Thermal hal
概述
根据温度的变化,调整和限制应用活动。借助该 Android 框架,设备制造商和应用开发者可以使用热数据来确保在设备开始过热时保持一致的用户体验。例如,当系统温度较高时,jobscheduler 作业会受到限制,如有必要,可启动框架热关机。通过注册的回调函数(位于 PowerManager 类中)接收高温通知的应用可妥善调整其用户体验。
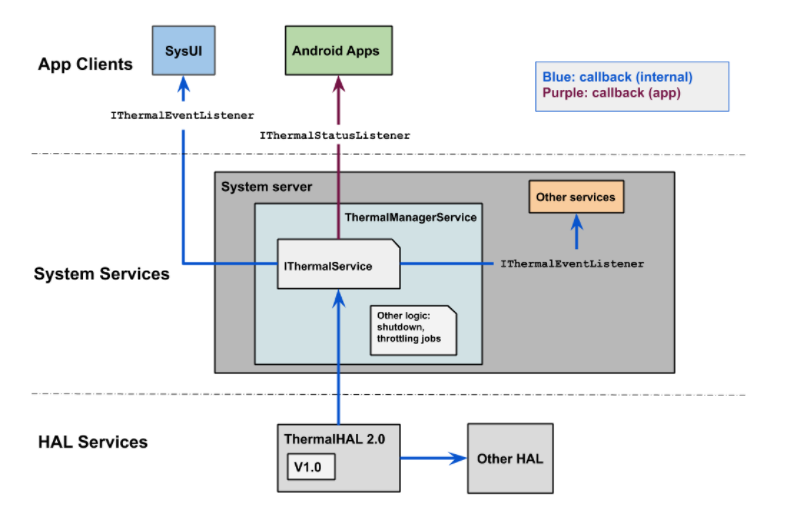
在 Android 10 中,框架中的热服务利用来自 Thermal HAL 2.0 的各种缓解信号不断进行监控,并向其客户端提供有关限制严重级别的反馈,其中包括内部组件和 Android 应用。该服务利用 2 个 Binder 回调接口,即作为回调提供的 IThermalEventListener 和 IThermalStatusListener。前者适用于内部平台和设备制造商,而后者适用于 Android 应用。
1. 接口
1.1 函数接口
// 1.0的接口
// 返回所有传感器的温度
getTemperatures() generates (ThermalStatus status, vec<Temperature> temperatures);
getCpuUsages() generates (ThermalStatus status, vec<CpuUsage> cpuUsages);
getCoolingDevices() generates (ThermalStatus status, vec<CoolingDevice> devices);
// 1.1的接口
registerThermalCallback(IThermalCallback callback);
// 2.0的接口
getCurrentTemperatures(bool filterType, TemperatureType type)
generates (ThermalStatus status, vec<Temperature> temperatures);
getTemperatureThresholds(bool filterType, TemperatureType type)
generates (ThermalStatus status, vec<TemperatureThreshold> temperatureThresholds);
// 注册回调函数,温度变化的时候,会反馈温度和温度等级给应用
registerThermalChangedCallback(IThermalChangedCallback callback,
bool filterType,
TemperatureType type) generates (ThermalStatus status);
unregisterThermalChangedCallback(IThermalChangedCallback callback)
generates (ThermalStatus status);
getCurrentCoolingDevices(bool filterType, CoolingType type)
generates (ThermalStatus status, vec<CoolingDevice> devices);
1.2 TemperatureType
enum TemperatureType : int32_t {
UNKNOWN = -1,
CPU = 0,
GPU = 1,
BATTERY = 2,
SKIN = 3,
};
/** Device temperature types */
enum TemperatureType : @1.0::TemperatureType {
USB_PORT = 4,
POWER_AMPLIFIER = 5,
/** Battery Charge Limit - virtual thermal sensors */
BCL_VOLTAGE = 6,
BCL_CURRENT = 7,
BCL_PERCENTAGE = 8,
/** Neural Processing Unit */
NPU = 9,
};
1.3 ThrottlingSeverity-温度的等级,严重-轻微-关机等
// 根据配置文件设置的温度,返回不同的严重程度
/** Device throttling severity */
enum ThrottlingSeverity : uint32_t {
// Not under throttling.
NONE = 0,
// Light throttling where UX is not impacted.
LIGHT,
// Moderate throttling where UX is not largely impacted.
MODERATE,
/**
* Severe throttling where UX is largely impacted.
* Similar to 1.0 throttlingThreshold.
*/
SEVERE,
// Platform has done everything to reduce power.
CRITICAL,
/**
* Key components in platform are shutting down due to thermal condition.
* Device functionalities will be limited.
*/
EMERGENCY,
// Need shutdown immediately.
SHUTDOWN,
};
2. dumpsys thermalservice打印
IsStatusOverride: false
ThermalEventListeners:
callbacks: 1
killed: false
broadcasts count: -1
ThermalStatusListeners:
callbacks: 1
killed: false
broadcasts count: -1
Thermal Status: 0
Cached temperatures:
Temperature{mValue=69.573006, mType=0, mName=cpu_thermal_zone, mStatus=0}
Temperature{mValue=30.000002, mType=5, mName=axp803-battery, mStatus=0}
Temperature{mValue=61.466003, mType=1, mName=gpu_thermal_zone, mStatus=0}
HAL Ready: true
HAL connection:
ThermalHAL 2.0 connected: yes
Current temperatures from HAL:
Temperature{mValue=30.000002, mType=5, mName=axp803-battery, mStatus=0}
Temperature{mValue=49.071003, mType=0, mName=cpu_thermal_zone, mStatus=0}
Temperature{mValue=48.937004, mType=1, mName=gpu_thermal_zone, mStatus=0}
Current cooling devices from HAL:
CoolingDevice{mValue=0, mType=2, mName=thermal-cpufreq-0}
3. 应用接口
thermal_watcher监听sensors的uevent事件 -> 解析uevent事件 -> 并将sensors name传给thermalWatcherCallbackFunc回调函数 -> 将温度和温度等级信息传给sendThermalChangedCallback回调函数 -> 将温度和温度等级信息传给ThermalManagerService中的mThermalCallback20回调函数
3.1 PowerManager#addThermalStatusListener-应用可用
/**
* This function adds a listener for thermal status change, listen call back will be
* enqueued tasks on the main thread
*
* @param listener listener to be added,
*/
public void addThermalStatusListener(@NonNull OnThermalStatusChangedListener listener) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(listener, "listener cannot be null");
this.addThermalStatusListener(mContext.getMainExecutor(), listener);
}
3.2 ThermalManagerService#registerThermalEventListener-系统应用用
@Override
public boolean registerThermalEventListener(IThermalEventListener listener) {
getContext().enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.DEVICE_POWER, null);
synchronized (mLock) {
final long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (!mThermalEventListeners.register(listener, null)) {
return false;
}
// Notify its callback after new client registered.
