thrift实现多服务多线程的匹配系统
thrift实现多服务多线程的匹配系统
thrift学习教程:thrift官网
本博客代码:thrift_match_server
官网教程:进入官网->Tutorial->tutorial.thrift
Apache Thrift软件框架用于可伸缩的跨语言服务开发,它将软件栈和代码生成引擎结合在一起,以构建在C++、Java、Python、PHP、Ruby、Erlang、Perl、Haskell、C#、Cocoa、JavaScript、Node.js、Smalltalk、OCaml和Delphi等语言之间高效、无缝地工作的服务。
Thrift使用C++进行编写,在安装使用的时候需要安装依赖,windows安装方式见官网即可。安装方式:thrift官网介绍安装方式
项目目的
模拟一个多服务的游戏匹配系统,具体业务逻辑如下图:
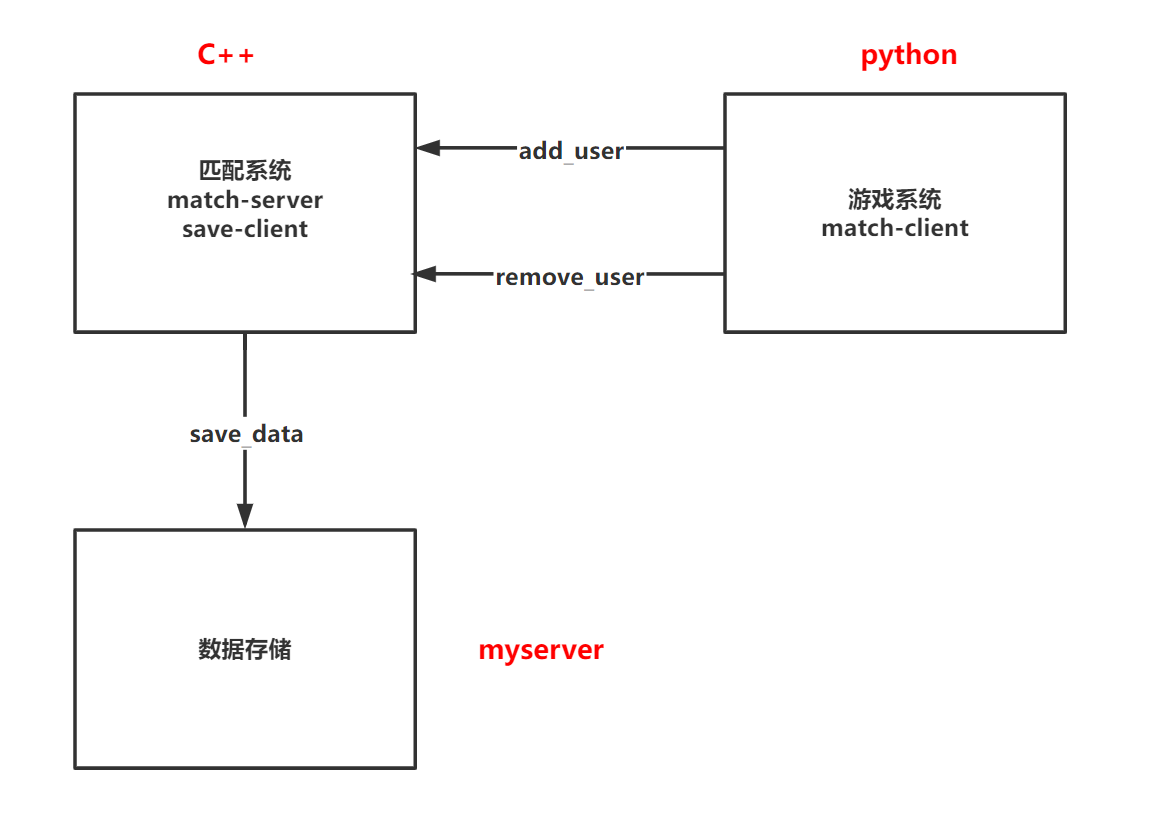
准备工作
创建项目结构
-
创建项目文件夹
thrift_demo -
游戏系统节点,创建game文件夹;匹配系统节点,创建match_system文件夹;thrift相关文件,创建thrift文件夹
结果如图:
thrift简单语法介绍
0.开发流程
- 对接口进行描述,定义接口描述文件:
.thrift文件,比如match.thrift - 使用
thrift将接口的描述文件自动成对应语言的版本的代码,包括服务端和客户端
1.命名空间
thrift文件命名一般都是以.thrift作为后缀:XXX.thrift,可以在该文件的开头为该文件加上命名空间限制,格式为:
namespace 语言名称 名称
例如对c++来说,有:
namespace cpp match_service
2.数据类型
大小写敏感,它共支持以下几种基本的数据类型:
string, 字符串类型,注意是全部小写形式;i16, 16位整形类型,i32,32位整形类型,对应C/C++/java中的int类型;i64,64位整形,对应C/C++/java中的long类型;byte,8位的字符类型,对应C/C++中的char,java中的byte类型bool, 布尔类型,对应C/C++中的bool,java中的boolean类型;double,双精度浮点类型,对应C/C++/java中的double类型;void,空类型,对应C/C++/java中的void类型;该类型主要用作函数的返回值,除上述基本类型外,ID还支持以下类型:
map,map类型,例如,定义一个map对象:map[HTML_REMOVED] newmap;set,集合类型,例如,定义set[HTML_REMOVED]对象:set[HTML_REMOVED] aSet;list,链表类型,例如,定义一个list[HTML_REMOVED]对象:list[HTML_REMOVED] aList;
struct,自定义结构体类型,在IDL中可以自己定义结构体,对应C中的struct,c++中的struct和class,java中的class。例如:
struct User{
1: i32 id,
2: string name,
3: i32 score
}
注意,在struct定义结构体时需要对每个结构体成员用序号标识:“序号: ”。
3.函数接口
文件中对所有接口函数的描述都放在service中,service的名字可以自己指定,该名字也将被用作生成的特定语言接口文件的名字。
接口函数需要对参数使用序号标号,除最后一个接口函数外,要以,结束对函数的描述。
比如:
namespace cpp match_service
struct User {
1: i32 id,
2: string name,
3: i32 score
}
service Match {
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*/
i32 add_user(1: User user, 2: string info),
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*/
i32 remove_user(1: User user, 2: string info),
}
具体运行流程,以下面匹配系统例子介绍。
服务端框架搭建
创建接口描述文件
对于匹配系统的thrift相关配置,我们在thrift文件夹下,创建match.thrift文件,用来生成匹配系统服务端的一系列文件。
vi thrift/match.thrift
参考:打开thrift官网,在上方选择
Tutorial项,查看thrift官方教程,点击下方的tutorial.thrift进入一个示例文件。
编写match.thrift配置文件,只需要在文件中写明接口和对象即可:
namespace cpp match_service
struct User {
1: i32 id,
2: string name,
3: i32 score
}
service Match {
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*/
i32 add_user(1: User user, 2: string info),
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*/
i32 remove_user(1: User user, 2: string info),
}
编译成对应语言的版本
进入到match_system文件夹,创建src文件夹。在src下执行语句:
# thrift -r --gen <语言名> <.thrift文件的路径>
thrift -r --gen cpp ../../thrift/match.thrift
这样就会生成各种配置和连接文件,还有代码框架,只需要在框架中实现自己的业务即可。默认是放在gen-cpp,可以修改为match_server,以便更好的划分业务模块。
同时其中Match_server.skeleton.cpp为服务端的代码框架,具体业务就是在这个文件编写实现,将Match_server.skeleton.cpp移动到match_system/src下并重命名为main.cpp,match_system的整个业务逻辑就是在这个文件中实现。
最后的文件结构如下:

代码生成以后最好先跑一下,然后再逐步添加功能,看一下是否成功,上述操作导致需要修改两个地方:
- 之前
main.cpp在match_server下,现在在match_system/src下,所以main.cpp中对Match.h头文件的引入需要修改路径。 - 文件中的两个函数
int32_t add_user和int32_t remove_user需要有返回值,原来没有,会报警告,需要手动加上。
// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server.
