uuasf')
if obj:
print obj.group()
Flags标志符
- re.I(re.IGNORECASE): 忽略大小写(括号内是完整写法,下同)
- M(MULTILINE): 多行模式,改变'^'和'$'的行为
- S(DOTALL): 改变'.'的行为,make the '.' special character match any character at all, including a newline; without this flag, '.' will match anything except a newline.
- X(re.VERBOSE) 可以给你的表达式写注释,使其更可读,下面这2个意思一样
a = re.compile(r"""\d + # the integral part
\. # the decimal point
\d * # some fractional digits""",
re.X)
b = re.compile(r"\d+\.\d*")
re.search(pattern, string, flags=0)
根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容,匹配单个
import re
obj = re.search('\d+', 'u123uu888asf')
if obj:
print obj.group()
re.findall(pattern, string, flags=0)
match and search均用于匹配单值,即:只能匹配字符串中的一个,如果想要匹配到字符串中所有符合条件的元素,则需要使用 findall。
import re
obj = re.findall('\d+', 'fa123uu888asf')
print obj
re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
用于替换匹配的字符串
>>>re.sub('[a-z]+','sb','武配齐是abc123',)
>>> re.sub('\d+','|', 'alex22wupeiqi33oldboy55',count=2)
'alex|wupeiqi|oldboy55'
相比于str.replace功能更加强大
re.split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
>>>s='9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14'
>>>re.split('[\*\-\/\+]',s)
['9', '2', '5', '3', '7', '3', '99', '4', '2998', '10', '568', '14']
>>> re.split('[\*\-\/\+]',s,3)
['9', '2', '5', '3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14']
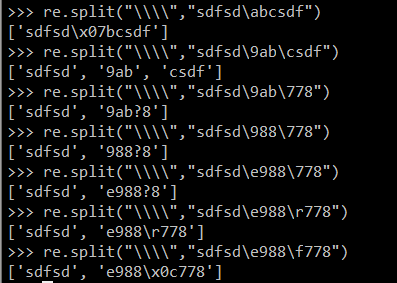
re.splist要使用反斜杠的时候得四个反斜杠一起才是代表以反斜杠作为分隔符。re.split("\\\\","sdfsd\9809sdf),并且还会出现很多问题:
![]()
re.fullmatch(pattern, string, flags=0)
整个字符串匹配成功就返回re object, 否则返回None
re.fullmatch('\w+@\w+\.(com|cn|edu)',"alex@oldboyedu.cn")
练习:
1.验证手机号是否合法
2.验证邮箱是否合法
3.开发一个简单的python计算器,实现加减乘除及拓号优先级解析
- 用户输入 1 - 2 * ( (60-30 +(-40/5) * (9-2*5/3 + 7 /3*99/4*2998 +10 * 568/14 )) - (-4*3)/ (16-3*2) )等类似公式后,必须自己解析里面的(),+,-,*,/符号和公式(不能调用eval等类似功能偷懒实现),运算后得出结果,结果必须与真实的计算器所得出的结果一致
hint:
re.search(r'\([^()]+\)',s).group()#可拿到最里层的括号中的值 '(-40/5)'


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号