DFS-中等
中等题
1、面试题 04.05. 合法二叉搜索树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/legal-binary-search-tree-lcci/
考点:
1、按题意思是要比较当前节点和左右子树的值,也就是先要计算出左右子树的列表,才可知当前节点是否满足要求。 由此可知为后序遍历
2、(技巧)每次节点比较时,只要和左右子树的集合比较即可,所以迭代要返回当前节点子树的结合
3、(注意)需要考虑到 左右子树为空,左子树为空,右子树为空,左右子树均不为空等情况
class Solution:
def helper(self, root, result):
if root == None:
return []
l_list = self.helper(root.left, result)
r_list = self.helper(root.right, result)
print(str(root.val) + "*" + str(l_list) + "*" + str(r_list))
if l_list == [] and r_list == []:
return [root.val]
elif l_list == [] and r_list and root.val < min(r_list):
r_list.append(root.val)
return r_list
elif r_list == [] and l_list and root.val > max(l_list):
l_list.append(root.val)
return l_list
elif ((l_list and root.val > max(l_list)) and (r_list and root.val < min(r_list))):
l_list.extend(r_list)
l_list.append(root.val)
return l_list
else:
result.append(False)
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
result = []
self.helper(root, result)
return False if False in result else True
2、面试题 16.19. 水域大小 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pond-sizes-lcci/
考点:
1、典型的二维数组 深度搜索问题,根据找到的某个位置,深度搜索满足条件的块
class Solution:
def helper(self, pos, now_pos, land):
row = len(land)
col = len(land[0])
i, j = pos
for x, y in [(i+1, j), (i-1, j), (i, j+1), (i, j-1), (i-1, j-1), (i+1, j-1), (i-1, j+1), (i+1, j+1)]:
if 0 <= x < row and 0 <= y < col and land[x][y] == 0 and (x, y) not in now_pos:
now_pos.append((x, y))
self.helper((x, y), now_pos, land)
return now_pos
def pondSizes(self, land: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
row = len(land)
col = len(land[0])
haved = []
result = []
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if land[i][j] == 0 and (i, j) not in haved:
now_pos = []
now_pos.append((i, j))
self.helper((i, j), now_pos, land)
result.append(len(now_pos))
haved.extend(now_pos)
result.sort()
return result
3、面试题 04.06. 后继者 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/successor-lcci/
考点
1、二叉树的中序遍历
2、(注意) 递归方法中设中间值和判断逻辑都在中序位置, 开始只做叶子节点返回值处理
class Solution:
def helper(self, root, p, find, result):
if root == None:
return
self.helper(root.left, p, find, result)
if True in find and root is not None and result is not None:
result.append(root)
if root == p:
find.append(True)
self.helper(root.right, p, find, result)
def inorderSuccessor(self, root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
find = []
result = []
self.helper(root, p, find, result)
return result[0] if result else None
4、面试题 17.22. 单词转换
考点:
1、深度搜索
按照常规的深度搜索+优先搜索 往目的字符串转的方式,还是会时间超时
class Solution:
def helper(self, beginWord, endWord, result, wordList, cur_list):
if len(result) > 0:
return
if cur_list[-1] == endWord:
result.append(cur_list)
return
word_len = len(beginWord)
choice_words = []
for i in range(word_len):
if not beginWord[i] == endWord[i]:
choice_words.append("%s%s%s" % (beginWord[0:i], endWord[i:i+1], beginWord[i+1:]))
# print(beginWord + "&" + str(choice_words))
for choice_word in choice_words:
if choice_word in wordList:
new_wordList = list(wordList)
new_wordList.remove(choice_word)
new_cur_list = list(cur_list)
new_cur_list.append(choice_word)
self.helper(choice_word, endWord, result, new_wordList, new_cur_list)
# print(beginWord + "*" + str(wordList))
for word in wordList:
# 判断相差1
bigger_diff = 0
for i in range(word_len):
if not beginWord[i] == word[i]:
bigger_diff += 1
if bigger_diff == 1:
new_wordList = list(wordList)
new_wordList.remove(word)
new_cur_list = list(cur_list)
new_cur_list.append(word)
# print(str(new_cur_list) + "**" + str(new_wordList))
self.helper(word, endWord, result, new_wordList, new_cur_list)