postEventListenerCurrentTemperatures(listener, null);
return true;
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
}
源码解析
1. Thermal类
thermal hal起来的时候,首先创建Thermal类,分析配置文件
1.1 Thermal构造函数
Thermal::Thermal()
: thermal_helper_(
std::bind(&Thermal::sendThermalChangedCallback, this, std::placeholders::_1)) {}
1.2 sendThermalChangedCallback-给应用发送温度和温度等级等信息
发送温度和温度等级等信息
void Thermal::sendThermalChangedCallback(const std::vector<Temperature_2_0> &temps) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> _lock(thermal_callback_mutex_);
for (auto &t : temps) {
LOG(INFO) << "Sending notification: "
<< " Type: " << android::hardware::thermal::V2_0::toString(t.type)
<< " Name: " << t.name << " CurrentValue: " << t.value << " ThrottlingStatus: "
<< android::hardware::thermal::V2_0::toString(t.throttlingStatus);
callbacks_.erase(
std::remove_if(callbacks_.begin(), callbacks_.end(),
[&](const CallbackSetting &c) {
if (!c.is_filter_type || t.type == c.type) {
// 调用应用的回调
Return<void> ret = c.callback->notifyThrottling(t);
// !ret.isOk()如果不ok,则是true,就删除掉callback了;如果ok则是false,就不删除callback了
return !ret.isOk();
}
LOG(ERROR)
<< "a Thermal callback is dead, removed from callback list.";
return false;
}),
callbacks_.end());
}
}
1.3 registerThermalChangedCallback-注册回调
Return<void> Thermal::registerThermalChangedCallback(const sp<IThermalChangedCallback> &callback,
bool filterType, TemperatureType_2_0 type,
registerThermalChangedCallback_cb _hidl_cb) {
ThermalStatus status;
if (callback == nullptr) {
status.code = ThermalStatusCode::FAILURE;
status.debugMessage = "Invalid nullptr callback";
LOG(ERROR) << status.debugMessage;
_hidl_cb(status);
return Void();
} else {
status.code = ThermalStatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> _lock(thermal_callback_mutex_);
if (std::any_of(callbacks_.begin(), callbacks_.end(), [&](const CallbackSetting &c) {
return interfacesEqual(c.callback, callback);
})) {
status.code = ThermalStatusCode::FAILURE;
status.debugMessage = "Same callback registered already";
LOG(ERROR) << status.debugMessage;
} else {
callbacks_.emplace_back(callback, filterType, type);
LOG(INFO) << "a callback has been registered to ThermalHAL, isFilter: " << filterType
<< " Type: " << android::hardware::thermal::V2_0::toString(type);
}
_hidl_cb(status);
return Void();
}
1.4 getCpuUsages-获取cpu的占用率
Return<void> Thermal::getCpuUsages(getCpuUsages_cb _hidl_cb) {
ThermalStatus status;
status.code = ThermalStatusCode::SUCCESS;
hidl_vec<CpuUsage> cpu_usages;
if (!thermal_helper_.isInitializedOk()) {
return setInitFailureAndCallback(_hidl_cb, cpu_usages);
}
// 填充cpu占用率的信息
if (!thermal_helper_.fillCpuUsages(&cpu_usages)) {
return setFailureAndCallback(_hidl_cb, cpu_usages, "Failed to get CPU usages.");
}
_hidl_cb(status, cpu_usages);
return Void();
}
2. ThermalHelper类-thermal hal的具体实现
2.1 ThermalHelper构造函数-解析配置文件
ThermalHelper::ThermalHelper(const NotificationCallback &cb)
// 创建ThermalWatcher对象
: thermal_watcher_(new ThermalWatcher(
// 注册thermalWatcherCallbackFunc回调函数
std::bind(&ThermalHelper::thermalWatcherCallbackFunc, this, std::placeholders::_1))),
// 保存回调函数
cb_(cb),
// 解析/vendor/etc/thermal_info_config.json文件,得到cooling_device的配置
// cooling_device就只有name和type
cooling_device_info_map_(ParseCoolingDevice(
"/vendor/etc/" +
android::base::GetProperty(kConfigProperty.data(), kConfigDefaultFileName.data()))),
// 解析/vendor/etc/thermal_info_config.json文件,得到sensor_info的配置
sensor_info_map_(ParseSensorInfo(
"/vendor/etc/" +
android::base::GetProperty(kConfigProperty.data(), kConfigDefaultFileName.data()))) {
for (auto const &name_status_pair : sensor_info_map_) {
sensor_status_map_[name_status_pair.first] = {
.severity = ThrottlingSeverity::NONE,
.prev_hot_severity = ThrottlingSeverity::NONE,
.prev_cold_severity = ThrottlingSeverity::NONE,
};
}
// <cpu_thermal_zone, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0>
auto tz_map = parseThermalPathMap(kSensorPrefix.data());
// <thermal-cpufreq-0, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/cooling_device0>
auto cdev_map = parseThermalPathMap(kCoolingDevicePrefix.data());
// initializeSensorMap函数 <cpu_thermal_zone, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp>
// initializeCoolingDevices函数 <thermal-cpufreq-0, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/cooling_device0/cur_state>
is_initialized_ = initializeSensorMap(tz_map) && initializeCoolingDevices(cdev_map);
if (!is_initialized_) {
// 如果thermal节点没有初始化成功,这里为FATAL类型的LOG,那么thermal会起不来,造成Android系统起不来
LOG(FATAL) << "ThermalHAL could not be initialized properly.";
}
// 没有需要monitor的sensor
std::set<std::string> monitored_sensors;
std::transform(sensor_info_map_.cbegin(), sensor_info_map_.cend(),
std::inserter(monitored_sensors, monitored_sensors.begin()),
[](std::pair<std::string, SensorInfo> const &sensor) {
if (sensor.second.is_monitor)
// 返回sensor的name
return sensor.first;
else
return std::string();
});
// 没有需要monitor的sensor,initializeTrip(tz_map)返回true
thermal_watcher_->registerFilesToWatch(monitored_sensors, initializeTrip(tz_map));
// Need start watching after status map initialized
// 启动FileWatcherThread ThermalWatcher线程
is_initialized_ = thermal_watcher_->startWatchingDeviceFiles();
if (!is_initialized_) {
// 如果thermal节点没有初始化成功,这里为FATAL类型的LOG,那么thermal会起不来,造成Android系统起不来
LOG(FATAL) << "ThermalHAL could not start watching thread properly.";
}
}
2.2 ParseSensorInfo-解析配置文件
std::map<std::string, SensorInfo> ParseSensorInfo(std::string config_path) {
std::ifstream in(config_path);
std::map<std::string, SensorInfo> sensors_parsed;
Json::Value root;
Json::CharReaderBuilder reader;
Json::String errs;
// 分析json文件
if (!Json::parseFromStream(reader, in, &root, &errs)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to parse JSON config";
return sensors_parsed;
}
Json::Value sensors = root["Sensors"];
std::size_t total_parsed = 0;
std::set<std::string> sensors_name_parsed;
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex i = 0; i < sensors.size(); ++i) {
const std::string &name = sensors[i]["Name"].asString();
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << i << "]'s Name: " << name;
if (name.empty()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read "
<< "Sensor[" << i << "]'s Name";
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
auto result = sensors_name_parsed.insert(name);
if (!result.second) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Duplicate Sensor[" << i << "]'s Name";
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
std::string sensor_type_str = sensors[i]["Type"].asString();