// You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it.
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
return 0;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
::std::shared_ptr<MatchHandler> handler(new MatchHandler());
::std::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new MatchProcessor(handler));
::std::shared_ptr<TServerTransport> serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port));
::std::shared_ptr<TTransportFactory> transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory());
::std::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
c++文件的编译、链接和运行
C++的编译过程
(注意大小写)假设我有一个main.cpp文件
-E:只对文件进行预处理,不进行编译和汇编。g++ -E main.cpp——>在dos命令行查看某文件的预处理过程,如果你想查看详细的预处理,可以重定向到一个文件中,如:g++ -E main.cpp -o main.i
-s:编译到汇编语言,不进行汇编和链接,即只激活预处理和编译,生成汇编语言,如果你想查看详细的编译,可以重定向到一个文件中,如:g++ -S main.cpp -o main.s
-c:编译到目标代码,g++ -c main.s -o 文件名.o
-o:生成链接文件: 如果该文件是独立的,与其他自己编写的文件无依赖关系。直接g++ main.o -o 生成的可执行文件的文件名,假设该文件依赖其他源文件(不需要加入头文件)
temp.cpp,在对temp.cpp文件进行预处理->编译->汇编后,使用指令g++ temp.o main.o -o main
.\:执行文件,输出结果。如:.\main,当然你可以直接g++ main.cpp temp.cpp -o main生成目标文件让编译器自动为你处理其他流程。
步骤
-
编译
src文件夹下的所有.cpp文件g++ -c main.cpp match_server/*.cpp -
将所有生成的
.o文件链接成一个可执行文件,要用到thrift动态链接库g++ *.o -o main -lthrift -
执行生成的可执行文件
main./main为了判断文件是否正确执行,可以在
main.cpp中写一些输出语句,验证效果 -
将项目版本提交git,提交时,一般会删除中间生成的文件和可执行文件
git add . git restore --stage *.o git restore --stage match_system/src/main git commit -m "first can run"
客户端框架搭建
跟上面一样的步骤
-
在
game下创建src,在src下执行:thrift -r --gen py ../../thrift/match.thrift这样,thrift服务端的一系列文件就会生成在
src文件夹中的gen-py文件夹下,为了划分业务模块将gen-py重命名为match_client文件结构如下:
. |-- Match.o |-- main |-- main.cpp |-- main.o |-- match_client | |-- __init__.py | `-- match | |-- Match-remote | |-- Match.py | |-- __init__.py | |-- constants.py | `-- ttypes.py |-- match_server | |-- Match.cpp | |-- Match.h | |-- match_types.cpp | `-- match_types.h `-- match_types.o因为我们只需要实现客户端,不需要服务端,所以可以把
Match-remote删除 -
在
src下创建文件client.py,将 Apache Thrift - Python 页面中,client中的代码复制到该文件中,并将代码进行适当的改动和删除,client.py中的初始代码如下:from match_client.match import Match from match_client.match.ttypes import User from thrift import Thrift from thrift.transport import TSocket from thrift.transport import TTransport from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol def main(): # Make socket transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090) # Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport) # Wrap in a protocol protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport) # Create a client to use the protocol encoder client = Match.Client(protocol) # Connect! transport.open() # 具体业务代码 user = User(1, 'sdz', 1500) client.add_user(user, "") # Close! transport.close() if __name__ == "__main__": main() -
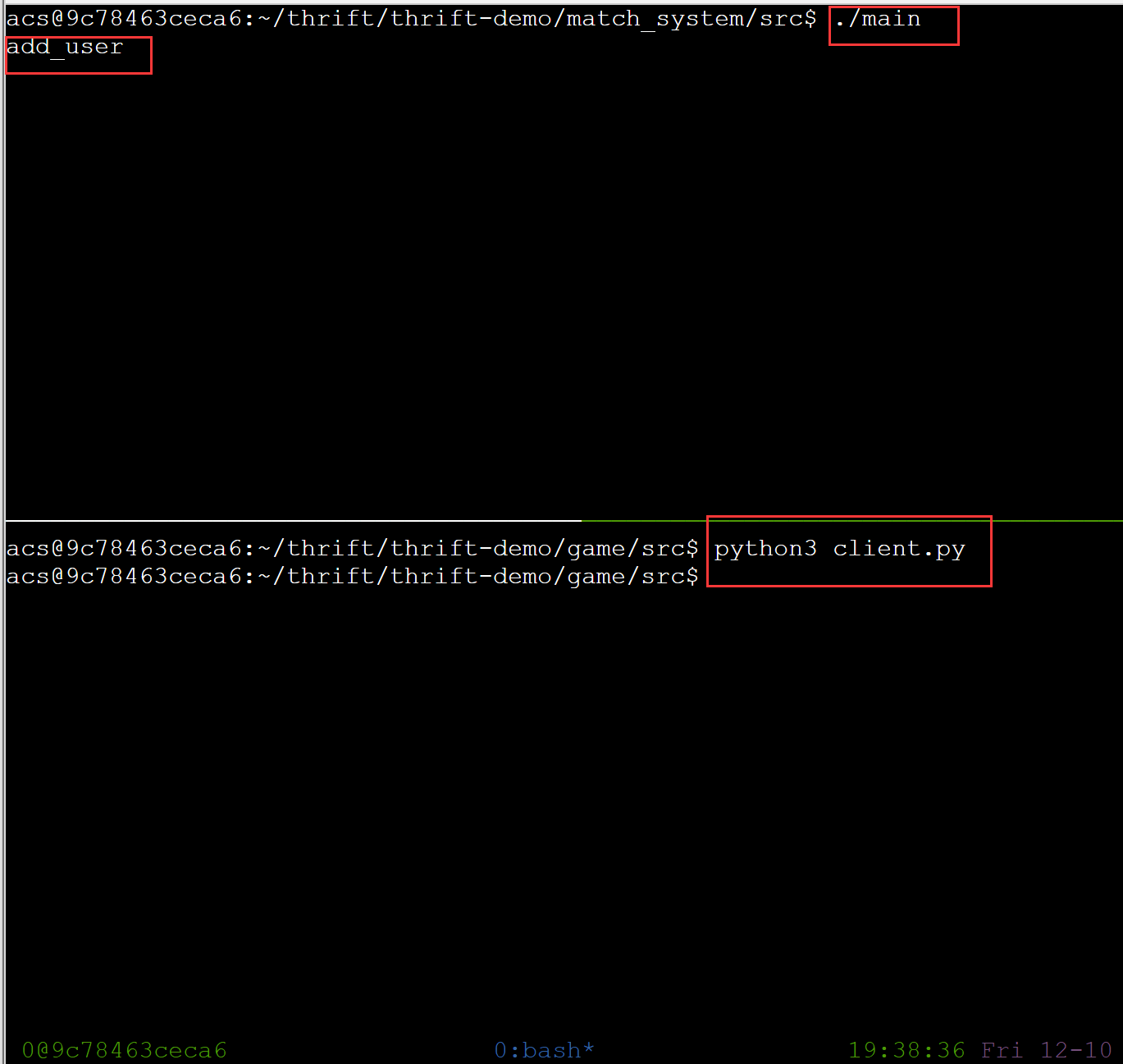
运行一下
-
先在
thrift_demo/match_system/src下,执行:./main,使服务端运行 -
再在
thrift_demo/game/src下,执行:python3 client.py,使客户端运行 -
观察服务端运行处有无相应输出,若有,说明成功运行
-
-
git保存一下git add . git restore --stage *.pyc # pyc文件为中间结果文件,类似c++的.o文件 git commit -m "add match client"
客户端完善
