Python开发【第二篇】:Python基础知识
Python基础知识
一、初识基本数据类型
类型:
int(整型)
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
long(长整型)
跟C语言不同,Python的长整数没有指定位宽,即:Python没有限制长整数数值的大小,但实际上由于机器内存有限,我们使用的长整数数值不可能无限大。
注意,自从Python2.2起,如果整数发生溢出,Python会自动将整数数据转换为长整数,所以如今在长整数数据后面不加字母L也不会导致严重后果了。
float(浮点型)
浮点数用来处理实数,即带有小数的数字。类似于C语言中的double类型,占8个字节(64位),其中52位表示底,11位表示指数,剩下的一位表示符号。
complex(复数)
复数由实数部分和虚数部分组成,一般形式为x+yj,其中的x是复数的实数部分,y是复数的虚数部分,这里的x和y都是实数。
注:Python中存在小数字池:-5 ~ 257
1、数字
2 是一个整数的例子。
长整数 不过是大一些的整数。
3.23和52.3E-4是浮点数的例子。E标记表示10的幂。在这里,52.3E-4表示52.3 * 10-4。
(-5+4j)和(2.3-4.6j)是复数的例子
 更多
更多
2、布尔值
真或假 1 或 0
3、字符串
"hello world"
万恶的字符串拼接:
python中的字符串在C语言中体现为是一个字符数组,每次创建字符串时候需要在内存中开辟一块连续的空,并且一旦需要修改字符串的话,就需要再次开辟空间,万恶的+号每出现一次就会在内从中重新开辟一块空间。
字符串格式化
name = "alex" print "i am %s " % name #输出: i am alex
PS: 字符串是 %s;整数 %d;浮点数%f
字符串常用功能:- 移除空白
- 分割
- 格式化
- 长度
- 索引
- 切片
- 查找
- 其他
移除空白:
# 默认去除前后空格,()中可指定 username.strip()
分割:
# 分割
a='abc,ddc,adc'
b=a.split(',')
# 按符号合并
print('|'.join(a))
格式化:
# 格式化
msg='Hello,{name},I age is{age}'
msg_print=msg.format(name='luke',age=101)
print(msg_print)
------------------------------------------------
msg2='ha{0},ddd{1}'
print(msg2.format('luke',33))
#简单格式化
a='yy'
b=12
print('你好 我是%s,我的年龄是%d'%(a,b))
长度:
#长度
a='yy ddd hh'
num=a.count('y')
print(num)
-----------------------
num=len(a)
print(num)
索引:
# 索引 a='yy ddd hh' print(a[1])
切片:
# 切片 a='yy ddd hh' print(a[0:4])
查找:
# 查找 -1代表没找到
a='yy ddd hh'
b=a.find('h')
print(b)
其他:
# 填充字符 print(a.center(40,'-'))
# 判断是否为数字 age=12 age.isdigit()
# 判断是否有特殊字符,有为(False),没有为(True) a='yy!sdf' print(a.isalnum())
#判断以什么字符结尾
a='yy!sdf'
print(a.endswith('df'))
# 大小写转换 a='yysdf' b='YYYDIS' print(a.upper()) print(b.lower()) print(a.upper().lower())
 更多
更多4、列表
创建列表:
name_list = ['tlh', 'hello','seven', 'eric'] 或 name_list = list(['tlh','hello','seven', 'eric'])
注:操作前必须创建列表
基本操作:
- 索引
- 切片
- 追加
- 删除
- 长度
- 循环
- 包含
- 其他
索引
# 修改 name_list[0]='n' # 获取 name=name_list[3]
切片
# 直接取元素 print(name_list[0]) # 取列表中的一段 print(name_list[0:])# 表示取全部 print(name_list[1:3])# 取第一到二个元素 # 步长 print(name_list[0::2])
追加
# 在最后面追加
name_list.append('dd')
print(name_list)
#插入
name_list.insert(3,'dd')
print(name_list)
删除
# 删除列表多个值(删除内存中的值)
del name_list[0:2]
# 删除所有
del name_list
# 删除列表单个值
name_list.remove('tlh')
长度
#值为tlh的有几个
a=name_list.count('tlh')
包含
# in用于包含
if 'tlh' in name_list:
print('正确')
name_list = ['tlh', 'hello','seven', 'eric']
name_new_list=['cc','dd']
#包含另一个列表
name_list.extend(name_new_list)
print(name_list)
循环
for i in range(name_list.count('tlh')):
name_tag=name_list.index('tlh')
name_list[name_tag]=999999999
print(name_list)
其他:
直接获取元素
# 直接从列表中获取 name_list.pop(2) #获取最后一个 name_list.pop()
反转
#反转 name_list.reverse() print(name_list)
排序
# 排序 name_list.sort()
复制
# 复制是共享一份数据,而嵌套的数据是内存的地址。分为浅cope和深cope #浅cope,最外面一层, name_list.copy() #深cope,完全复制一份,独立 import copy copy.deepcopy()
 更多
更多5、元组(有序且只能传数字)
创建元组:
ages = (11, 22, 33, 44, 55) 或 ages = tuple((11, 22, 33, 44, 55))
基本操作:

lass tuple(object): """ tuple() -> empty tuple tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. """ def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """ return 0 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. """ return 0 def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported. """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of tuple.__init__ """ tuple() -> empty tuple tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes """ pass
PS:循环,range,continue 和 break
6、字典(无序)
创建字典:
person = {"name": "mr.wu", 'age': 18}
或
person = dict({"name": "mr.wu", 'age': 18})
例:
name={
1:{
'id':1,
'name':'aa',
'age':12,
'addr':'sh'
},
2: {
'id': 2,
'name': 'aa',
'age': 20,
'addr': 'st'
},
3: {
'id': 3,
'name': 'aa',
'age': 12,
'addr': 'su'
}
}
常用操作:
- 索引
- 新增
- 删除
- 获取
- 键、值、键值对
- 循环
- 长度
- 其他
索引
# 索引 print(name[1]) name[1]['name']='nihao' print(name[1])
新增
name[1]['qq_num']='399333'# 没有即创建
删除
# 删除
del name[1]['qq_num']
------------------------------
name[1].pop('qq_num')
获取
#获取 v=name.get(1) print(v)
键、值、键值对
#键、值、键值对 print(name.keys()) print(name.values()) print(name)
循环
#循环
for key in name:
print(name[key])
print(name[key].get('addr'))
其他
#覆盖更新
dic2={
'name':'aaa',
1: {
'id': 'www',
'name': 'aa',
'age': 12,
'addr': 'sh'
},
}
name.update(dic2)
print(name)
# 字典转换为列表 print(name.items())
# 包含
name.has_key(1) #only in 2.x
if 1 in name:
print('True') #equals to above has key(x)
# 设置默认的key值 name.setdefault(5,'错误') #取一个key值,如果不存在,就设置一个key值 print(name)
# 把列表中的元素当做key,所有value为dd print(dict.fromkeys([1,2,3,4],'dd'))
#随机删 print(name.popitem())
 更多
更多7、set集合
set集合,是一个无序且不重复的元素集合
如:{"123","456","789"},{"abc","dce"}
#新建 s1={11,22,33} s2=set() s3=set([11,22,33])
常用操作:
- 新增
- 差异
- 删除
- 父、子序列
- 循环
- 长度
- 其他
新增
#增加 s=set() s.add(123)
#迭代增加
s1=set()
l1=[11,22,33,11]
l2=(11,22,44,55)
l3='abcdeadd'
s1.update(l1)
s1.update(l2)
s1.update(l3)
差异
#查找差异(不改变原值) s1={11,22,33} s2={22,33,44} #1、A中存在,B中不存在 s3=s1.difference(s2) # 2、对称差集 s3=s1.symmetric_difference(s2) ------------------------------------------------ #查找差异(改变原值) s1={11,22,33} s2={22,33,44} #1、A中存在,B中不存在结果更新到A s1.difference_update(s2) # 2、对称差集更新到A s1.symmetric_difference_update(s2) ------------------------------------------------- #交集 s3=s1.intersection(s2)
s1.intersection(s2)
s4=s1.isdisjoint(s2)如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False
#并集
s3=s1.union(s2)
结果:{11,22,33,44}
s1.union(s2)
删除
#移除指定元素 s1={11,22,33} s2={22,33,44} #1、不存在不保错 s1.discard(11) #2、随机移除 ret=s1.pop() #3、不存在报错 s1.remove(11)
父、子序列
父序列包含子序列 s1={11,22,33} 父序列 s2={22,33} 子序列 #判断s2是否是s1的子序列,是返回True,否返回False s3=s2.issubset(s1) #判断s1是否是s2的父序列,是返回True,否返回False s3=s1.issuperset(s2)

old_dict={ "#1": 8G "#2": 4G "#3": 2G } new_dict={ "#1": 4G "#2": 4G "#3": 2G } 需求: #应该删除那几个编号的内存条 #应该更新那几个编号的内存条 #应该增加那几个编号的内存条 ----------------程序------------------ old_set=set(old_dict.keys()) new_set=set(new_dict.keys()) add_set=new_set.difference(old_set) update_set=old_set.intersection(new_dict)

class set(object): """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. """ def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Add an element to a set,添加元素 This has no effect if the element is already present. """ pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements from this set. 清除内容""" pass def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a shallow copy of a set. 浅拷贝 """ pass def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. A中存在,B中不存在 (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.) """ pass def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements of another set from this set. 从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素""" pass def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing. 移除指定元素,不存在不保错 """ pass def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. 交集 (i.e. all elements that are in both sets.) """ pass def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. 取交集并更更新到A中 """ pass def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return True if two sets have a null intersection. 如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False""" pass def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Report whether another set contains this set. 是否是子序列""" pass def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Report whether this set contains another set. 是否是父序列""" pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty. 移除元素 """ pass def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. 移除指定元素,不存在保错 """ pass def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. 对称差集 (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.) """ pass def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. 对称差集,并更新到a中 """ pass def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the union of sets as a new set. 并集 (i.e. all elements that are in either set.) """ pass def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the union of itself and others. 更新 """ pass
8、流程控制指令
8.1.1、for循环
用户按照顺序循环可迭代对象中的内容,
PS:break、continue
li = [11,22,33,44]
for item in li:
print item
8.1.2、while
1、基本循环
while 条件: # 循环体 # 如果条件为真,那么循环体则执行 # 如果条件为假,那么循环体不执行