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s Type: " << sensor_type_str;
TemperatureType_2_0 sensor_type;
if (!getTypeFromString(sensor_type_str, &sensor_type)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s Type: " << sensor_type_str;
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
std::array<float, kThrottlingSeverityCount> hot_thresholds;
hot_thresholds.fill(NAN);
std::array<float, kThrottlingSeverityCount> cold_thresholds;
cold_thresholds.fill(NAN);
std::array<float, kThrottlingSeverityCount> hot_hysteresis;
hot_hysteresis.fill(0.0);
std::array<float, kThrottlingSeverityCount> cold_hysteresis;
cold_hysteresis.fill(0.0);
Json::Value values = sensors[i]["HotThreshold"];
// 由此可见,HotThreshold是必须要配置上的,不然就会出错了
if (values.size() != kThrottlingSeverityCount) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotThreshold count" << values.size();
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
} else {
float min = std::numeric_limits<float>::min();
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex j = 0; j < kThrottlingSeverityCount; ++j) {
hot_thresholds[j] = getFloatFromValue(values[j]);
if (!std::isnan(hot_thresholds[j])) {
if (hot_thresholds[j] < min) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotThreshold[j" << j
<< "]: " << hot_thresholds[j] << " < " << min;
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
min = hot_thresholds[j];
}
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotThreshold[" << j
<< "]: " << hot_thresholds[j];
}
}
values = sensors[i]["HotHysteresis"];
if (values.size() != kThrottlingSeverityCount) {
LOG(INFO) << "Cannot find valid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotHysteresis, default all to 0.0";
} else {
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex j = 0; j < kThrottlingSeverityCount; ++j) {
hot_hysteresis[j] = getFloatFromValue(values[j]);
if (std::isnan(hot_hysteresis[j])) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotHysteresis: " << hot_hysteresis[j];
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotHysteresis[" << j
<< "]: " << hot_hysteresis[j];
}
}
values = sensors[i]["ColdThreshold"];
if (values.size() != kThrottlingSeverityCount) {
LOG(INFO) << "Cannot find valid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s ColdThreshold, default all to NAN";
} else {
float max = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex j = 0; j < kThrottlingSeverityCount; ++j) {
cold_thresholds[j] = getFloatFromValue(values[j]);
if (!std::isnan(cold_thresholds[j])) {
if (cold_thresholds[j] > max) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s ColdThreshold[j" << j
<< "]: " << cold_thresholds[j] << " > " << max;
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
max = cold_thresholds[j];
}
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s ColdThreshold[" << j
<< "]: " << cold_thresholds[j];
}
}
values = sensors[i]["ColdHysteresis"];
if (values.size() != kThrottlingSeverityCount) {
LOG(INFO) << "Cannot find valid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s ColdHysteresis, default all to 0.0";
} else {
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex j = 0; j < kThrottlingSeverityCount; ++j) {
cold_hysteresis[j] = getFloatFromValue(values[j]);
if (std::isnan(cold_hysteresis[j])) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name
<< "]'s ColdHysteresis: " << cold_hysteresis[j];
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s ColdHysteresis[" << j
<< "]: " << cold_hysteresis[j];
}
}
float vr_threshold = NAN;
vr_threshold = getFloatFromValue(sensors[i]["VrThreshold"]);
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s VrThreshold: " << vr_threshold;
float multiplier = sensors[i]["Multiplier"].asFloat();
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s Multiplier: " << multiplier;
bool is_monitor = false;
if (sensors[i]["Monitor"].empty() || !sensors[i]["Monitor"].isBool()) {
LOG(INFO) << "Failed to read Sensor[" << name << "]'s Monitor, set to 'false'";
} else {
is_monitor = sensors[i]["Monitor"].asBool();
}
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s Monitor: " << std::boolalpha << is_monitor
<< std::noboolalpha;
// Sensors项可以配置的项
// name是/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/type下的名字
sensors_parsed[name] = {
.type = sensor_type, // 见TemperatureType支持的类型
.hot_thresholds = hot_thresholds, // 高温阈值
.cold_thresholds = cold_thresholds,
.hot_hysteresis = hot_hysteresis,
.cold_hysteresis = cold_hysteresis,
.vr_threshold = vr_threshold,
.multiplier = multiplier, // 得到的值应该乘以多少,才得到真正的温度;比如读CPU的节点的温度为47530,需要乘以0.001
.is_monitor = is_monitor,
};
++total_parsed;
}
LOG(INFO) << total_parsed << " Sensors parsed successfully";
return sensors_parsed;
}
2.3 parseThermalPathMap
std::map<std::string, std::string> parseThermalPathMap(std::string_view prefix) {
std::map<std::string, std::string> path_map;
// 打开/sys/devices/virtual/thermal文件夹
std::unique_ptr<DIR, int (*)(DIR *)> dir(opendir(kThermalSensorsRoot.data()), closedir);
if (!dir) {
return path_map;
}
// std::filesystem is not available for vendor yet
// see discussion: aosp/894015
while (struct dirent *dp = readdir(dir.get())) {
if (dp->d_type != DT_DIR) {
continue;
}
// thermal_zone名字开头的文件夹
if (!android::base::StartsWith(dp->d_name, prefix.data())) {
continue;
}
// 读/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/type cpu_thermal_zone
std::string path = android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s/%s", kThermalSensorsRoot.data(),
dp->d_name, kThermalNameFile.data());
std::string name;
if (!android::base::ReadFileToString(path, &name)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read from " << path;
continue;
}
// <cpu_thermal_zone, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0>
// <thermal-cpufreq-0, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/cooling_device0>
path_map.emplace(
android::base::Trim(name),
android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", kThermalSensorsRoot.data(), dp->d_name));
}
return path_map;
}
2.4 initializeSensorMap
bool ThermalHelper::initializeSensorMap(const std::map<std::string, std::string> &path_map) {
for (const auto &sensor_info_pair : sensor_info_map_) {
// sensor_name对应cpu_thermal_zone
std::string_view sensor_name = sensor_info_pair.first;
// 确保在/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/目录能找得到cpu_thermal_zone
if (!path_map.count(sensor_name.data())) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not find " << sensor_name << " in sysfs";
continue;
}
// /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp文件