from match_client.match import Match
from match_client.match.ttypes import User
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
# python读取命令行参数包
from sys import stdin
def operate(op, user_id, username, score):
# Make socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090)
# Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# Wrap in a protocol
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# Create a client to use the protocol encoder
client = Match.Client(protocol)
# Connect!
transport.open()
# 具体业务代码
user = User(user_id, username, score)
if op == "add":
client.add_user(user, "")
elif op == "remove":
client.remove_user(user, "")
# Close!
transport.close()
def main():
for line in stdin:
op, user_id, username, score = line.split(' ')
operate(op, int(user_id), username, int(score))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
进行运行查错步骤并做正确输入,如果服务端处有相应输出,说明函数调用成功,运行成功
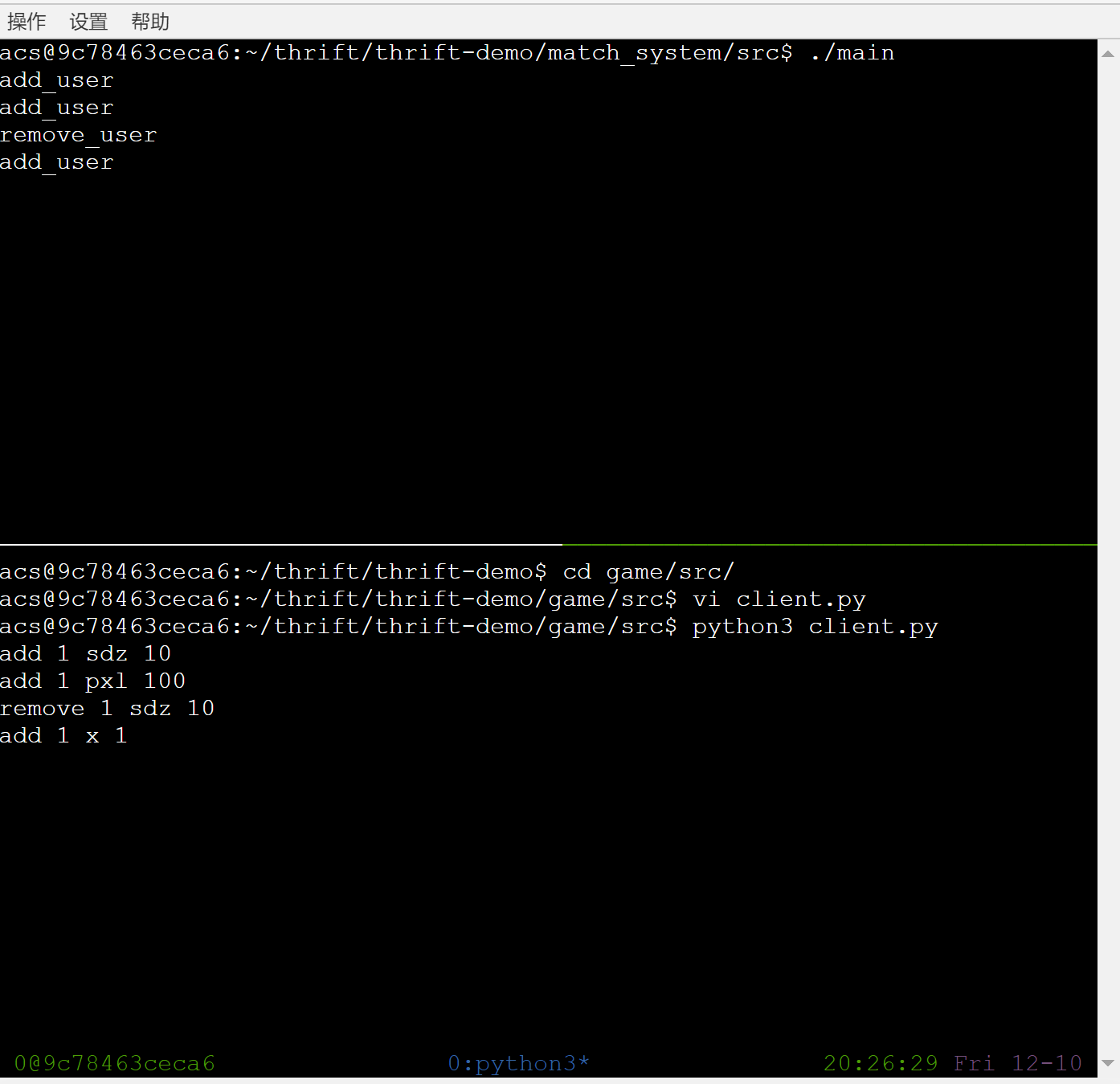
git保存一下:
git add client.py
git commit -m "finsh client.py"
服务端完善
服务端主要有两个功能:
- 接收客户端(
game)的添加和删除用户请求 - 完成匹配工作
这两个功能需要并行执行,为了防止阻塞接收client请求,需要开一个线程去不停地进行匹配。实现逻辑图如下:
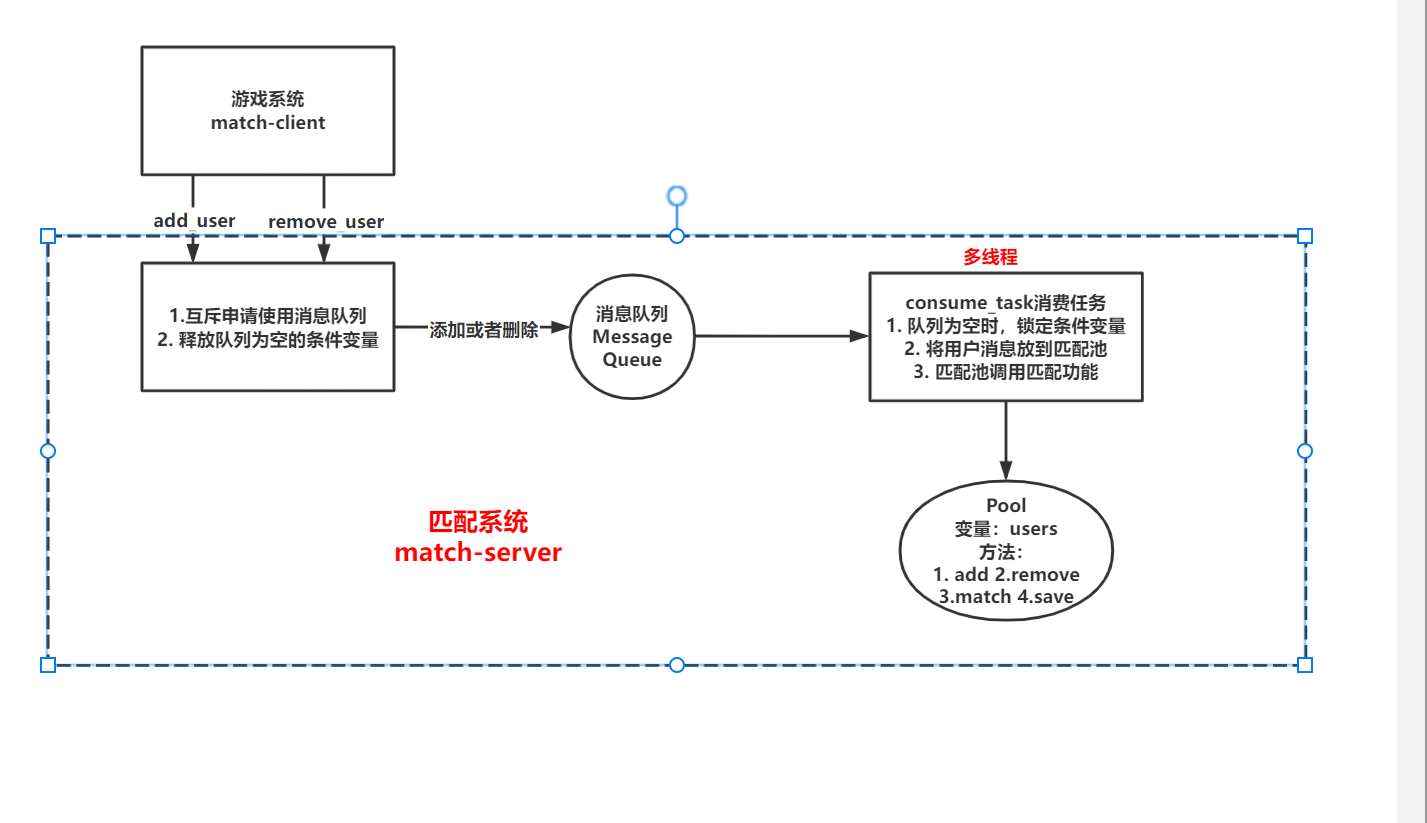
每一次只选前两个匹配版main.cpp:
// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server.
// You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it.
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task
{
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue
{
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
}message_queue;
class Pool
{
public:
void save_result(int a, int b){
printf("Match result : %d, %d\n", a, b);
}
void match(){
while (users.size() > 1){
User a = users[0], b = users[1];
users.erase(users.begin());
users.erase(users.begin());
save_result(a.id, b.id);
}
}
void add(User user){
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user){
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
//通过消息队列中的锁将方法锁着。
//好处:你不需要进行解锁操作,当方法执行完毕,这个变量就会自动注销
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
//唤醒所有条件变量
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task(){
while (true){
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()){
/* 因为消费者线程(不止一个)会频繁判断队列是否为空,导致CPU做无用功。
* 所以使用条件变量的wait()函数可使得当前线程阻塞,直至条件变量唤醒。
* 当线程阻塞的时候,该函数会自动解锁,允许其他线程执行。
**/
message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
} else {
Task task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
::std::shared_ptr<MatchHandler> handler(new MatchHandler());
::std::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new MatchProcessor(handler));
::std::shared_ptr<TServerTransport> serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port));
::std::shared_ptr<TTransportFactory> transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory());
::std::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory);
printf("Start Match Server\n");
thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
只修改了main.cpp,只编译链接main.cpp
先编译main.cpp,在链接时,要用到thrift动态链接库和线程相关的动态链接库,所以链接时应该执行:
g++ -c main.cpp
g++ *.o -o main -lthrift -pthread
测试一下
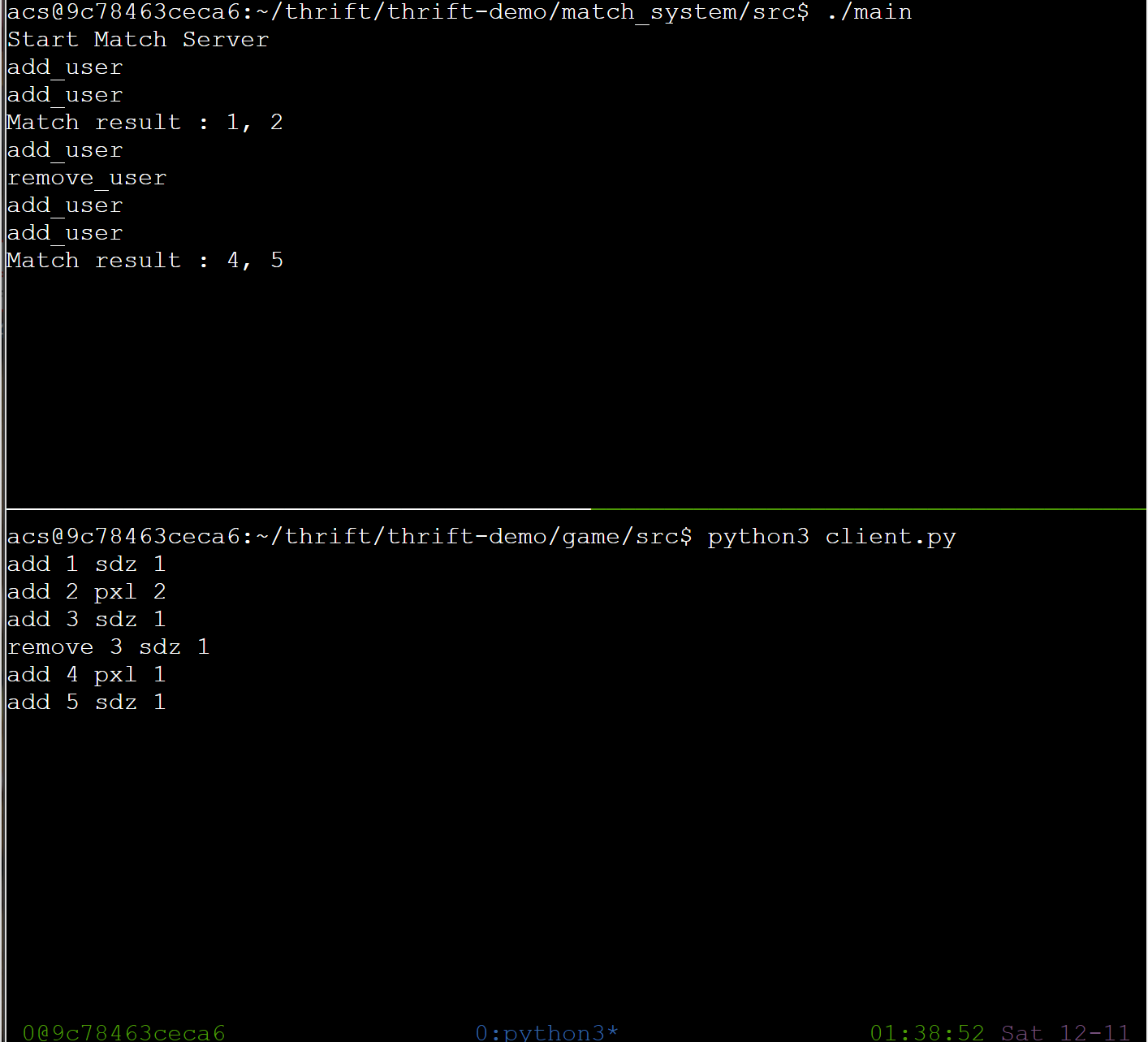
git 保存一下