type=True a=1 while(type): if a==1: type=False
8.1.3、break
break用于退出所有循环
break用于退出所有循环
while True: print "123" break print "456"
8.1.4、continue
continue用于退出当前循环,继续下一次循环
while True: print "123" continue print "456"
8.1.4、pass(pass语句块中不会报错)
pass是一个特殊的语句,当你只想好框架没想好语句时,可以使用pass。
#我定义了一个type函数,但我并没有写语句 def type(): pass
8.3.if
用于判断条件
a=10 if a==10: a=1 else: a=2
8.4、enumrate
为可迭代的对象添加序号
li = [11,22,33]
for k,v in enumerate(li, 1):
print(k,v)
8.5、range
指定范围,生成指定的数字
print range(1, 10) # 结果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print range(1, 10, 2) # 结果:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9] print range(30, 0, -2) # 结果:[30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2]
9、深浅拷贝
一、数字和字符串
对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址
import copy # ######### 数字、字符串 ######### n1 = 123 # n1 = "i am alex age 10" print(id(n1)) # ## 赋值 ## n2 = n1 print(id(n2)) # ## 浅拷贝 ## n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n2)) # ## 深拷贝 ## n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n3))

二、其他基本数据类型
对于字典、元祖、列表 而言,进行赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝时,其内存地址的变化是不同的。
1、赋值
赋值,只是创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址,如:
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}
n2 = n1
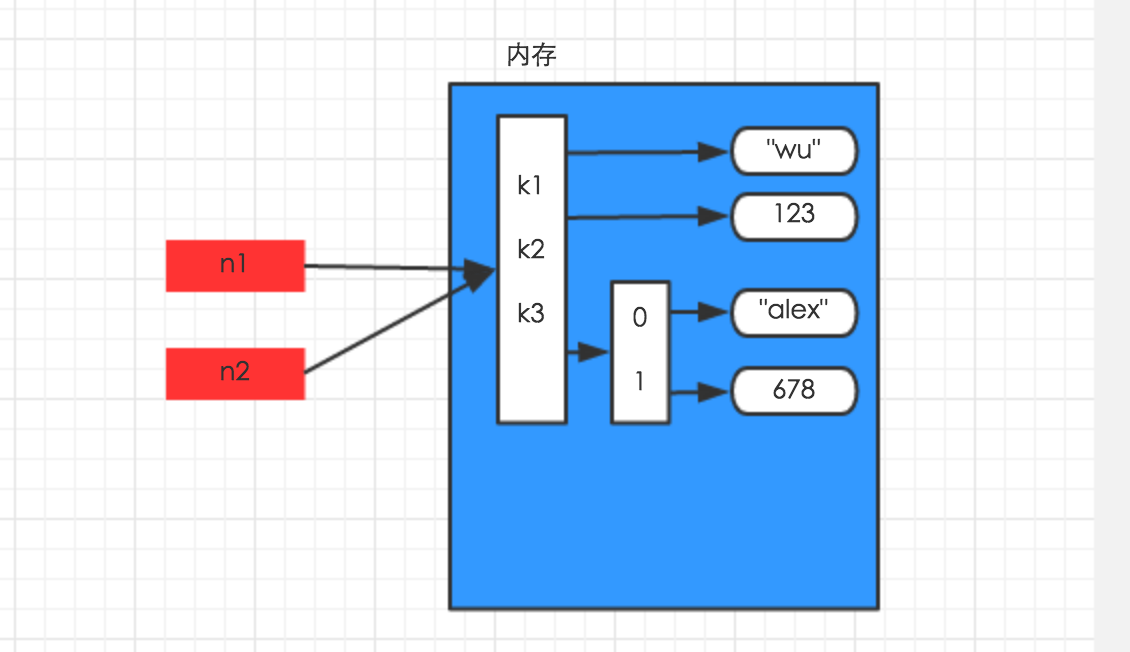
2、浅拷贝
浅拷贝,在内存中只额外创建第一层数据
import copy n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]} n3 = copy.copy(n1)

二、运算
算数运算:

比较运算:

赋值运算:

逻辑运算:

成员运算:

身份运算:

位运算:

 例
例三元运算(三目运算),是对简单的条件语句的缩写
# 书写格式 result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2 # 如果条件成立,那么将 “值1” 赋值给result变量,否则,将“值2”赋值给result变量
运算符优先级:

更多内容:
http://www.runoob.com/python/python-operators.html
三、数据结构中特殊的方法
在列表、字典、元组、集合或者其他中,都会有__init__这样的特殊方法,它是在我们对方数据进行操作时,在python内部自动帮我们执行的方法。后续会在面向对象篇中写到。
查看:
print(dir(list))
如:
li=[11,22,33] #执行list __init__ li() #执行list __call__ li[0] #执行list __getitem__ li[0]=123 #执行list __setitem__ def li[1] #执行list __delitem__



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号