std::string path = android::base::StringPrintf(
"%s/%s", path_map.at(sensor_name.data()).c_str(), kSensorTempSuffix.data());
// 添加<cpu_thermal_zone, /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp>
if (!thermal_sensors_.addThermalFile(sensor_name, path)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not add " << sensor_name << "to sensors map";
}
}
// 配置文件的 等于 添加到thermal_sensors的
if (sensor_info_map_.size() == thermal_sensors_.getNumThermalFiles()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.5 initializeTrip-看是否检测sensors的温度
bool ThermalHelper::initializeTrip(const std::map<std::string, std::string> &path_map) {
for (const auto &sensor_info : sensor_info_map_) {
if (sensor_info.second.is_monitor) {
std::string_view sensor_name = sensor_info.first;
std::string_view tz_path = path_map.at(sensor_name.data());
std::string tz_policy;
std::string path = android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", (tz_path.data()),
kSensorPolicyFile.data());
// 读/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/policy
if (!android::base::ReadFileToString(path, &tz_policy)) {
LOG(ERROR) << sensor_name << " could not open tz policy file:" << path;
return false;
}
// Check if thermal zone support uevent notify
tz_policy = android::base::Trim(tz_policy);
// 我们的为power_allocator
// 如果policy的值不为user_space的,则返回false
if (tz_policy != kUserSpaceSuffix) {
LOG(ERROR) << sensor_name << " does not support uevent notify";
return false;
}
// Update thermal zone trip point
for (size_t i = 0; i < kThrottlingSeverityCount; ++i) {
if (!std::isnan(sensor_info.second.hot_thresholds[i]) &&
!std::isnan(sensor_info.second.hot_hysteresis[i])) {
// Update trip_point_0_temp threshold
// 将配置文件中hot_thresholds的值写到/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/trip_point_0_temp节点
// 相当于给驱动配置了热的阈值了
std::string threshold = std::to_string(static_cast<int>(
sensor_info.second.hot_thresholds[i] / sensor_info.second.multiplier));
path = android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", (tz_path.data()),
kSensorTripPointTempZeroFile.data());
if (!android::base::WriteStringToFile(threshold, path)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "fail to update " << sensor_name
<< " trip point: " << threshold << path;
return false;
}
// Update trip_point_0_hyst threshold
// 将配置文件中hot_hysteresis的值写到/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/trip_point_0_hyst节点
// 相当于给驱动配置了热滞后的阈值了
threshold = std::to_string(static_cast<int>(
sensor_info.second.hot_hysteresis[i] / sensor_info.second.multiplier));
path = android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", (tz_path.data()),
kSensorTripPointHystZeroFile.data());
if (!android::base::WriteStringToFile(threshold, path)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "fail to update " << sensor_name << "trip hyst" << threshold
<< path;
return false;
}
break;
} else if (i == kThrottlingSeverityCount - 1) {
LOG(ERROR) << sensor_name << ":all thresholds are NAN";
return false;
}
}
}
}
// 没有monitor的sensor,也会直接返回true
return true;
}
2.6 thermalWatcherCallbackFunc
thermal_watcher监听sensors的uevent事件 -> 解析uevent事件 -> 并将sensors name传给回调函数
// This is called in the different thread context and will update sensor_status
// uevent_sensors is the set of sensors which trigger uevent from thermal core driver.
bool ThermalHelper::thermalWatcherCallbackFunc(const std::set<std::string> &uevent_sensors) {
std::vector<Temperature_2_0> temps;
bool thermal_triggered = false;
for (auto &name_status_pair : sensor_status_map_) {
Temperature_2_0 temp;
TemperatureThreshold threshold;
SensorStatus &sensor_status = name_status_pair.second;
const SensorInfo &sensor_info = sensor_info_map_.at(name_status_pair.first);
// Only send notification on whitelisted sensors
// 没有配置monitor的话,略过
if (!sensor_info.is_monitor) {
continue;
}
// If callback is triggered by uevent, only check the sensors within uevent_sensors
if (uevent_sensors.size() != 0 &&
uevent_sensors.find(name_status_pair.first) == uevent_sensors.end()) {
if (sensor_status.severity != ThrottlingSeverity::NONE) {
thermal_triggered = true;
}
continue;
}
std::pair<ThrottlingSeverity, ThrottlingSeverity> throtting_status;
// 读sensors的温度
if (!readTemperature(name_status_pair.first, &temp, &throtting_status)) {
LOG(ERROR) << __func__
<< ": error reading temperature for sensor: " << name_status_pair.first;
continue;
}
// 读sensors的
if (!readTemperatureThreshold(name_status_pair.first, &threshold)) {
LOG(ERROR) << __func__ << ": error reading temperature threshold for sensor: "
<< name_status_pair.first;
continue;
}
{
// writer lock
std::unique_lock<std::shared_mutex> _lock(sensor_status_map_mutex_);
if (throtting_status.first != sensor_status.prev_hot_severity) {
sensor_status.prev_hot_severity = throtting_status.first;
}
if (throtting_status.second != sensor_status.prev_cold_severity) {
sensor_status.prev_cold_severity = throtting_status.second;
}
if (temp.throttlingStatus != sensor_status.severity) {
temps.push_back(temp);
sensor_status.severity = temp.throttlingStatus;
}
}
if (sensor_status.severity != ThrottlingSeverity::NONE) {
thermal_triggered = true;
LOG(INFO) << temp.name << ": " << temp.value;
}
}
if (!temps.empty() && cb_) {
// 调用thermal类的回调
cb_(temps);
}
return thermal_triggered;
}
2.7 readTemperature
bool ThermalHelper::readTemperature(
std::string_view sensor_name, Temperature_2_0 *out,
std::pair<ThrottlingSeverity, ThrottlingSeverity> *throtting_status) const {
// Read the file. If the file can't be read temp will be empty string.
std::string temp;
// 读/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp的值
if (!thermal_sensors_.readThermalFile(sensor_name, &temp)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "readTemperature: sensor not found: " << sensor_name;
return false;
}
if (temp.empty()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "readTemperature: failed to read sensor: " << sensor_name;
return false;
}
const auto &sensor_info = sensor_info_map_.at(sensor_name.data());
out->type = sensor_info.type;
out->name = sensor_name.data();
out->value = std::stof(temp) * sensor_info.multiplier;
std::pair<ThrottlingSeverity, ThrottlingSeverity> status =
std::make_pair(ThrottlingSeverity::NONE, ThrottlingSeverity::NONE);
// Only update status if the thermal sensor is being monitored
// 如果是monitor的
// 根据配置文件配置的温度阈值,返回当前温度的水平:是严重,还是轻微等级
if (sensor_info.is_monitor) {
ThrottlingSeverity prev_hot_severity, prev_cold_severity;
{
// reader lock, readTemperature will be called in Binder call and the watcher thread.