数据存储客户端的实现
-
在
thrift文件夹下,编辑save.thrift,用来生成数据存储客户端的一系列文件namespace cpp save_service service Save { /** * username: myserver的名称 * password: myserver的密码的md5sum的前8位 * 用户名密码验证成功会返回0,验证失败会返回1 * 验证成功后,结果会被保存到myserver:homework/lesson_6/result.txt中 */ i32 save_data(1: string username, 2: string password, 3: i32 player1_id, 4: i32 player2_id) } -
在
match_system/src下执行:thrift -r --gen cpp ../../thrift/save.thrift这样,
thrift服务端的一系列文件就会生成在src文件夹中的gen-cpp文件夹下,为了划分业务模块将gen-cpp重命名为save_client注意:
由于c++整个项目只能有一个
main函数,而整个服务端的逻辑都在thrift_project/match_system/src下的main.cpp实现。所以一定要删除thrift_project/match_system/src/save_client下的Save_server.skeleton.cpp。而python没有这个问题,所以在用python实现客户端时,主框架文件可删可不删。 -
改动
main.cpp将数据存储端的业务写进去官方参考地址:Tutorial- > C++的client,的主要改动点:
-
引入缺少头文件,即
save_client/Save.h,thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>和<thrift/transport/TSocket.h> -
补全命名空间,即添加
using namespace ::save_service; -
在
class Pool中的save_resut函数中,添加官网 C++样例的client中的main函数中的所有代码 -
由于数据存储是实现在
myserver上,所以在连接时要更改ip地址。myserver的ip地址可以执行homework 4 getinfo查看。即自己的数据存储服务器 -
将
CalculatorClient改为SaveClient -
将
transport->open()和transport->close();之间的教程代码删除,在此之间实现自己的业务// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server. // You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it. #include "match_server/Match.h" #include "save_client/Save.h" #include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h> #include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h> #include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h> #include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h> #include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h> #include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h> #include <thread> #include <mutex> #include <condition_variable> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <iostream> using namespace ::apache::thrift; using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol; using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport; using namespace ::apache::thrift::server; using namespace ::match_service; using namespace ::save_service; using namespace std; struct Task { User user; string type; }; struct MessageQueue { queue<Task> q; mutex m; condition_variable cv; }message_queue; class Pool { public: void save_result(int a, int b){ std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090)); std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket)); std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport)); SaveClient client(protocol); puts("w"); try { transport->open(); int res = client.save_data("acs_2104", "fcf05d68", a, b); if (!res) puts("数据存储成功!"); else puts("数据存取失败!"); transport->close(); } catch (TException& tx) { cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl; } printf("Match result : %d, %d\n", a, b); } void match(){ while (users.size() > 1){ User a = users[0], b = users[1]; users.erase(users.begin()); users.erase(users.begin()); save_result(a.id, b.id); } } void add(User user){ users.push_back(user); } void remove(User