def findLadders(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> List[str]:
if endWord not in wordList:
return []
result = []
cur_list = [beginWord]
self.helper(beginWord, endWord, result, wordList, cur_list)
# print(result)
if len(result) > 0:
return result[0]
else:
return []
换个思路,引入字典: 使用*代表任意字符,构建字典如下:
使用*代表任意字符,构建字典如下:
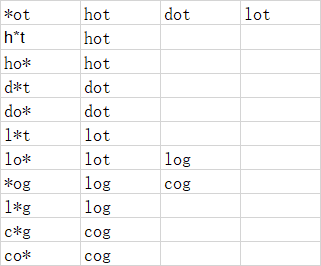
第一列为key,后面列为value;
按照startword 每个位置* 替换后开始深度搜索
考点:
1、数据结构,引入dict快速索引深度遍历元素
2、函数中函数,好处是 内部函数可以使用外部函数的参数; 注意内不函数要给外部函数参数赋值,需要将参数值定义为类变量 self.变量名
3、技巧:引入marked,已经访问过的单次没必要访问,因为只要访问过,该单词后面的路径计算就属于重复计算
5、面试题 04.12. 求和路径 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/paths-with-sum-lcci/ 最后差2个用例由于事件超时,以后研究
考点:
1、树的路径遍历,先序遍历(注意路径不同的path要复制list,防止互相影响)
2、list连续子列表等于某值,主要该题列表中的值可正可负,不能使用左右指针
class Solution:
# 先序遍历所有的路径
def helper(self, cur, cur_path, results):
if cur == None:
return
if cur.left == None and cur.right == None:
cur_path.append(cur)
results.append(cur_path)
else:
cur_path.append(cur)
l_cur_path = list(cur_path)
self.helper(cur.left, l_cur_path, results)
r_cur_path = list(cur_path)
self.helper(cur.right, r_cur_path, results)
def isum(self, ilist):
iss = 0
for i in range(len(ilist)):
# print("***" + str(left) + "&"+str(right)+"&"+ str(i))
iss += ilist[i].val
# print(str(ilist) + "*"+str(iss))
return iss
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> int:
results = []
cur_path = []
self.helper(root, cur_path, results)
# print(results)
rresult = []
# 满足条件的路径
for result in results:
# 双指针 统计满足 -- 当 整数值恒正,才会用到左右指针
# le = len(result)
# left = 0
# for right in range(1, le+1):
# if self.isum(result[left:right]) == tt:
# rresult += 1
# while self.isum(result[left:right]) > tt and right > left + 1:
# left += 1
# if self.isum(result[left:right]) == tt:
# rresult += 1
# 由于值存在正负,直接用遍历
for i in range(1, len(result)+1):
for j in range(i):
if self.isum(result[j:i]) == tt:
if result[j:i] not in rresult:
rresult.append(result[j:i])
return len(rresult)
6、剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ju-zhen-zhong-de-lu-jing-lcof/
考点:
1、深度搜索题,先找到满足第一个字符的位置,然后进行迭代的深度搜索
2、一定要主要 判断满足条件实在迭代函数的判断逻辑中,不是在迭代最开始的地方
class Solution:
def helper(self, cur, have, next_pos, result, word, board):
if True in result:
return
row = len(board)
col = len(board[0])
cur_i, cur_j = cur
for i,j in [(cur_i - 1, cur_j),(cur_i, cur_j - 1),(cur_i+1, cur_j),(cur_i, cur_j+1)]:
if 0 <= i < row and 0 <= j < col and (i, j) not in have:
if board[i][j] == word[next_pos]:
if next_pos == len(word)-1:
result.append(True)
return
else:
new_have = list(have)
new_have.append((i, j))
self.helper((i, j), new_have, next_pos + 1, result, word, board)
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
row = len(board)
col = len(board[0])
if not board:
return False
result = []
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
if len(word) == 1:
return True
else:
have = set()
have.add((i, j))
self.helper((i, j), have, 1, result, word, board)
if True in result:
return True
else:
return False
7 1466. 重新规划路线 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-routes-to-make-all-paths-lead-to-the-city-zero/
考点:
1、层次的深度搜索
2、基础层次深度搜索会时间超时;然后使用dict来加速
class Solution:
change = 0
# def helper(self, cur_list, rest_lists):
# if len(rest_lists) == 0:
# return
# next_list = []
# for cur in cur_list:
# for rest_list in list(rest_lists):
# if cur in rest_list:
# if cur == rest_list[0]:
# self.change += 1
# next_list.append(rest_list[1])
# else:
# next_list.append(rest_list[0])
# rest_lists.remove(rest_list)
# self.helper(next_list, rest_lists)
def helper(self, cur_list, connections_dict):