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> _lock(sensor_status_map_mutex_);
prev_hot_severity = sensor_status_map_.at(sensor_name.data()).prev_hot_severity;
prev_cold_severity = sensor_status_map_.at(sensor_name.data()).prev_cold_severity;
}
status = getSeverityFromThresholds(sensor_info.hot_thresholds, sensor_info.cold_thresholds,
sensor_info.hot_hysteresis, sensor_info.cold_hysteresis,
prev_hot_severity, prev_cold_severity, out->value);
}
if (throtting_status) {
*throtting_status = status;
}
out->throttlingStatus = static_cast<size_t>(status.first) > static_cast<size_t>(status.second)
? status.first
: status.second;
return true;
}
2.8 fillCpuUsages
bool ThermalHelper::fillCpuUsages(hidl_vec<CpuUsage> *cpu_usages) const {
cpu_usages->resize(kMaxCpus);
parseCpuUsagesFileAndAssignUsages(cpu_usages);
return true;
}
2.9 parseCpuUsagesFileAndAssignUsages-解析cpu的占用率
// 读/sys/devices/system/cpu/present文件为0-3,然后3-0+1最后算出cpu的个数了
std::size_t getNumberOfCores() {
std::string file;
if (!android::base::ReadFileToString(kCpuPresentFile.data(), &file)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error reading Cpu present file: " << kCpuPresentFile;
return 0;
}
std::vector<std::string> pieces = android::base::Split(file, "-");
if (pieces.size() != 2) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error parsing Cpu present file content: " << file;
return 0;
}
auto min_core = std::stoul(pieces[0]);
auto max_core = std::stoul(pieces[1]);
if (max_core < min_core) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error parsing Cpu present min and max: " << min_core << " - " << max_core;
return 0;
}
return static_cast<std::size_t>(max_core - min_core + 1);
}
const std::size_t kMaxCpus = getNumberOfCores();
// 读/proc/stat文件
cpu 74650 66142 132614 6213547 2722 49330 7128 0 0 0
cpu0 18925 17871 23390 1533578 818 41512 2878 0 0 0
cpu1 18988 17866 21865 1581251 687 1565 1074 0 0 0
cpu2 14774 14833 45030 1556995 605 3835 1973 0 0 0
cpu3 21961 15570 42327 1541721 612 2417 1202 0 0 0
void parseCpuUsagesFileAndAssignUsages(hidl_vec<CpuUsage> *cpu_usages) {
uint64_t cpu_num, user, nice, system, idle;
std::string cpu_name;
std::string data;
// 读/proc/stat文件
if (!android::base::ReadFileToString(kCpuUsageFile.data(), &data)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error reading Cpu usage file: " << kCpuUsageFile;
return;
}
std::istringstream stat_data(data);
std::string line;
while (std::getline(stat_data, line)) {
// 找到带有cpu的这一行,并且第三个还要是数字,所以就是cpu0,cpu1,cpu2和cpu3了
if (line.find("cpu") == 0 && isdigit(line[3])) {
// Split the string using spaces.
std::vector<std::string> words = android::base::Split(line, " ");
cpu_name = words[0];
cpu_num = std::stoi(cpu_name.substr(3));
if (cpu_num < kMaxCpus) {
user = std::stoi(words[1]);
nice = std::stoi(words[2]);
system = std::stoi(words[3]);
idle = std::stoi(words[4]);
// cpu0 18925 17871 23390 1533578 818 41512 2878 0 0 0
// cpu0 user nice system idle iowait irq softirq steal guest guest_nice
// Check if the CPU is online by reading the online file.
std::string cpu_online_path =
StringPrintf("%s/%s/%s", kCpuOnlineRoot.data(), cpu_name.c_str(),
kCpuOnlineFileSuffix.data());
std::string is_online;
// 看/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/online来看cpu是否在线
if (!android::base::ReadFileToString(cpu_online_path, &is_online)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not open Cpu online file: " << cpu_online_path;
return;
}
is_online = android::base::Trim(is_online);
(*cpu_usages)[cpu_num].name = cpu_name;
(*cpu_usages)[cpu_num].active = user + nice + system;
(*cpu_usages)[cpu_num].total = user + nice + system + idle;
(*cpu_usages)[cpu_num].isOnline = (is_online == "1") ? true : false;
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unexpected cpu number: " << words[0];
return;
}
}
}
}
linux-5.4/fs/proc/stat.c文件
for_each_online_cpu(i) {
struct kernel_cpustat *kcs = &kcpustat_cpu(i);
/* Copy values here to work around gcc-2.95.3, gcc-2.96 */
user = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_USER];
nice = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_NICE];
system = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_SYSTEM];
idle = get_idle_time(kcs, i);
iowait = get_iowait_time(kcs, i);
irq = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_IRQ];
softirq = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_SOFTIRQ];
steal = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_STEAL];
guest = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_GUEST];
guest_nice = kcs->cpustat[CPUTIME_GUEST_NICE];
seq_printf(p, "cpu%d", i);
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(user));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(nice));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(system));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(idle));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(iowait));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(irq));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(softirq));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(steal));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(guest));
seq_put_decimal_ull(p, " ", nsec_to_clock_t(guest_nice));
seq_putc(p, '\n');
}
3. ThermalWatcher类-监测sensor变化
监控sensors的uevent事件,调用应用的回调函数
3.1 ThermalWatcher构造函数
ThermalWatcher(const WatcherCallback &cb)
// 回调函数
: Thread(false), cb_(cb), looper_(new Looper(true)) {}
3.2 registerFilesToWatch
void ThermalWatcher::registerFilesToWatch(const std::set<std::string> &sensors_to_watch,
bool uevent_monitor) {
// 这个是空的
monitored_sensors_.insert(sensors_to_watch.begin(), sensors_to_watch.end());
// 这个是true,不会走这里
if (!uevent_monitor) {
is_polling_ = true;
return;
}
// 打开uevent的socket,监听uevent事件
uevent_fd_.reset((TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(uevent_open_socket(64 * 1024, true))));
if (uevent_fd_.get() < 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "failed to open uevent socket";
is_polling_ = true;
return;
}
fcntl(uevent_fd_, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
looper_->addFd(uevent_fd_.get(), 0, Looper::EVENT_INPUT, nullptr, nullptr);
is_polling_ = false;
thermal_triggered_ = true;
last_update_time_ = boot_clock::now();
}
3.3 startWatchingDeviceFiles