user){ for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) { if (users[i].id == user.id) { users.erase(users.begin() + i); break; } } } private: vector<User> users; }pool; class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf { public: MatchHandler() { // Your initialization goes here } /** * user: 添加的用户信息 * info: 附加信息 * 在匹配池中添加一名用户 * * @param user * @param info */ int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) { // Your implementation goes here printf("add_user\n"); //通过消息队列中的锁将方法锁着。 //好处:你不需要进行解锁操作,当方法执行完毕,这个变量就会自动注销 unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m); message_queue.q.push({user, "add"}); //唤醒所有条件变量 message_queue.cv.notify_all(); return 0; } /** * user: 删除的用户信息 * info: 附加信息 * 从匹配池中删除一名用户 * * @param user * @param info */ int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) { // Your implementation goes here printf("remove_user\n"); unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m); message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"}); message_queue.cv.notify_all(); return 0; } }; void consume_task(){ while (true){ unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m); if (message_queue.q.empty()){ /* 因为消费者线程(不止一个)会频繁判断队列是否为空,导致CPU做无用功。 * 所以使用条件变量的wait()函数可使得当前线程阻塞,直至条件变量唤醒。 * 当线程阻塞的时候,该函数会自动解锁,允许其他线程执行。 **/ message_queue.cv.wait(lck); } else { Task task = message_queue.q.front(); message_queue.q.pop(); lck.unlock(); if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user); else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user); pool.match(); } } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int port = 9090; ::std::shared_ptr<MatchHandler> handler(new MatchHandler()); ::std::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new MatchProcessor(handler)); ::std::shared_ptr<TServerTransport> serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port)); ::std::shared_ptr<TTransportFactory> transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory()); ::std::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory()); TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory); printf("Start Match Server\n"); thread matching_thread(consume_task); server.serve(); return 0; }
-
-
编译运行
g++ -c save_client/*.cpp g++ -c main.cpp g++ *.o -o main -lthrift -pthread -
验证结果,登录到myserver服务器上查看存储的结果:
ssh myserver cd homework/lesson_6 cat result.txt
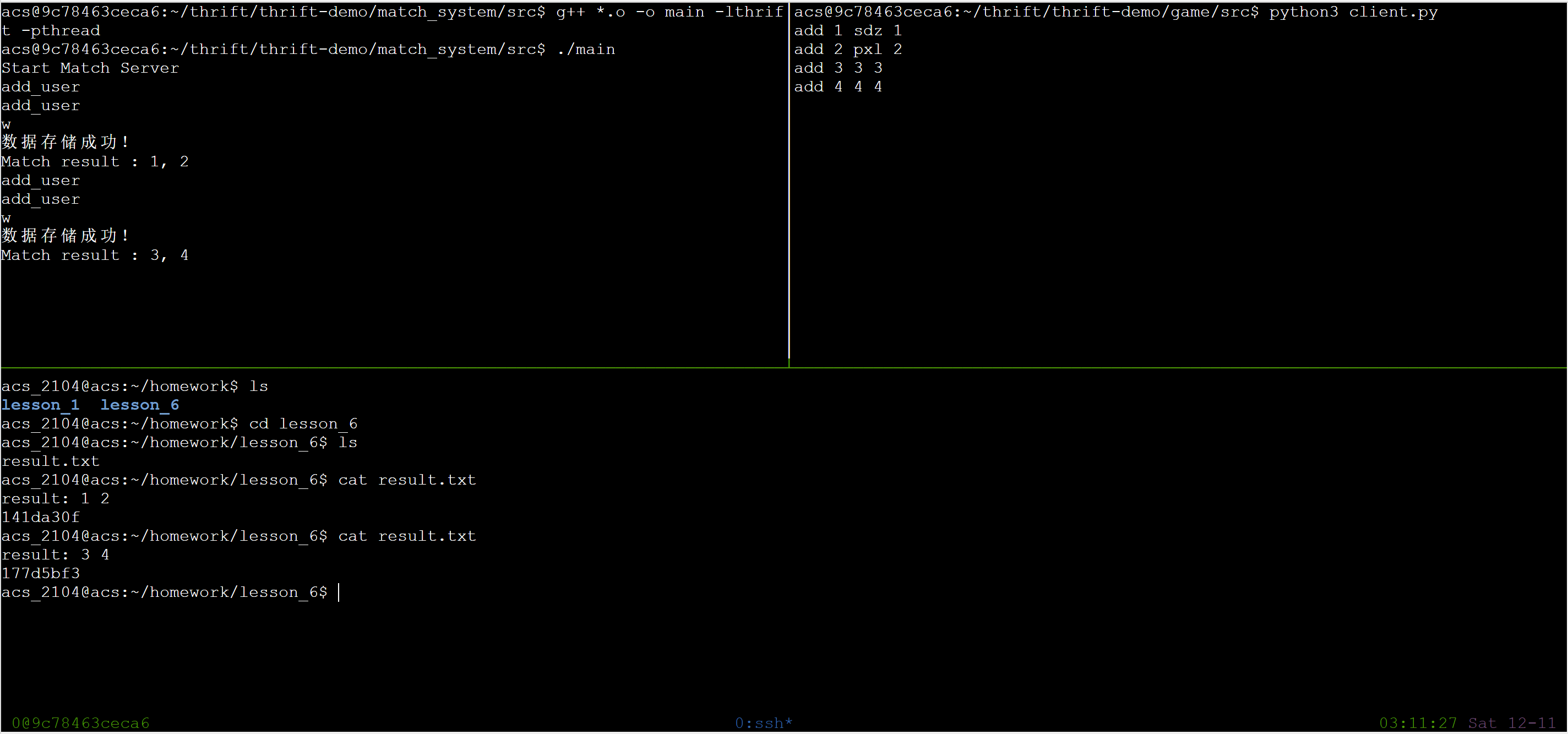
注意保存提交到git。
匹配系统升级1:按照分差匹配用户
实现思路:每一秒钟匹配一次,只要发现一对分差<=50的匹配成功。
注意,match函数的实现的功能只要匹配一对即可,修改下一消耗消息队列函数和匹配函数即可。
main.cpp改动如下:
// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server.
// You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it.
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include "save_client/Save.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace ::save_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task
{
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue
{
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
}message_queue;
class Pool
{
public:
void save_result(int a, int b){