if len(connections_dict) == 0:
return
next_list = []
for cur in cur_list:
all_lists = connections_dict.get(cur)
for all_list in all_lists:
if all_list[0] == cur:
self.change += 1
next_list.append(all_list[1])
connections_dict[all_list[1]].remove(all_list)
else:
next_list.append(all_list[0])
connections_dict[all_list[0]].remove(all_list)
del connections_dict[cur]
self.helper(next_list, connections_dict)
def minReorder(self, n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
connections_dict = dict()
for i in range(len(connections)):
connection = connections[i]
if connections_dict.get(connection[0]):
connections_dict.get(connection[0]).append(connection)
else:
connections_dict[connection[0]] = [connection]
if connections_dict.get(connection[1]):
connections_dict.get(connection[1]).append(connection)
else:
connections_dict[connection[1]] = [connection]
# print(connections_dict)
cur_list = [0]
self.helper(cur_list, connections_dict)
# self.helper(cur_list, connections)
return self.change
8 971. 翻转二叉树以匹配先序遍历 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flip-binary-tree-to-match-preorder-traversal/
考点:
1、先序遍历
2、技巧,主要逻辑(判断值是否和list中相等,是否置换左右子树 )均放在先序 位置上
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
Failed = False
def helper(self, root, voyage, result):
if self.Failed == True or root == None or voyage == None:
return
if not root.val == voyage[0]:
self.Failed = True
return
del voyage[0]
if root.left and not root.left.val == voyage[0]:
tmp = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = tmp
result.append(root.val)
self.helper(root.left, voyage, result)
self.helper(root.right, voyage, result)
def flipMatchVoyage(self, root: TreeNode, voyage: List[int]) -> List[int]:
result = []
if root == None:
return [-1]
self.helper(root, voyage, result)
if self.Failed:
return [-1]
else:
return result
9 面试题 17.07. 婴儿名字 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/baby-names-lcci/
考点:
1、并查集,比常规并查集复杂的地方在 需要维护一个字典保存各元素位置
2、注意:在关系中的名字不一定在实际中存在,所有 按照实际有的名字建立 需要进行并查集的列表。 将要进行并查集建立关系的元素,需要2个元素都在并查集列表中,才需要进行。要不然没有必要按照并查集建立关系
class Solution:
def search(self, name, name_list, name_index):
if name_list[name_index.get(name)] != name:
name_list[name_index.get(name)] = self.search(name_list[name_index.get(name)], name_list, name_index)
return name_list[name_index.get(name)]
def union(self, name1, name2, name_list, name_index):
if name1 in name_index and name2 in name_index:
name1_first = self.search(name1, name_list, name_index)
name2_first = self.search(name2, name_list, name_index)
# print("&&"+ str(name1_first) + str(name2_first))
if name1_first > name2_first:
name_list[name_index.get(name1_first)] = name2_first
else:
name_list[name_index.get(name2_first)] = name1_first
def trulyMostPopular(self, names: List[str], synonyms: List[str]) -> List[str]:
name_num = dict()
name_index = dict()
index = 0
name_list = []
for name in names:
iname = name[:name.index("(")]
num = int(name[name.index("(") + 1: -1])
name_num[iname] = num
name_index[iname] = index
index = index + 1
name_list.append(iname)
# print(name_num)
# print(name_index)
# print(name_list)
# 并查集,找到相同真实名字
for syno in synonyms:
sname_list = syno[1:-1].split(",")
name1 = sname_list[0]
name2 = sname_list[1]
self.union(name1, name2, name_list, name_index)
# print("*"+str(name_list))
for iname in name_index.keys():
self.search(iname, name_list, name_index)
# print(name_list)
# 计算总个数
result = {}
for name, num in name_num.items():
if result.get(name_list[name_index.get(name)]):
result[name_list[name_index.get(name)]] = result.get(name_list[name_index.get(name)]) + num