bool ThermalWatcher::startWatchingDeviceFiles() {
if (cb_) {
auto ret = this->run("FileWatcherThread", PRIORITY_HIGHEST);
if (ret != NO_ERROR) {
LOG(ERROR) << "ThermalWatcherThread start fail";
return false;
} else {
LOG(INFO) << "ThermalWatcherThread started";
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
3.4 threadLoop
bool ThermalWatcher::threadLoop() {
LOG(VERBOSE) << "ThermalWatcher polling...";
// Polling interval 2s
static constexpr int kMinPollIntervalMs = 2000;
// Max uevent timeout 5mins
static constexpr int kUeventPollTimeoutMs = 300000;
int fd;
std::set<std::string> sensors;
auto time_elapsed_ms = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(boot_clock::now() -
last_update_time_)
.count();
int timeout = (thermal_triggered_ || is_polling_) ? kMinPollIntervalMs : kUeventPollTimeoutMs;
if (time_elapsed_ms < timeout && looper_->pollOnce(timeout, &fd, nullptr, nullptr) >= 0) {
if (fd != uevent_fd_.get()) {
return true;
}
// 解析uevent事件
parseUevent(&sensors);
// Ignore cb_ if uevent is not from monitored sensors
// 没有monitor,sensors肯定为0,则不会调用回调函数
if (sensors.size() == 0) {
return true;
}
}
// 调用回调函数
thermal_triggered_ = cb_(sensors);
last_update_time_ = boot_clock::now();
return true;
}
3.5 parseUevent-解析thermal类型的uevent事件
void ThermalWatcher::parseUevent(std::set<std::string> *sensors_set) {
bool thermal_event = false;
constexpr int kUeventMsgLen = 2048;
char msg[kUeventMsgLen + 2];
char *cp;
while (true) {
int n = uevent_kernel_multicast_recv(uevent_fd_.get(), msg, kUeventMsgLen);
if (n <= 0) {
if (errno != EAGAIN && errno != EWOULDBLOCK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error reading from Uevent Fd";
}
break;
}
if (n >= kUeventMsgLen) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Uevent overflowed buffer, discarding";
continue;
}
msg[n] = '\0';
msg[n + 1] = '\0';
cp = msg;
while (*cp) {
std::string uevent = cp;
if (!thermal_event) {
// uevent事件中SUBSYSTEM=thermal
if (uevent.find("SUBSYSTEM=") == 0) {
if (uevent.find("SUBSYSTEM=thermal") != std::string::npos) {
// 说明是thermal的事件
thermal_event = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
} else {
// 下一个事件
auto start_pos = uevent.find("NAME=");
if (start_pos != std::string::npos) {
start_pos += 5;
std::string name = uevent.substr(start_pos);
// 找NAME=xx和monitor_sensors_中的name对应
if (std::find(monitored_sensors_.begin(), monitored_sensors_.end(), name) !=
monitored_sensors_.end()) {
sensors_set->insert(name);
}
break;
}
}
while (*cp++) {
}
}
}
}
4. ThermalManagerService-java层的接口服务
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/power/ThermalManagerService.java
4.1 ThermalManagerService构造函数
// frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
t.traceBegin("StartThermalManager");
// 启动ThermalManagerService服务
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ThermalManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
// 创建ThermalManagerService对象
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
// 调用ThermalManagerService类的onStart函数
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
public ThermalManagerService(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public void onStart() {
// 注册THERMAL_SERVICE服务
publishBinderService(Context.THERMAL_SERVICE, mService);
}
4.2 onActivityManagerReady
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
t.traceBegin("StartActivityManagerReadyPhase");
// 启动PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY阶段
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
t.traceEnd();
。。。。
}
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, @NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("PhaseActivityManagerReady");
....
// 执行上面的函数
if (goingCallback != null) goingCallback.run();
....
}
public void startBootPhase(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t, int phase) {
if (phase <= mCurrentPhase) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Next phase must be larger than previous");
}
mCurrentPhase = phase;
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting phase " + mCurrentPhase);
try {
t.traceBegin("OnBootPhase_" + phase);
final int serviceLen = mServices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < serviceLen; i++) {
final SystemService service = mServices.get(i);
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
t.traceBegin("OnBootPhase_" + phase + "_" + service.getClass().getName());
try {
// 调用service的onBootPhase函数
service.onBootPhase(mCurrentPhase);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to boot service "
+ service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onBootPhase threw an exception during phase "
+ mCurrentPhase, ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onBootPhase");
t.traceEnd();
}
} finally {
t.traceEnd();
}
if (phase == SystemService.PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED) {
final long totalBootTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - mRuntimeStartUptime;
t.logDuration("TotalBootTime", totalBootTime);
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
}
}
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
if (phase == SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY) {
onActivityManagerReady();
}
}
private void onActivityManagerReady() {
synchronized (mLock) {
// Connect to HAL and post to listeners.
boolean halConnected = (mHalWrapper != null);
if (!halConnected) {
// 连接thermal 2.0 hal
mHalWrapper = new ThermalHal20Wrapper();
halConnected = mHalWrapper.connectToHal();
}
if (!halConnected) {
mHalWrapper = new ThermalHal11Wrapper();
halConnected = mHalWrapper.connectToHal();
}
if (!halConnected) {
mHalWrapper = new ThermalHal10Wrapper();
halConnected = mHalWrapper.connectToHal();
}
mHalWrapper.setCallback(this::onTemperatureChangedCallback);
if (!halConnected) {
Slog.w(TAG, "No Thermal HAL service on this device");
return;
}
// 通过thermal hal获取温度
List<Temperature> temperatures = mHalWrapper.getCurrentTemperatures(false,
0);
final int count = temperatures.size();
if (count == 0) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Thermal HAL reported invalid data, abort connection");
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
onTemperatureChanged(temperatures.get(i), false);
}
onTemperatureMapChangedLocked();