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
int res = client.save_data("acs_2104", "fcf05d68", a, b);
if (!res) puts("数据存储成功!");
else puts("数据存取失败!");
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
printf("Match result : %d, %d\n", a, b);
}
void match(){
while (users.size() > 1){
sort(users.begin(), users.end(), [&](User& a, User b){
return a.score < b.score;
});
bool flag = true;
for(uint32_t i = 1; i < users.size(); i++){
User a = users[i], b = users[i - 1];
if (a.score - b.score <= 50) {
save_result(a.id, b.id);
users.erase(users.begin() + i - 1, users.begin() + i + 1);
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) break;
}
}
void add(User user){
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user){
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
//通过消息队列中的锁将方法锁着。
//好处:你不需要进行解锁操作,当方法执行完毕,这个变量就会自动注销
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
//唤醒所有条件变量
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task(){
while (true){
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()){
/* 因为消费者线程(不止一个)会频繁判断队列是否为空,导致CPU做无用功。
* 所以使用条件变量的wait()函数可使得当前线程阻塞,直至条件变量唤醒。
* 当线程阻塞的时候,该函数会自动解锁,允许其他线程执行。
**/
// message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
lck.unlock();
pool.match();
sleep(1);
} else {
Task task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
::std::shared_ptr<MatchHandler> handler(new MatchHandler());
::std::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new MatchProcessor(handler));
::std::shared_ptr<TServerTransport> serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port));
::std::shared_ptr<TTransportFactory> transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory());
::std::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory);
printf("Start Match Server\n");
thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
测试一下然后git保存一下:
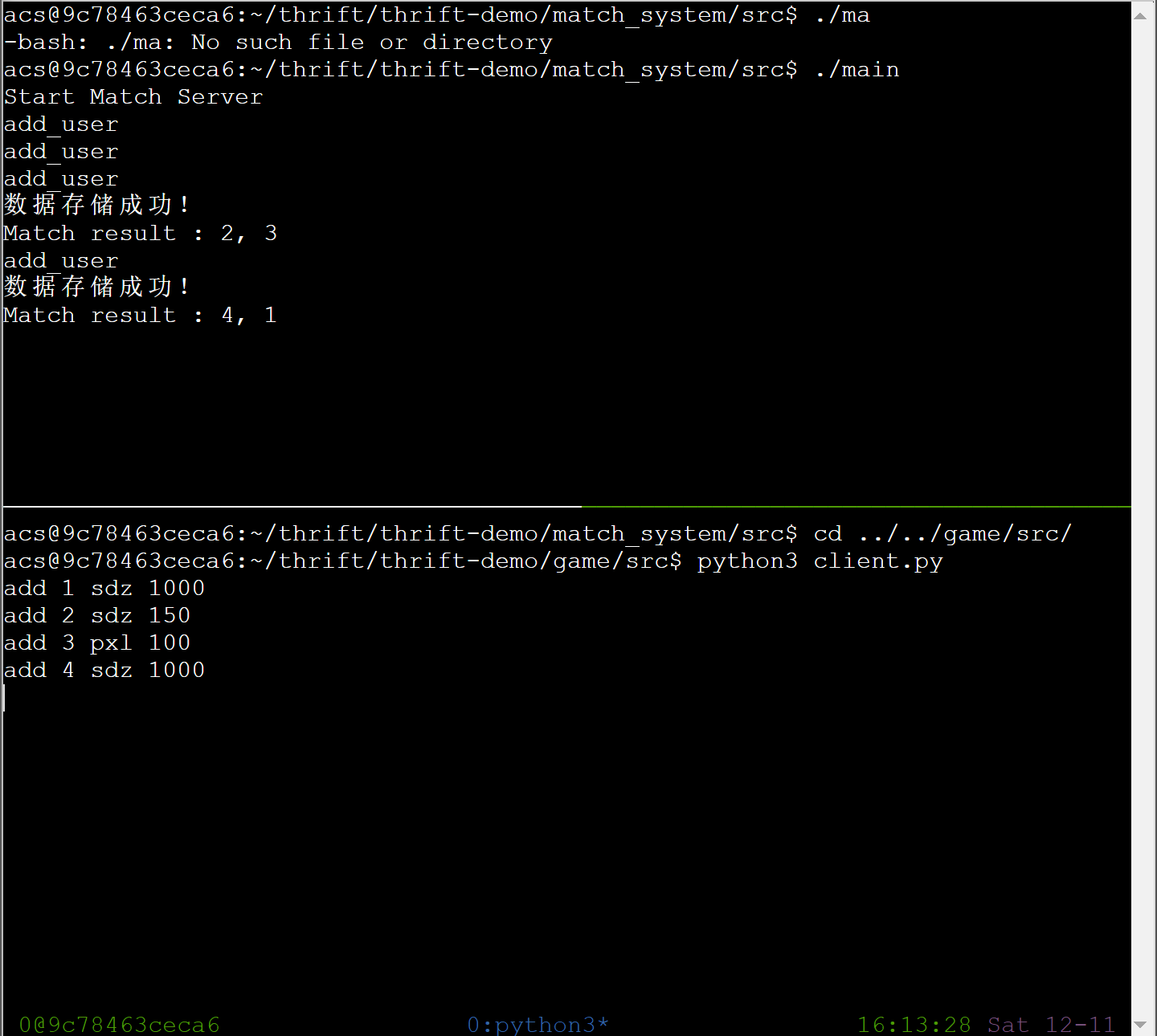
匹配系统升级2:多线程服务器
之前的版本都是用一个线程来add user和remove user,想要提高效率和并发量,可以将服务端升级为多线程版本。
-
引入官网 C++样例的
Server中,main.cpp没有的头文件。 -
将
main函数中的TSimpleServer即相关函数,替换成官网 C++样例的Server中的main函数中的TThreadedServer相关内容 -
将官网 C++样例的
Server中的工厂类class CalculatorCloneFactory相关内容加进来 -
将文件中的所有
Calculator替换为Match,在vim中的具体操作为::1,$s/Calculator/Match/g -
::shared::SharedServiceIf*改为MatchIf*
修改后的main.cpp为:
// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server.
// You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it.
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include "save_client/Save.h"
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadPoolServer.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadedServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/TToString.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace ::save_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task
{
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue
{
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
}message_queue;
class Pool
{
public:
void save_result(int a, int b){
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