else:
result[name_list[name_index.get(name)]] = num
# 拼接成返回格式
result_list = []
for name, num in result.items():
result_list.append(name + "(%d)" % num)
return result_list
947. 移除最多的同行或同列石头
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/most-stones-removed-with-same-row-or-column/submissions/
10 721. 账户合并 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/accounts-merge/
考点:
1、一看该题,考查的比较像并查集,但是 注意里面 长度要求不高,直接使用递归暴力求解方法
2、注意,既然该题考查是并查集,也就是merge_list 方法一遍遍历不出来结果,所以该出使用递归
class Solution:
def merge_list(self, mails_list):
change = False
all_result = []
for mails in list(mails_list):
is_find = False
for mail in mails:
for idx in range(len(all_result)):
if mail in all_result[idx]:
all_result[idx].extend(mails)
all_result[idx] = list(set(all_result[idx]))
is_find = True
change = True
break
if is_find:
continue
if is_find:
continue
else:
all_result.append(mails)
if change:
return self.in_list(all_result)
else:
return mails_list
def add_result(self, name, all_list, results):
for s_list in all_list:
result = [name]
tmp = list(set(s_list))
tmp.sort()
result.extend(tmp)
results.append(result)
def accountsMerge(self, accounts: List[List[str]]) -> List[List[str]]:
# 按照account 计算map
accounts_dict = collections.defaultdict(list)
for account in accounts:
name = account[0]
accounts_dict[name].append(account[1:])
results = []
for name, mails_list in accounts_dict.items():
all_list = self.merge_list(mails_list)
self.add_result(name, all_list, results)
return results
11. 1026. 节点与其祖先之间的最大差值 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-difference-between-node-and-ancestor/
考点:
1、深度搜索,之前有道题目是 计算每个节点及子节点最大,最小值,可以很快得到 最大距离
class Solution:
def set_max(self, a, b):
if a - b > self.max_dis:
self.max_dis = a - b
elif b - a > self.max_dis:
self.max_dis = b - a
def helper(self, root):
if root == None:
return None, None
l_min, l_max = self.helper(root.left)
r_min, r_max = self.helper(root.right)
# 左右节点都为空
if l_min==None and r_min==None:
return root.val, root.val
# 左节点为空
elif l_min==None:
self.set_max(r_min, root.val)
self.set_max(r_max, root.val)
return min(r_min, root.val), max(r_max, root.val)
elif r_min==None:
self.set_max(l_min, root.val)
self.set_max(l_max, root.val)
return min(l_min, root.val), max(l_max, root.val)
else:
self.set_max(r_min, root.val)
self.set_max(r_max, root.val)
self.set_max(l_min, root.val)
self.set_max(l_max, root.val)
return min(min(l_min, r_min), root.val), max(max(l_max, r_max), root.val)
def maxAncestorDiff(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# 使用后续遍历,计算每个节点最小值和最大值
self.max_dis = 0
self.helper(root)
return self.max_dis
12 1376. 通知所有员工所需的时间 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/time-needed-to-inform-all-employees/
考点:
1、深度搜索
直接按照深度搜索 时间超时
class Solution:
def helper(self, n, cur, manager, informTime, cur_time):
not_end = False
# 找到下一层
for i in range(n):
if manager[i] == cur:
self.helper(n, i, manager, informTime, cur_time+informTime[cur])
not_end = True
if not not_end:
if self.all_time < cur_time:
self.all_time = cur_time
def numOfMinutes(self, n: int, headID: int, manager: List[int], informTime: List[int]) -> int:
cur_list = [headID]
self.all_time = 0
self.helper(n, headID, manager, informTime, 0)
return self.all_time
引入dict表示这种2层关系,通过
class Solution:
def helper(self, n, cur, manager_dict, informTime, cur_time):
if manager_dict[cur]:
for chre in manager_dict[cur]:
self.helper(n, chre, manager_dict, informTime, cur_time+informTime[cur])
not_end = True
else:
if self.all_time < cur_time:
self.all_time = cur_time