mTemperatureWatcher.updateSevereThresholds();
mHalReady.set(true);
}
}
4.3 notifyThrottling
@Override
public void notifyThrottling(
android.hardware.thermal.V2_0.Temperature temperature) {
Temperature thermalSvcTemp = new Temperature(
temperature.value, temperature.type, temperature.name,
temperature.throttlingStatus);
final long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// 这里是调用onTemperatureChangedCallback函数
mCallback.onValues(thermalSvcTemp);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
};
4.4 onTemperatureChangedCallback
private void onTemperatureChangedCallback(Temperature temperature) {
final long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
onTemperatureChanged(temperature, true);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
4.5 onTemperatureChanged
private void onTemperatureChanged(Temperature temperature, boolean sendStatus) {
shutdownIfNeeded(temperature);
synchronized (mLock) {
Temperature old = mTemperatureMap.put(temperature.getName(), temperature);
if (old == null || old.getStatus() != temperature.getStatus()) {
// 这里是调用eventlistener的回调的
notifyEventListenersLocked(temperature);
}
if (sendStatus) {
onTemperatureMapChangedLocked();
}
}
}
4.6 onTemperatureMapChangedLocked-调用statuslistener的回调
private void postStatusListener(IThermalStatusListener listener) {
final boolean thermalCallbackQueued = FgThread.getHandler().post(() -> {
try {
// 调用statuslistener的回调
listener.onStatusChange(mStatus);
} catch (RemoteException | RuntimeException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Thermal callback failed to call", e);
}
});
if (!thermalCallbackQueued) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Thermal callback failed to queue");
}
}
private void notifyStatusListenersLocked() {
final int length = mThermalStatusListeners.beginBroadcast();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
final IThermalStatusListener listener =
mThermalStatusListeners.getBroadcastItem(i);
// 调用statuslistener的回调
postStatusListener(listener);
}
} finally {
mThermalStatusListeners.finishBroadcast();
}
}
// 调用statuslistener的回调
private void onTemperatureMapChangedLocked() {
int newStatus = Temperature.THROTTLING_NONE;
final int count = mTemperatureMap.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Temperature t = mTemperatureMap.valueAt(i);
if (t.getType() == Temperature.TYPE_SKIN && t.getStatus() >= newStatus) {
newStatus = t.getStatus();
}
}
// Do not update if override from shell
if (!mIsStatusOverride) {
// 调用statuslistener的回调
setStatusLocked(newStatus);
}
}
private void setStatusLocked(int newStatus) {
if (newStatus != mStatus) {
mStatus = newStatus;
// 调用statuslistener的回调
notifyStatusListenersLocked();
}
}
4.7 notifyEventListenersLocked-调用eventlistener的回调
private void postEventListener(Temperature temperature,
IThermalEventListener listener,
@Nullable Integer type) {
// Skip if listener registered with a different type
if (type != null && type != temperature.getType()) {
return;
}
final boolean thermalCallbackQueued = FgThread.getHandler().post(() -> {
try {
// 调用eventlistener的回调
listener.notifyThrottling(temperature);
} catch (RemoteException | RuntimeException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Thermal callback failed to call", e);
}
});
if (!thermalCallbackQueued) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Thermal callback failed to queue");
}
}
private void notifyEventListenersLocked(Temperature temperature) {
final int length = mThermalEventListeners.beginBroadcast();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
final IThermalEventListener listener =
mThermalEventListeners.getBroadcastItem(i);
final Integer type =
(Integer) mThermalEventListeners.getBroadcastCookie(i);
// 调用eventlistener的回调
postEventListener(temperature, listener, type);
}
} finally {
mThermalEventListeners.finishBroadcast();
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.THERMAL_CHANGED, temperature.getName(),
temperature.getType(), temperature.getValue(), temperature.getStatus(), mStatus);
}
4.8 connectToHal - 注册回调函数
@Override
protected boolean connectToHal() {
synchronized (mHalLock) {
try {
mThermalHal20 = android.hardware.thermal.V2_0.IThermal.getService(true);
mThermalHal20.linkToDeath(new DeathRecipient(), THERMAL_HAL_DEATH_COOKIE);
// 注册回调函数
mThermalHal20.registerThermalChangedCallback(mThermalCallback20, false,
0 /* not used */);
Slog.i(TAG, "Thermal HAL 2.0 service connected.");
} catch (NoSuchElementException | RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Thermal HAL 2.0 service not connected.");
mThermalHal20 = null;
}
return (mThermalHal20 != null);
}
}
配置
thermal_info_config.json文件
{
"Sensors":[
{
// name是/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/type下的名字
"Name":"cpu_thermal_zone",
// 见TemperatureType支持的类型
"Type":"CPU",
// 温度阈值,和ThrottlingSeverity相对应
"HotThreshold":[
"NAN", // NONE
75.0, // LIGHT
"NAN", // MODERATE
85.0, // SEVERE
"NAN", // CRITICAL
"NAN", // EMERGENCY
110.0 // SHUTDOWN
],
"VrThreshold":"NAN",
// 读节点的值,乘以Multiplier,等于实际温度值;比如读CPU的节点的温度为47530,需要乘以0.001
"Multiplier":0.001
},
{
"Name":"gpu_thermal_zone",
"Type":"GPU",
"HotThreshold":[
"NAN",
"NAN",
"NAN",
85.0,
"NAN",
"NAN",
110.0
],
"VrThreshold":"NAN",
"Multiplier":0.001
},
{
"Name":"axp803-battery",
"Type":"POWER_AMPLIFIER",
"HotThreshold":[
"NAN",
"NAN",
"NAN",
85.0,
"NAN",
"NAN",
110.0
],
"VrThreshold":"NAN",
"Multiplier":0.001
}
],
"CoolingDevices":[
{
// name和/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/cooling_device0/type相对应
// /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/cooling_device0/cur_state节点对应当前的调温策略,它的值为0表示不限制频率
// 例如:为1则限制cpu频率为1.3G等等
"Name":"thermal-cpufreq-0",
"Type":"CPU"
}
]
}
补充
1. c++特性
1.1 std::bind功能
//1. 可调用对象:普通函数,lambda表达式,函数对象类,类成员函数指针
// 普通函数
int add(int a, int b){return a+b;}
// lambda表达式
auto mod = [](int a, int b){ return a % b;}
// 函数对象类
struct divide{
int operator()(int denominator, int divisor){
return denominator/divisor;
}
};
// 类成员函数指针
// 2. 使用std::function,可以处理除类成员函数指针之外的所有可调用对象
std::function<int(int ,int)> a = add;
std::function<int(int ,int)> b = mod ;
std::function<int(int ,int)> c = divide();
// 3. std::bind:接受一个可调用对象,生成一个新的可调用对象来"适应"原对象的参数列表
// std::bind将可调用对象与其参数一起进行绑定,绑定后的结果可以使用std::function保存
struct Foo {