int res = client.save_data("acs_2104", "fcf05d68", a, b);
if (!res) puts("数据存储成功!");
else puts("数据存取失败!");
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
printf("Match result : %d, %d\n", a, b);
}
void match(){
while (users.size() > 1){
sort(users.begin(), users.end(), [&](User& a, User b){
return a.score < b.score;
});
bool flag = true;
for(uint32_t i = 1; i < users.size(); i++){
User a = users[i], b = users[i - 1];
if (a.score - b.score <= 50) {
save_result(a.id, b.id);
users.erase(users.begin() + i - 1, users.begin() + i + 1);
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) break;
}
}
void add(User user){
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user){
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
//通过消息队列中的锁将方法锁着。
//好处:你不需要进行解锁操作,当方法执行完毕,这个变量就会自动注销
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
//唤醒所有条件变量
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task(){
while (true){
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()){
/* 因为消费者线程(不止一个)会频繁判断队列是否为空,导致CPU做无用功。
* 所以使用条件变量的wait()函数可使得当前线程阻塞,直至条件变量唤醒。
* 当线程阻塞的时候,该函数会自动解锁,允许其他线程执行。
**/
// message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
lck.unlock();
pool.match();
sleep(1);
} else {
Task task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
class MatchCloneFactory : virtual public MatchIfFactory {
public:
~MatchCloneFactory() override = default;
MatchIf* getHandler(const ::apache::thrift::TConnectionInfo& connInfo) override
{
std::shared_ptr<TSocket> sock = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<TSocket>(connInfo.transport);
cout << "Incoming connection\n";
cout << "\tSocketInfo: " << sock->getSocketInfo() << "\n";
cout << "\tPeerHost: " << sock->getPeerHost() << "\n";
cout << "\tPeerAddress: " << sock->getPeerAddress() << "\n";
cout << "\tPeerPort: " << sock->getPeerPort() << "\n";
return new MatchHandler;
}
void releaseHandler(MatchIf* handler) override {
delete handler;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
TThreadedServer server(
std::make_shared<MatchProcessorFactory>(std::make_shared<MatchCloneFactory>()),
std::make_shared<TServerSocket>(9090), //port
std::make_shared<TBufferedTransportFactory>(),
std::make_shared<TBinaryProtocolFactory>());
printf("Start Match Server\n");
thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
编译运行测试并保存git:
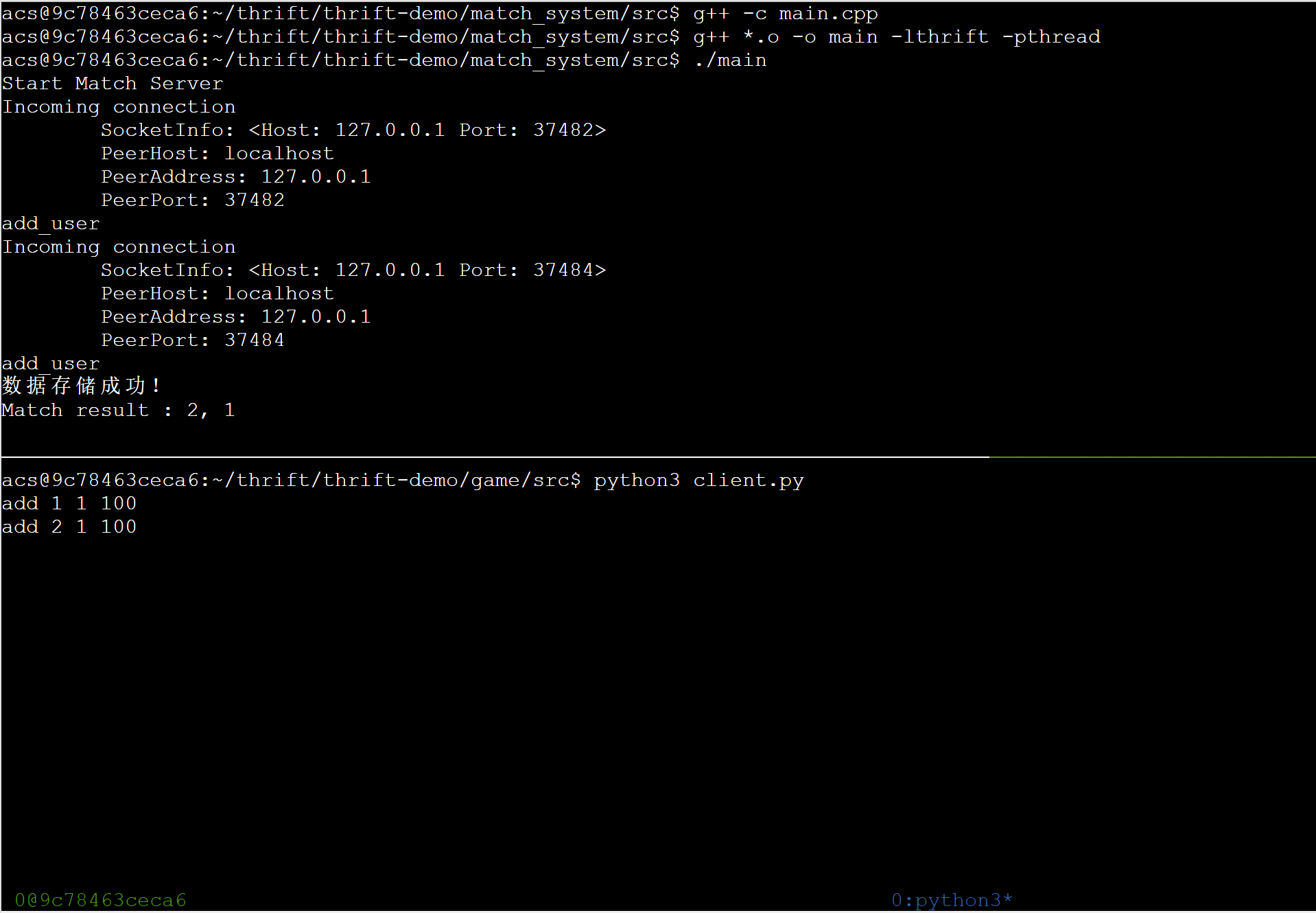
匹配系统升级3:随时间扩大匹配阈值
匹配机制:等待时间越长,阈值越大。即匹配的范围随时间的推移而变大 故需要记录当前玩家在匹配池中等待的秒数。
// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server.
// You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it.
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include "save_client/Save.h"
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadPoolServer.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadedServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/TToString.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace ::save_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task
{
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue
{
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