def numOfMinutes(self, n: int, headID: int, manager: List[int], informTime: List[int]) -> int:
# 管理者关系字典
manager_dict = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i in range(n):
if not manager[i] == -1:
manager_dict[manager[i]].append(i)
cur_list = [headID]
self.all_time = 0
self.helper(n, headID, manager_dict, informTime, 0)
return self.all_time
13 638. 大礼包 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shopping-offers/
考点:
1。深度搜索, 假设 套餐肯定比单独购买便宜,所以优先遍历递归套餐,然后遍历递归单个商品
超出时间限制
class Solution:
def helper(self, price, special, needs, cur_price):
if needs == [0] * len(needs):
if cur_price < self.total_price:
self.total_price = cur_price
return
for i in range(len(special)):
tmp_need = list(needs)
fil_condition = True
for j in range(len(needs)):
new_j = tmp_need[j] - special[i][j]
if new_j >= 0:
tmp_need[j] = tmp_need[j] - special[i][j]
else:
fil_condition = False
break
if fil_condition:
# print(tmp_need, cur_price + special[i][-1])
self.helper(price, special, tmp_need, cur_price + special[i][-1])
for i in range(len(needs)):
tmp_need = list(needs)
if tmp_need[i] > 0:
tmp = tmp_need[i]
tmp_need[i] = 0
self.helper(price, special, tmp_need, cur_price + tmp * price[i])
def shoppingOffers(self, price: List[int], special: List[List[int]], needs: List[int]) -> int:
self.total_price = 0
for i in range(len(needs)):
self.total_price += needs[i] * price[i]
self.helper(price, special, needs, 0)
return self.total_price
考虑加速递归过程,考虑2个方面优化后通过: 1、 已经知道不满足要求的套餐,删除,下次不用再递归 2、单独购买商品,套餐参数设置为空数组,均不用 递归遍历套餐了(基于套餐肯定比单独购买便宜,前面已经穷尽套餐了,所有参数传递的套餐设置为空数组)
class Solution:
def helper(self, price, special, needs, cur_price):
if needs == [0] * len(needs):
if cur_price < self.total_price:
self.total_price = cur_price
return
# 选择可遍历的list
for i in range(len(special)):
tmp_need = list(needs)
special_new = list(special)
fil_condition = True
for j in range(len(needs)):
new_j = tmp_need[j] - special[i][j]
if new_j >= 0:
tmp_need[j] = tmp_need[j] - special[i][j]
else:
fil_condition = False
special_new.remove(special[i])
break
if fil_condition:
self.helper(price, special_new, tmp_need, cur_price + special[i][-1])
for i in range(len(needs)):
tmp_need = list(needs)
if tmp_need[i] > 0:
tmp = tmp_need[i]
tmp_need[i] = 0
self.helper(price, [], tmp_need, cur_price + tmp * price[i])
def shoppingOffers(self, price: List[int], special: List[List[int]], needs: List[int]) -> int:
self.total_price = 0
for i in range(len(needs)):
self.total_price += needs[i] * price[i]
self.helper(price, special, needs, 0)
return self.total_price
14 1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pseudo-palindromic-paths-in-a-binary-tree/
考点:
1、 二叉树中 路径个数,使用深度搜索
2、 判断数列是否构成回文窜,判断逻辑是 如果字符出现奇数次的 个数大于等于1,则不能构成回文。 <=1 则可以构成回文
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def helper(self, root, cur_path):
if root == None:
return
if root.left == None and root.right == None:
tmp_path = list(cur_path)
tmp_path.append(root.val)
self.paths.append(tmp_path)
return
tmp_path = list(cur_path)
tmp_path.append(root.val)
self.helper(root.left, tmp_path)
self.helper(root.right, tmp_path)
def pseudoPalindromicPaths (self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
self.paths = []
# 1.找到所有路径
self.helper(root, [])
# print(self.paths)
# 2.数列是否是回文(判断字符出现奇数次是否大于1,此处引入字典)
result = 0
for path in self.paths:
result_dict = dict()
for item in path:
if result_dict.get(item):
result_dict[item] = result_dict.get(item) + 1
else:
result_dict[item] = 1
ji_count = 0
for key, value in result_dict.items():
if not value % 2 == 0:
ji_count += 1
if ji_count <= 1:
result += 1
return result


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号