void print_sum(int n1, int n2)
{
std::cout << n1+n2 << '\n';
}
int data = 10;
};
int main()
{
Foo foo;
// 绑定一个成员函数:第一个参数表示对象的成员函数的指针,第二个参数表示对象的地址,第三个参数表示传入的参数值
// 第四个参数std::placeholders::_1表示占位符
auto f = std::bind(&Foo::print_sum, &foo, 95, std::placeholders::_1);
f(5); // 100
}
1.2 std::transform功能-循环执行函数,并保存结果
std::set<std::string> monitored_sensors;
std::transform(sensor_info_map_.cbegin(), sensor_info_map_.cend(),
std::inserter(monitored_sensors, monitored_sensors.begin()),
[](std::pair<std::string, SensorInfo> const &sensor) {
if (sensor.second.is_monitor)
return sensor.first;
else
return std::string();
});
相当于for循环,遍历first1到last1的值,并将值传给unary_op函数,将unary_op函数的返回值保存到d_first中
first1和last1和d_first参数都要是迭代器类型
template<class InputIt1, class InputIt2,
class OutputIt, class BinaryOperation>
OutputIt transform(InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1, InputIt2 first2,
OutputIt d_first, BinaryOperation binary_op)
{
while (first1 != last1) {
*d_first++ = binary_op(*first1++, *first2++);
}
return d_first;
}
1.3 std::inserter功能-插入到指定位置
只有具备有迭代器的四种基本操作:取值(*),递增(++)比较(== !=) 赋值(=)它就是迭代器。
back_inserter(container) 使用push_back()在容器尾端安插元素
front_inserter(container) 在内部调用push_front()成员函数,将元素安插于容器中最前端
inserter(container,pos) 在内部调用insert()成员函数,将元素插入第二个参数所指的位置
1.4 cbegin和cend-迭代器const开始和结束
1.iterator,const_iterator作用:遍历容器内的元素,并访问这些元素的值。iterator可以改元素值,但const_iterator不可改。跟C的指针有点像。
2.const_iterator 对象可以用于const vector 或非 const vector,它自身的值可以改(可以指向其他元素),但不能改写其指向的元素值。
3.cbegin()和cend()是C++11新增的,它们返回一个const的迭代器,不能用于修改元素。
auto i1 = Container.begin(); // i1 is Container<T>::iterator
auto i2 = Container.cbegin(); // i2 is Container<T>::const_iterator
1.5 vector.erase函数和std::remove_if函数-删除符合条件的元素
callbacks_.erase(
std::remove_if(callbacks_.begin(), callbacks_.end(),
[&](const CallbackSetting &c) {
if (!c.is_filter_type || t.type == c.type) {
// 调用应用的回调
Return<void> ret = c.callback->notifyThrottling(t);
// !ret.isOk()如果不ok,则是true,就删除掉callback了;如果ok则是false,就不删除callback了
return !ret.isOk();
}
LOG(ERROR)
<< "a Thermal callback is dead, removed from callback list.";
return false;
})
iterator erase (iterator position); //删除指定元素
iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last); //删除指定范围内的元素
remove_if(begin,end,op);
remove_if的参数是迭代器,前两个参数表示迭代的起始位置和这个起始位置所对应的停止位置。
最后一个参数:传入一个回调函数,如果回调函数返回为真,则将当前所指向的参数移到尾部。
返回值是被移动区域的首个元素。
remove_if和erase一起使用,用以删除容器中的元素的
2. libjsoncppc-解析json文件
external/jsoncpp目录下
json文件的格式就是key:value的形式的
2.1 libjsoncpp接口使用
// 打开文件
std::ifstream in(config_path);
Json::Value root;
Json::CharReaderBuilder reader;
Json::String errs;
// 分析文件
Json::parseFromStream(reader, in, &root, &errs)
// 得到文件中的值
Json::Value sensors = root["Sensors"];
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex i = 0; i < sensors.size(); ++i) {
const std::string &name = sensors[i]["Name"].asString();
std::string sensor_type_str = sensors[i]["Type"].asString();
Json::Value values = sensors[i]["HotThreshold"];
values = sensors[i]["HotHysteresis"];
// 没有配置HotHysteresis,或者配置的个数没有到kThrottlingSeverityCount那么多个
if (values.size() != kThrottlingSeverityCount) {
LOG(INFO) << "Cannot find valid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotHysteresis, default all to 0.0";
} else {
for (Json::Value::ArrayIndex j = 0; j < kThrottlingSeverityCount; ++j) {
hot_hysteresis[j] = getFloatFromValue(values[j]);
if (std::isnan(hot_hysteresis[j])) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid "
<< "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotHysteresis: " << hot_hysteresis[j];
sensors_parsed.clear();
return sensors_parsed;
}
LOG(INFO) << "Sensor[" << name << "]'s HotHysteresis[" << j
<< "]: " << hot_hysteresis[j];
}
}
}
3. java新特性
3.1 FunctionalInterface-函数接口
函数式接口(Functional Interface)就是一个有且仅有一个抽象方法,但是可以有多个非抽象方法的接口。
// 1. 定义函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
interface TemperatureChangedCallback {
void onValues(Temperature temperature);
}
/** Temperature callback. */
protected TemperatureChangedCallback mCallback;
@VisibleForTesting
protected void setCallback(TemperatureChangedCallback cb) {
mCallback = cb;
}
// 2. 变量赋值
mHalWrapper.setCallback(this::onTemperatureChangedCallback);
// 3. 函数定义,函数参数和返回值一样,就可以直接赋值了
private void onTemperatureChangedCallback(Temperature temperature) {
final long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
onTemperatureChanged(temperature, true);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
// 4. 函数调用
mCallback.onValues(temperatures.get(i));
问题
1. thermal hal初始化失败,Android无法起来
ThermalHelper构造函数中,有两句LOG(FATAL)
is_initialized_ = initializeSensorMap(tz_map) && initializeCoolingDevices(cdev_map);
if (!is_initialized_) {
// 如果thermal节点没有初始化成功,这里为FATAL类型的LOG,那么thermal会起不来,造成Android系统起不来
LOG(FATAL) << "ThermalHAL could not be initialized properly.";
}
is_initialized_ = thermal_watcher_->startWatchingDeviceFiles();
if (!is_initialized_) {
// 如果thermal节点没有初始化成功,这里为FATAL类型的LOG,那么thermal会起不来,造成Android系统起不来
LOG(FATAL) << "ThermalHAL could not start watching thread properly.";
}
2. 驱动不支持user_space配置,以及没有配置monitor sensor
驱动不支持user_space配置,配置了monitor也没用。
没有配置monitor sensor,所以,即使应用注册了回调,也不会去调用应用的回调。
参考
1. C++11 中的std::function和std::bind
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f191e88dcc80
2. Linux Thermal Framework分析及实施
https://www.cnblogs.com/arnoldlu/p/11207142.html
3. Android/Linux Thermal Governor之IPA分析与使用
https://www.cnblogs.com/arnoldlu/p/6388112.html
4. Thermal 框架梳理
https://dongka.github.io/2018/06/25/thermal/thermal_framework/
5. begin( )和cbegin( )异同
https://blog.csdn.net/u010987458/article/details/70949112
6. PowerManager
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/android/os/PowerManager?hl=zh-cn#addThermalStatusListener(java.util.concurrent.Executor,%20android.os.PowerManager.OnThermalStatusChangedListener)
7. 热缓解
https://source.android.com/devices/architecture/hidl/thermal-mitigation?hl=zh-cn
8. java8函数式接口(Functional Interface)
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903784808710152
9. c++ vector erase用法
https://blog.csdn.net/u013654125/article/details/77321081
10. std:;remove_if用法讲解
https://blog.csdn.net/KFLING/article/details/80187847
11. /proc/stat解析
http://gityuan.com/2017/08/12/proc_stat/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号