}message_queue;
class Pool
{
public:
void save_result(int a, int b){
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
int res = client.save_data("acs_2104", "fcf05d68", a, b);
if (!res) puts("数据存储成功!");
else puts("数据存取失败!");
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
printf("Match result : %d, %d\n", a, b);
}
bool check_match(int i, int j){
User a = users[i], b = users[j];
int dt = abs(a.score - b.score);
int a_max_dif = wt[i] * 50;
int b_max_dif = wt[j] * 50;
return dt <= a_max_dif && dt <= b_max_dif;
}
void match(){
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < wt.size(); i ++)
wt[i]++; // 等待秒数 + 1
while (users.size() > 1){
bool flag = true;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++){
for (uint32_t j = i + 1; j < users.size(); j++) {
User a = users[i], b = users[j];
if (check_match(i, j)){
// 注意删除顺序先j后i
users.erase(users.begin() + j);
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
wt.erase(wt.begin() + j);
wt.erase(wt.begin() + i);
save_result(a.id, b.id);
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (!flag) break;
}
if (flag) break;
}
}
void add(User user){
users.push_back(user);
wt.push_back(0);
}
void remove(User user){
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
wt.erase(wt.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
vector<int> wt; // 等待时间,单位:s
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
//通过消息队列中的锁将方法锁着。
//好处:你不需要进行解锁操作,当方法执行完毕,这个变量就会自动注销
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
//唤醒所有条件变量
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task(){
while (true){
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()){
/* 因为消费者线程(不止一个)会频繁判断队列是否为空,导致CPU做无用功。
* 所以使用条件变量的wait()函数可使得当前线程阻塞,直至条件变量唤醒。
* 当线程阻塞的时候,该函数会自动解锁,允许其他线程执行。
**/
// message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
lck.unlock();
pool.match();
sleep(1);
} else {
Task task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
}
}
}
class MatchCloneFactory : virtual public MatchIfFactory {
public:
~MatchCloneFactory() override = default;
MatchIf* getHandler(const ::apache::thrift::TConnectionInfo& connInfo) override
{
std::shared_ptr<TSocket> sock = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<TSocket>(connInfo.transport);
cout << "Incoming connection\n";
cout << "\tSocketInfo: " << sock->getSocketInfo() << "\n";
cout << "\tPeerHost: " << sock->getPeerHost() << "\n";
cout << "\tPeerAddress: " << sock->getPeerAddress() << "\n";
cout << "\tPeerPort: " << sock->getPeerPort() << "\n";
return new MatchHandler;
}
void releaseHandler(MatchIf* handler) override {
delete handler;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
TThreadedServer server(
std::make_shared<MatchProcessorFactory>(std::make_shared<MatchCloneFactory>()),
std::make_shared<TServerSocket>(9090), //port
std::make_shared<TBufferedTransportFactory>(),
std::make_shared<TBinaryProtocolFactory>());
printf("Start Match Server\n");
thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
额外知识点
c++编译很慢,所以对于未修改的文件不需要修改
make:识别那些文件修改。

